![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
83 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sensory perception
|
Cerebral Cortex
|
|
|
Voluntary control of movement
|
Cerebral Cortex
|
|
|
Language
|
Cerebral Cortex
|
|
|
Personality traits
|
Cerebral Cortex
|
|
|
sophisticated mental events - thinking memory decision making, creativity, self consciousness
|
Cerebral Cortex
|
|
|
Inhibition of muscle tone
|
Basal nuclei
|
|
|
Coordination of slow sustained movements
|
Basal nuclei
|
|
|
suppression of useless patterns of movement
|
Basal nuclei
|
|
|
Relay station for synaptic input
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
Crude awareness of sensation
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
Some degree of consciousness
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
role in motor control
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
Regulation of many homeostatic functions - temp, thirst, urine output, food intake
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
important link between nervous and endocrine systems
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
extensive involvement with emotion and basic behavioral patterns
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
role in sleep-wake cycle
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
maintenance of balance
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
enhancement of muscle tone
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
coordination and planning of skilled voluntary muscle activity
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
origin of majority of peripheral cranial nerves
|
brain stem
|
|
|
cardiovascular, respiratory and digestive control centers
|
brain stem
|
|
|
regulation of muscle reflexes involved with equilibrium and posture
|
brain stem
|
|
|
reception and integration of all synaptic input from spinal cord; arousal and activation of cerebral cortex
|
brain stem
|
|
|
role in sleep-wake cycle
|
brain stem
|
|
|
concerned with maintaining proper position of the body in space and subconscious coordination of motor activity
|
brain stem
|
|
|
brain stem consists of
|
midbrain, pons, medulla
|
|
|
subcortical region of the brain
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
______plans, initiates and times movements by sending input to the motor areas of ________
|
cerebellum, cortex
|
|
|
key role in learning skilled motor tasks
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
Where is seratonin made?
|
raphe nuclei in the pons, midbrain, and medulla
|
|
|
Where is dopamine made?
|
ventral tegmental area/substantia nigra - two midbrain nuclei
|
|
|
NE is made?
|
locus coeruleus, a nucleus in the pons. NE for all the brain is made here
|
|
|
What pathway degenerates in Parkinson's?
|
The DA nigrostriatal pathway - from the substantia nigra to the striatum
|
|
|
What is the main 'feel good' pathway?
|
substantia nigra, where cocaine, amphetamines work
|
|
|
What is the striatum
|
term for the main two basal ganglia structures - caudate and putamen
|
|
|
What structure was affected by contaminated opiate and led to instant Parkinson's
|
striatum, important for motor processing
|
|
|
Diencephalon components
|
Hypothalamus, Thalamus
|
|
|
ANS coordinating center
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Coordinates all smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, exocrine glands
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Most involved in regulating internal environment
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Some primitive sensory processing
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
Screens out insignificant signals (dripping faucet) and routes important sensory impulses to appropriate areas
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
Helps direct attention to stimuli of interest
|
Thalamus
|
|
|
80% of brain weight
|
Cerebrum
|
|
|
_______connects the two hemispheres of the ________
|
corpus callosum, cerebrum
|
|
|
______ is the Thin outer shell of gray matter that coveres each hemisphere of the ________
|
Cerebral cortex, cerebrum
|
|
|
the 4 major lobes of the _______ are:
|
cerebral cortex; occipital, temporal,parietal, frontal
|
|
|
______carries out initial processing of visual input. Is in the _____
|
Occipital lobe; cerebral cortex
|
|
|
_______ receives initial auditory sensation, is in the _______
|
Temporal lobe, cerebral cortex
|
|
|
______ receives and processes sensory input. Is in the ____
|
Parietal Lobe, cerebral cortex
|
|
|
______ handles somatosensory processing. Is in the ________
|
Parietal Lobe, cerebral cortex
|
|
|
_____ is responsible for voluntary motor activity. Is in the ____--
|
Frontal lobe, cerebral cortex
|
|
|
______ is responsible for speaking ability. Is in the _____
|
Frontal lobe, cerebral cortex
|
|
|
______ is responsible for elaboration of thought. Is in the _____
|
Frontal lobe, cerebral cortex
|
|
|
Image
|
Central sulcus
|
|
|
Image
|
Frontal lobe
|
|
|
Image
|
parietal lobe
|
|
Image
|
parietooccipital notch
|
|
|
Image
|
occipital lobe
|
|
|
Image
|
preoccipital notch
|
|
|
Image
|
cerebellum
|
|
|
Image
|
brain stem
|
|
|
Image
|
temporal lobe
|
|
|
Image
|
lateral fissure
|
|
|
Where is the primary motor cortex?
|
In Frontal lobe, (ventral?/anterior?) to central sulcus.
|
|
|
the Primary motor cortex controls what?
|
voluntary control over skeletal muscles, 80% of which have crossed over
|
|
|
Motor homonculus
|
info
|
|
|
Where is the somatosensory cortex?
|
In the cerebral cortex, in the parietal lobe, behind the central sulcus
|
|
|
What is processed at somatosensory cortex?
|
discriminitive touch, pain/temp; processed first through thalamus and complex relationship b/t sensory inputs are processed in the somatosensory ctx
|
|
|
Supplementary Motor area
|
on inner surface of cerebral cortex, plans/prepares/programs for complex movements
|
|
|
Dorsal somatosensory pathway
|
discriminitive touch
|
|
|
pathway for pain and temperature
|
spinothalamic
|
|
|
pathway for proprioception
|
spinocerebellar
|
|
|
_________ pairs of spinal nerves
|
31
|
|
|
Somatosensory system
|
3 modalities: discriminative touch; pan/itch/tickle/proprioception
|
|
|
Describe the fine touch pathway
|
Actually 2 pathways; fasciculus cuneatus (upper trunk & arms) and f. gracilus (lower trunk & legs).
|
|
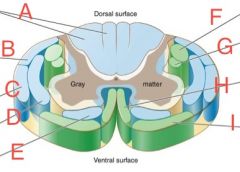
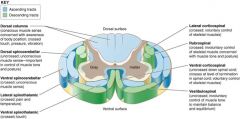
Dorsal spinocerebellar
|
B
|
|
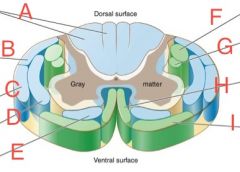
Ventral Spinocerebellar
|
C
|
|
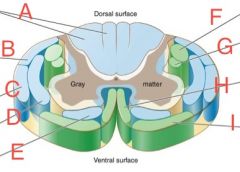
Lateral Corticospinal
|
F
|
|
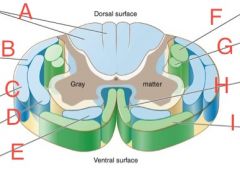
Ventral Corticospinal
|
H
|
|
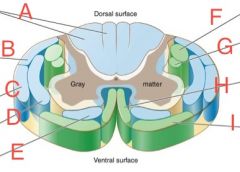
Ventral spinothalamic
|
E
|
|
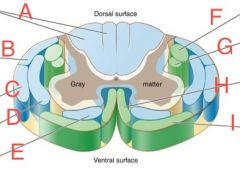
Lateral spinothalamic
|
D
|
|
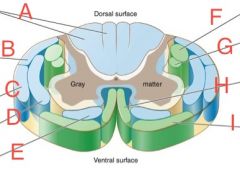
Ventral spinothalamic
|
E
|

