![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
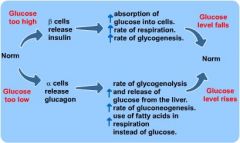
What inhibits release of glucagon?
|
Glucose.
|
|
|
What is the difference between the actions of glucagon and insulin?
|
The actions of glucagon antagonize those of insulin.
|
|
|
What is glucagon's principal target tissue?
|
Liver.
|
|
|
What is glycogenolysis?
|
Glycogenolysis is the conversion of glycogen polymers to glucose monomers.
|
|
|
What is gluconeogenesis?
|
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon substrates such as lactate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids.
|
|
|
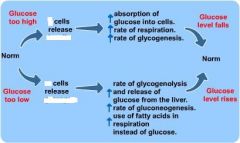
What is the main effect of glucogon?
|
- Incr. glucose output;
- Incr. glycogenolysis; - Incr. gluconeogenesis; - Decr. fatty acid synthesis -> Incr. ketone bodies -> Can be used as fuel by muscle and CNS when glucose is low. |
|
|
What is the effect of growth hormone in regulation of blood glucose?
|
Inhibition of insulin-induced glucose utilisation.
- Inhibits glucose uptake and lipogenesis; - Increases glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis; - But protect protein. |
|
|
What is lypogenesis?
|
Lipogenesis is the process by which acetyl-CoA is converted to fats.
|
|
|
What is the effect of glucocorticoids in regulation of blood glucose?
|
Protects from hypoglycemia during stress.
- Stimulation of gluconeogenesis - Inhibits effects of insulin - Increase effects of glucagon and adrenaline. |
|
|
What is the role of adrenaline in blood glucose regulation?
|
Maintain glucose supply to brain.
- Stimulate lipolysis in adipose tissue; - Stimulate liver gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis. |
|
|
What is diabetes mellitus?
|
Diabetes mellitus, often simply referred to as diabetes—is a group of metabolic diseases in which a person has high blood sugar, either because the body does not produce enough insulin, or because cells do not respond to the insulin that is produced.
|
|
|
How do you find out about diabetes mellitus?
|
Take a sample of urine. Person with diabetes has glucose in the urine due to chronic hyperglycemia.
|
|
|
Name two types of diabetes.
|
Type 1 - insulin-dependent (there is no production of insulin); 5-10% of cases.
Type 2 - insulin-independent (insulin resistance in target tissues); 90-95% of cases. |
|
|
Person has high insulin level AND high glucose level in blood, what could that mean?
|
It has diabetes type 2, where insulin is produced, but target tissues are resistant to it.
|
|
|
What is the main treatment for diabetes type 2?
|
Diet and exercise, but also antidiabetic drugs.
|
|
|
Name hormone-producing cells in pituitary.
|
Somatotrophs (GH, liver, bone, muscle growth),
Lactotrophs (PRL, stimulates milc production in breasts), Thyrotrophs (TSH, thyroid), Corticotrophs (ACTH, adrenal cortex), Gonadotrophs (FSH/LH, ovary, testis). |
|
|
Which hormone in the hypothalamus inhibits production of GH by somatotrophs?
|
Somatostatin.
|
|
|
Which hormone in the hypothalamus stimulates production of GH by somatotrophs?
|
GHRH.
|
|
|
Is GH a steroid of peptide hormone?
|
Peptide.
|
|
|
How does GH circulates in the plasma?
|
Bind to proteins (although it is peptide hormone).
|
|
|
Which gland secretes GH?
|
Petuitary.
|
|
|
What is the effect of GH on protein?
|
Increases protein synthesis.
|
|
|
What is the effect of GH on lipogenesis?
|
It reduces it.
|
|
|
Does GH reduce or increase blood levels of glucose?
|
Increase.
|
|
|
What increases GH secretion?
|
Hypothalamic peptides (GHRH),
Hypoglycemia (starvation, etc.), Peripheral hormones (Ghrelin). |
|
|
What inhibits GH secretion?
|
Hypothalamic peptides (somatostatin);
Obesity; IGF-I (insulin-like growth factor). |
|
|
What is Somatomedin?
|
Somatomedin is a group of hormones that is produced, when stimulated by somatotropin (STH), to promote cell growth and division. In this way, they mediate the effect of somatotropin (growth hormone).
|
|
|
What happens if there is GH excess appearing in adulthood?
|
Acromegaly - There is no longitudinal growth of bones, there is increase in thickness.
|
|
|
What are 5 main functions of thyroid gland?
|
1. Regulation of energy metabolism;
2. Growth and development; 3. Body temperature; 4. Carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism; 5. Regulation of nervous system, cardiovascular, muscolo-skeltal and reproduction. |
|
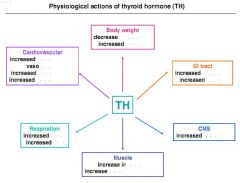
Fill in blanks.
|
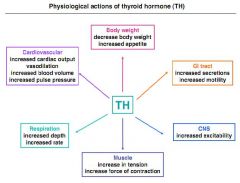
|
|
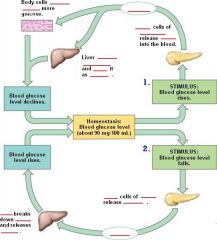
Fill in blanks.
|
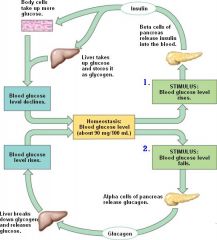
|
|
Fill in blanks.
|
|
|
|
Which substance is required for generating T3 and T4? (From diet).
|
Iodine.
|
|
|
Name two thyroid hormones.
|
T3 (3 iodines) and T4 (4 iodines).
|
|
|
What is the function of thyroglobulin?
|
Tg is used by the thyroid gland to produce the thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). It is presumed that Tg and thyroid are also an important storage of iodine for all body needs, in particular, for many iodine-concentrating organs such as breast, stomach, salivary glands, thymus, etc.
|
|
|
In the follicular cells of thyroid gland, what is added by enzymes to thyroglubulin to make T3 and T4?
|
Iodine.
|
|
|
Which hormone is released more often - T3 or T4?
|
90% of released hormone is T4, 10% - T3.
|
|
|
Which of two hormones is more active - T3 or T4?
|
T3 is 5x more active.
|
|
|
Why in target tissues T4 is deiodinated to T3?
|
Because T3 is more active.
|
|
|
What is half-life of T4 and T3 hormones' release?
|
T3 is one day, T4 is 6 days.
|
|
|
Where are receptors of the target cells for thyroid hormones situated?
|
In the nucleus of the cell.
|
|
|
How can you explain the multiple effects of thyroid hormone in different target cells?
|
TH binds to receptors in the target cell nucleus and then to promoter elements which activates gene transcription.
|
|
|
Name 6 effects of thyroid hormones.
|
1. Incr. basal metabolic rate;
2. Makes more glucose available to meet elevated metabolic demand; 3. Stimulate the synthesis of enzymes and structural proteins; 4. Incr. lipid metabolism; 5. Stimulate heart rate, cardiac outout, blood flow.; 6. Incr. neural transmission and neuronal development. |
|
|
What does TSH stand for?
|
Thyroid stimulating hormone.
|
|
|
In response to what is TSH released from pituitary?
|
In response to secretion of hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing-hormone (TRH).
|
|
|
Which two substances inhibit TRH secretion?
|
Cortisol and GH.
|
|
|
What stimulates TRH release from hypothalamus?
|
Sympathetic activation and cold.
|

