![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
All neuronal information is carried and encoded in the form of __________ __________
|
action potentials
|
|
|
A cell must be depolarized to the point of its __________ for an action potential to be generated
|
threshold
|
|
|
Action potentials vary in amplitude depending on the size of the stimulus (True/False)
|
False (action potentials are all-or-none) (digital) (action potential FREQUENCY can be altered by the size and duration of a stimulus)
|
|
|
What sets the limit on the frequency of action potentials?
|
The absolute refractory period
|
|
|
Na+ conductance is highest during what phase of an action potential?
|
depolarization
|
|
|
gNa is __________ (greater than, equal to, less than) gK at the peak of an action potential
|
equal to
|
|
|
During an action potential, there is ____________ (inward/outward) Na+ conductance and _________ (inward/outward) K+ conductance
|
inward, outward
|
|
|
During an action potential, the extracellular concentration of Na+ decreases and extracellular K+ increases, and the concentrations must be returned to normal by the Na/K ATPase before the next action potential can occur. (True/False)
|
False (the amount of ions exchanged in order to depolarize the membrane is not significant enough to affect the ion concentrations. Even without the Na/K ATPase, the cell could depolarize thousands of times before the concentrations would be significantly affected.
|
|
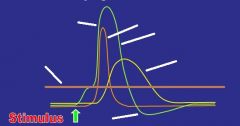
Label
|
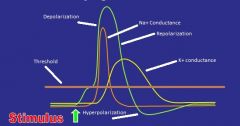
|
|
|
Voltage-gated Na+ channels open under a ________ _________ process
|
positive feedback
|
|
|
What must the voltage-gated Na+ channels overcome in order to initiate an action potential?
|
The K+ efflux
|
|
|
hyperparathyroidism leads to __________calcemia which leads to __________ excitability which leads to muscle ___________
|
hyper, deceased, weakness
|
|
|
What are the two main factors that prevent a membrane potential from reaching the nernst potential of Na+ during an action potential?
|
Decreased driving force of Na+ at the peak of the action potential and the closing of innactivation gates on the voltage-gated Na+ channels cause the Na+ influx to be brief and only depolarize the membrane to ~+30mV
|
|
|
During repolarization the activation gate on the Na+ channel is __________ and the inactivation gate is ___________
|
closed, closed
|
|
|
During the peak of an action potential the activation gate on the Na+ channel is __________ and the inactivation gate is ___________
|
open, closed
|
|
|
During depolarization the activation gate on the Na+ channel is __________ and the inactivation gate is ___________
|
open, open
|
|
|
The Na+ activation gate swings ________ with depolarization and the inactivation gate swings _________
|
open, shut
|
|
|
What causes the refractory period?
|
The refractory period is caused by the recovery period of the membrane from Na+ gate innactivation. The membrane must have enough innactivation gates re-open in order for a Na+ influx significant enough to trigger the next action potential
|
|
|
What effect would a drug have that prolongs the time of recovery of Na+ inactivation channels?
|
It would cause a prolonged absolute refractory period
|
|
|
Hyperkalemia causes __________
|
inexcitability (high levels of extracellular K+ make the membrane potential more positive, thus closing the innactivation gates before the activation gates open)
|
|
|
Which channels account for the high K+ permeability at rest?
|
The "inward rectifier" channels
|
|
|
Action potential duration is dependent on the magnitude of ____ currents
|
K+
|
|
|
Smaller K+ currents trigger ________ action potential duration
|
longer
|
|
|
What is responsible for the plateau in a cardiac action potential
|
The Ca++ influx
|
|
|
decreased internal resistance will result in a _________ space constant and __________ conduction velocity
|
increased, increased
|
|
|
Myelination increases _________ resistance thereby increasing conduction velocity
|
membrane
|

