![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what are the 5 functions of the heart?
|
1 - self nutrition
2 - regular self excitation 3 - effective contraction/relaxation 4 - effective intra-cardiac blood flow path 5 - reulation of Pre-Load (pressure) |
|
|
What is the heart disfunction concerned with "self nutrition"?
|
ischemia - not enough O2 supplied
|
|
|
What is the heart disfunction concerned with self excitation?
|
arrythmia
|
|
|
What is the heart disfunction concerned with effective contraction?
|
cardiomyopathies
|
|
|
What is the heart disfunction concerned with intra-cardial blood flow?
|
valve/septal defects
|
|
|
what is a septal defect?
|
a hole in the intra-atrial or intraventricular septum
|
|
|
What is the heart disfunction concerned with regulation of pre-load?
|
congestive heart failure - can't supply body's needs
|
|
|
2 major inflow vessels of heart?
|
inf/sup vena cava, pulmonary veins
|
|
|
2 major outflow vessels of hearts?
|
aorta, pulmonary trunk
|
|
|
Valve between RA and RV?
|
tricuspid
|
|
|
valve after R ventricle?
|
Pulmonic valve
|
|
|
valve after L ventricle?
|
aortic valve
|
|
|
valve between LV and LA
|
mitral (bicuspid) valve
|
|
|
3 major types of cardiac muscle?
|
atrial, vventricular, specialized pacemaker muscle
|
|
|
What allows cardiac cells to function in concert? (2 things)
|
intercalated discs and gap junctions
|
|
|
What type of metablosim do cardiac cells use? what cell structure does this necessitate?
|
Aerobic metabolism, needing mitochondria
|
|
|
What is the initial pacemaker of the heart?
|
SA NODE
|
|
|
describe the path of the electrical current of the herat?
|
SA node - atrial depol - AV node - purkinje fibers - ventricle depol
|
|
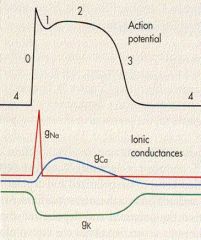
label 0-4
|
4 - RMP
0 - rapid depolarization 1 - outward K/Cl 2 - calcium influx 3 - repolarization |
|
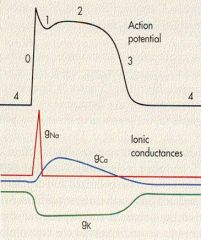
what is 0 due to?
|
FAST influx of Na thru voltage gated
|
|
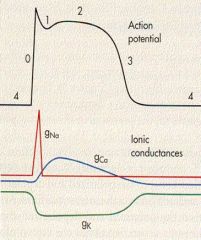
what is 1 due to?
|
outward K/Cl
|
|
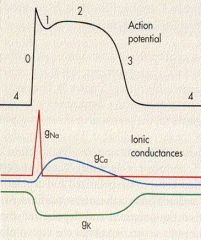
what is 2 due to?
|
calcium INFLUX
|
|
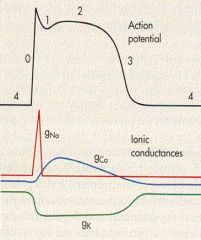
What is 3 due to?
|
efflux of K thru VOLTAGE
|
|
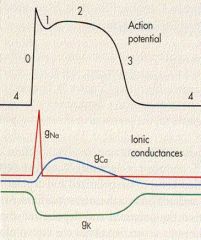
Where is ARP?
RRP? |
ARP - 0--->1/2 of 3
RRP - 1/2 of 3 to 4 |
|
|
When are non-pacemaker cells able to take over funciton of heart beat?
|
RRP
|
|
|
What is the normal blood volume of a person?
|
5 L
|
|
|
What is comploiance of systemic veins measured in? what is the normal value?
|
mL/ mmHG
50 |
|
|
mean systemic filling pressure?
units? normal value? |
measure of DEGREE OF FILLING OF CIRCULATION - driving pressure
mmHg 7 |
|
|
Extravasulcar pressure?
|
Skeletal muscle tone
|
|
|
Central Venous Pressure?
unites? usualy value? |
mmHg
RAP -determines DIASTOLIC filling of RV 0 for RAP |
|
|
vanous return
units value |
L/min
5 blood to R.A - cardiac output follows this value |
|
|
Cardiac output
unit value |
L/min
blood into aorta 5 same as venous return |
|
|
Total peripheral resistance
|
sum of resistance impeding floow between aorta and R.A
mmHg/ (L/min) |
|
|
Mean atrial pressure
|
100 mm Hg normal
time of arterial pressure - pressure for flow to tissues |
|
|
Percentages of where blood is
Pulmonary? Systemic? Heart? |
systemic - 85%
heart - 5% pulmonary circ - 10% |
|
|
% of blood in the systemic circ
veins? arteries? capillaries? |
veins - 65%
arteries - 13% cap - 7% |
|
|
6 vascular segments?
|
veins
large arteries arterioles capillaries metarterioles venuoles |
|
|
veins
large arteries arterioles capillaries metarterioles venuoles Which responds to nerves? |
veins
|
|
|
veins
large arteries arterioles capillaries metarterioles venuoles which stores energy |
large artery
|
|
|
veins
large arteries arterioles capillaries metarterioles venuoles which responds to local factors for resistance? |
arterioles and metarteroiles
|
|
|
veins
large arteries arterioles capillaries metarterioles venuoles which increases permeability with inflammatoin? |
venuoles
|
|
|
a - 100
b - 98 c - 85 d - 30 e - 10 f - 98 g - 85 h - 30 i - 10 j - 0 |
|
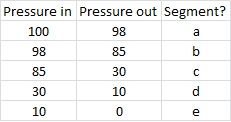
|
a - aorta/large arteries
b - regional arteries c - arterioles d - capillaries e large veins |
|
|
Best answer: The blood flow toe each tissue of the body is ALMOST ALWAYS controlled by?
|
tissue's metabolic needs
|
|
|
cardiac output is controlled mainly by
|
sum of systemic tissue flows (venous return to R.A.)
|
|
|
Arterial pressure is controlled iNDEPENDENTLY of 2 things:
|
local blood flow and cardiac output
|
|
|
guyton's 3 principles?
|
1 - blood flow to tissue goverend by metabolic needs
2 - sum of systemic tissue flows controls cardiac output 3 - local blood flow and cardiac output are indepent of arterial pressure |
|
|
Ohm's law
MAP = ? |
(Q x TPR) + RAP
|
|
|
Laminar flow vs. turbulent flow
|
laminar is linear, streamline
turbulent is murmur causing |
|
|
doubling length of tube
doubling diameeter of tube doubling viscocity of blood which decreases resistance? |
doubling diameter, by 1/16
|
|
|
what is hematrocrit? normal level?
|
40 - percent of blood that is cells
|
|
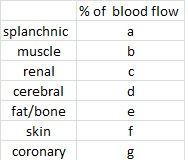
|
27
20 20 15 8 7 5 |
|
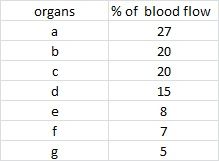
|
splanchnic
renal skeletal muscle cerebral fat/bone skin coronary |
|
|
what are the 2 highest priority organs? what mechanism controls their flow?
|
brrain and heart - local control
|
|
|
what are the 2 lowest priority organs for blood? what controls them?
|
kidney and skin - baroreceptor reflex
|
|
|
rank the following in relative blood flow. what are the units?
GI brain kidney heart other |
kidney
GI heart brain other ml/min/100g |
|
|
which has the lowest oxygen in the venous blood leaving its capillary bed?
|
heart
|
|
|
2 esential purposes of CV system
|
blood flow
capillary exchange |

