![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
233 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Blood volume in arteries is called
|
stress volume
|
|
|
Site of highest resistance in CVS?
|
arterioles
|
|
|
2 adrenergic receptors of arterioles?
|
a1, b2
|
|
|
a1 is found?
|
skin, splanchnic, renal
|
|
|
b2 is found?
|
sk muscle
|
|
|
Have largest total cross-sectional and surface area
|
capillaries
|
|
|
Highest proportion of blood in CVS found in
|
veins
|
|
|
blood volume in veins called
|
unstress volume
|
|
|
adrenergic receptor of veins?
|
a1
|
|
|
velocity eqn?
|
V = Q/A (velocity = flow/cross-sectional area)
|
|
|
blood flow eqn?
|
Q = DP/R (CO = MAP-RAP/TPR)
|
|
|
Poiseuille's resistance eqn?
|
R = 8hl/pr^4
|
|
|
Eqn for SV?
|
EDV - ESV
|
|
|
Eqn for CO?
|
SV x HR
|
|
|
Eqn for EF?
|
EF = SV/EDV
|
|
|
Eqn for SW?
|
SV x Aortic pressure
|
|
|
Eqn for O2 consumption?
|
CO x ([O2] pulm vein - [O2] pulm artery)
|
|
|
When a vessel is added in parallel, resistance
|
dec
|
|
|
Thus pressure
|
incr
|
|
|
When a vessel is added in series, resistance
|
incr
|
|
|
Thus pressure
|
dec
|
|
|
Reynolds number predicts if blood flow is
|
laminar or turbulent
|
|
|
Audible vibrations of turbulence are called
|
bruits
|
|
|
Shear force is highest
|
at the wall of vessel
|
|
|
2 words meaning the distensibility of a vessel
|
capacitance, compliance
|
|
|
Capacitance eqn?
|
C = V/P (capacitance = volume/pressure)
|
|
|
What is the fx of age?
|
Compliance dec
|
|
|
Explain why veins are more compliant than arteries?
|
Less pressure
|
|
|
Describe the pressure profile of large blood vessels
|
Highest pressure in aorta; lowest in vena cavae
|
|
|
What do arterioles have the largest dec in pressure?
|
Highest resistance
|
|
|
Is arterial pressure constant during cardiac cycle?
|
No, it's pulsatile
|
|
|
Systolic pressure is after
|
the heart contracts
|
|
|
Diastolic pressure is after
|
the heart relaxes
|
|
|
Pulse pressure defined as
|
SBP - DBP
|
|
|
Most important determinant of pulse pressure is
|
stroke volume
|
|
|
MAP (mean arterial pressure) is defined as?
|
DBP + (SBP/3)
|
|
|
LAP is estimated by?
|
pulm wedge pressure
|
|
|
P wave represents
|
atrial depolarization
|
|
|
Why isn't atrial repolarization shown
|
buried in QRS
|
|
|
PR interval defined as
|
BEGINNING of P to BEGINNING of Q
|
|
|
Varies with?
|
Conduction of AV node
|
|
|
Fx of SNS?
|
dec PR
|
|
|
Fx of PNS?
|
Incr PR
|
|
|
QRS represents?
|
depolarization of ventricles
|
|
|
QT interval defined as
|
BEGINNING of Q to END of T
|
|
|
Represents?
|
ENTIRE depolarization & repolarization of ventricles
|
|
|
ST segment defined as
|
END of S to BEGINNING of T
|
|
|
Should have what characteristic?
|
Isoelectric
|
|
|
Represents?
|
when ventricles depolarized
|
|
|
T wave represents
|
ventricular repolarization
|
|
|
Resting membrane potential determined by
|
K conductance (I-K1)
|
|
|
5 phases of atria, ventricles, Purkinje
|
Phase 0-4
|
|
|
Phase 0 is the
|
Upstroke
|
|
|
Caused by transient incr in
|
Na conductance (I-Na)
|
|
|
Phase 1 is the
|
initial repolarization
|
|
|
Determined by 2
|
K flow out; dec Na conductance
|
|
|
Phase 2 is the
|
plateau
|
|
|
Caused by transient incr in
|
Ca conductance (I-Ca)
|
|
|
Phase 3 is the
|
repolarization
|
|
|
Determined by 2
|
K conductance incr (I-K); Ca conductance dec
|
|
|
What makes the SA node the pacemaker?
|
Phase 4 depolarization (automaticity)
|
|
|
2 latent pacemakers if SA node is suppresed?
|
AV node > His-Purkinje
|
|
|
What 2 phases are not present in SA node?
|
Phase 1, 2
|
|
|
What defines phase 0 in SA node?
|
Incr Ca conductance (I-Ca)
|
|
|
How does this differ from other parts of heart?
|
Not about Na conductance
|
|
|
What phase is similar in the SA node and other parts of heart?
|
Phase 3
|
|
|
Phase 4 current is defined by
|
Incr Na conductance (I-f)
|
|
|
What is the action potential?
|
Slow repolarization
|
|
|
How is it activated?
|
I-f turned on by repolarization of membrane potential
|
|
|
How is the AV node similar to SA node?
|
Phase 0 upstroke is also I-Ca
|
|
|
Conduction velocity is determined by
|
size of inward current during upstroke
|
|
|
Fastest in
|
Purkinje system
|
|
|
Slowest in
|
AV node (PR interval)
|
|
|
Fx of faster AV conduction?
|
Ventricular filling compromised
|
|
|
Absolute refractory pd is
|
when no AP can be initiated
|
|
|
When does this occur?
|
Beginning of upstroke to end of plateau
|
|
|
Effective refractory pd is
|
when CONDUCTED AP can't be elicited
|
|
|
Relative refractory pd is
|
AP is elicited with a higher inward current
|
|
|
Chronotropic fx change
|
HR
|
|
|
Dromotropic fx change
|
Conduction of AV node (affect PR)
|
|
|
PNS innervates 3
|
SA node, AV node, atria
|
|
|
NT?
|
Ach
|
|
|
Acts on?
|
Muscarinic R
|
|
|
Fx? 3
|
Neg chronotropic, neg dromotropic, dec contractility (atria only)
|
|
|
Mech of neg chronotropic fx?
|
Dec I-f (SA phase 4)
|
|
|
Mech of neg dromotropic fx?
|
Dec I-Ca and incr I-K in AV node
|
|
|
NT of SNS?
|
Norepi
|
|
|
Acts on?
|
b1-R
|
|
|
Fx? 3
|
Post chronotropic, pos dromotropic, incr contractility
|
|
|
Mech of pos chronotropic fx?
|
Incr I-f (SA phase 4)
|
|
|
Mech of pos dromotropic fx?
|
Incr I-Ca in AV node
|
|
|
Fx on PR interval?
|
PNS incr, SNS dec
|
|
|
Purpose of intercalated disks? 2
|
Maintain cell-cell cohesion; gap junciton to sync
|
|
|
T tubles in cardiac muscle form
|
dyads
|
|
|
Purpose?
|
Carry AP into cell interior
|
|
|
Excitation-contraction coupling occur in which phase?
|
Phase 2
|
|
|
When Ca conductance incr, it travels thru?
|
L-type Ca channels = dihydropyridine R
|
|
|
What does this trigger?
|
Release of Ca from SR
|
|
|
What are the names of these channels
|
RYR (ryanodine receptors)
|
|
|
Magnitude of tension developed is proportional to
|
Intracellular [Ca]
|
|
|
Relaxation occurs by what mech?
|
Ca-ATPase pump on SR
|
|
|
Another name for contractility?
|
inotropism
|
|
|
Can be estimated by?
|
EF (ejection fraction)
|
|
|
What is a norm EF?
|
55% (0.55)
|
|
|
3 factors that incr contractility?
|
Incr HR, SNS stim, cardiac glycosides
|
|
|
Mech of incr HR?
|
More AP/unit time -> more Ca enters -> more Ca release from SR
|
|
|
What is the positive staircase?
|
Incr HR stepwise incr contractilty as intracellular [Ca] accumulates
|
|
|
What is postextrasystolic potentiation?
|
Beat after extrasystolic beat has extra Ca enter cells during extrasystole -> stronger contraction
|
|
|
Mech of SNS? 2
|
Incr Ca current, phopholamban-P incr activity of SR pump
|
|
|
Mech of cardiac glycosides?
|
Inh Na/K ATPase -> incr intracellular [Na] -> incr [Ca] intracellular by Na/Ca exchange
|
|
|
Factors that dec contractility? 1
|
PNS stim
|
|
|
Mech?
|
Decr Ca current
|
|
|
Preload of ventricular muscle is
|
EDV (related to LAP)
|
|
|
Afterload of ventricular muscle is
|
Aortic pressure (LV), pulm artery pressure (RV)
|
|
|
Sarcomere length determines 2
|
max # cross-bridges; max tension (force of contraction)
|
|
|
Velocity of contraction at fixed length determined by?
|
AFTERLOAD
|
|
|
What is the Frank-Starling relationship?
|
Incr venous return (EDV) -> Incr SV & CO
|
|
|
Mech?
|
Incr EDV -> incr ventricular fiber length -> incr tension
|
|
|
Pos inotropic effect shifts curve
|
Up
|
|
|
Neg inotropic effect shifts curve
|
down
|
|
|
In PV loop of LV, what is the x-axis? Y-axis?
|
X = LV volume; Y = LV pressure
|
|
|
R border is?
|
Isovolumetric contraction
|
|
|
L border is?
|
Isovolumetric relaxation
|
|
|
Superior border is?
|
Ventricular ejection
|
|
|
Inferior border is?
|
Ventricular filling
|
|
|
SV is represented by?
|
Width of loop
|
|
|
Stroke work represented by?
|
Area of loop
|
|
|
Incr preload shifts
|
R border more R
|
|
|
Hemodynamic fx?
|
SV inc (EDV inc)
|
|
|
Incr afterload shifts 2
|
Superior border up, L border more R
|
|
|
Hemodynamic fx?
|
Incr ESV -> dec SV
|
|
|
Incr contractility shifts 2
|
Superior border up, L border more L
|
|
|
Hemodynamic fx?
|
Dec ESV -> incr SV
|
|
|
CVS fxn curve: y-axes?
|
CO and venous return
|
|
|
CVS fxn curve: x-axes?
|
RAP and EDV
|
|
|
Which direction does venous return run?
|
Top L to bottom R
|
|
|
Which direction does CO run?
|
Top R to bottom L
|
|
|
X-intercept of Venous return represents?
|
Mean systemic pressure
|
|
|
What does that mean?
|
MSP = RAP when no flow in CVS
|
|
|
What incr MSP? 2
|
Incr blood volume, dec venous compliance
|
|
|
Which changes occur in the graph?
|
venous return curve shifts R
|
|
|
What fx does this have on CO?
|
Incr
|
|
|
What fx does this have on venous return?
|
Incr
|
|
|
What fx does this have on RAP?
|
Incr
|
|
|
Clockwise rotation of CO and counterclockwise rotation of venous returns represents
|
Incr TPR
|
|
|
What fx does this have on the RAP?
|
NONE
|
|
|
What fx does this have on CO?
|
Dec
|
|
|
What fx does this have on venous return?
|
Dec
|
|
|
What fx does this have on MSP?
|
NONE
|
|
|
How do pos inotropic agents change the graph?
|
Shift CO counterclockwise
|
|
|
What fx does this have on RAP?
|
Dec
|
|
|
What fx does this have on CO?
|
Incr
|
|
|
What fx does this have on venous return?
|
Incr
|
|
|
What fx does this have on MSP?
|
NONE
|
|
|
Atrial systole is preceded by what on EKG?
|
P wave
|
|
|
Incr atrial pressure (venous pressure) causes which wave on venous pulse curve?
|
a wave
|
|
|
What is the correlating heart sound?
|
S4
|
|
|
S1 correlates to what wave on EKG?
|
QRS
|
|
|
Which valves are closing?
|
MV, TV
|
|
|
Which of these close first?
|
MV
|
|
|
Most of the SV is ejected during?
|
Rapid ventricular ejection
|
|
|
What does this correlate with on EKG?
|
ST segment
|
|
|
During the onset of T wave, what is the status of LV?
|
Slow ventricular ejection
|
|
|
S2 correlates with what on EKG?
|
B/t T & P
|
|
|
Which valves are closing?
|
AV, PV
|
|
|
Which of these close first?
|
AV
|
|
|
What resp manuever splits S2?
|
Inspiration
|
|
|
Blip in aortic pressure tracing during isovolumetric relaxation is called
|
Dicrotic notch/incisura
|
|
|
Rapid filling of LV correlates with which heart sound?
|
S3
|
|
|
Is this sound pathological?
|
Not in children, but in adults
|
|
|
Longest phase of cardiac cycle
|
diastasis (reduce vent filling)
|
|
|
When LVP matches LAP, which valve changes?
|
MV
|
|
|
When LVP matches Aortic P, which valve changes?
|
AV
|
|
|
Cardiac cycle graph
|
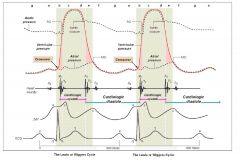
|
|
|
Fast mech?
|
Neuronal (Baroreceptor)
|
|
|
Slow mech?
|
Hormonal (RAAS)
|
|
|
Baroreceptors located 2
|
Bifurcation of common carotid, aortic arch
|
|
|
What's the difference
|
Aortic arch only sense incr; bifurcation both
|
|
|
Afferent limb is which nerve
|
CN IX
|
|
|
Where does this information transmit to?
|
Vasomotor center of medulla
|
|
|
How does the Valsalva maneuver test the baroreceptor mech? 4
|
Incr intrathoracic pressure -> dec venous return -> dec CO -> SNS response: incr HR
|
|
|
Where is renin produced?
|
Juxtaglomerular cells of afferent arteriole
|
|
|
Role of renin?
|
Angiotensinogen -> angiotensin
|
|
|
ACE conversion occurs in which organ?
|
lungs
|
|
|
2 Rx that interfere with angiotensin?
|
ACE-I (captopril), ARB (losartan)
|
|
|
What is the other fxn of ACE that causes the side fx of ACE-I?
|
Cleave bradykinin; promote cough
|
|
|
4 fxn of AII
|
Stim aldosterone,
Inc Na/H exchange in PCT, Inc thirst, Vasoconstrion of arterioles |
|
|
Cushing rxn is
|
response to cerebral ischemia
|
|
|
Mech? 7
|
Incr ICP -> vessel compression -> ischemia -> incr PCO2 -> vasomotor chemoreceptor -> incr SNS -> incr arterial pressure
|
|
|
Peripheral chemoreceptors located
|
Carotid bifuration, aortic arch
|
|
|
What chemical do these detect?
|
PO2
|
|
|
2 fx of vasopressin (ADH)?
|
Incr TPR, reabsorb H2O
|
|
|
Which receptors facilitate this?
|
V1R on arterioles, V2 on DCT and collecting duct
|
|
|
3 fx of ANP?
|
Dec TPR, incr H2O excretion by Na, inh renin
|
|
|
Blood flow thru cap regulated by
|
precapillary sphincters
|
|
|
Lipid cross cap wall by
|
simple diffusion
|
|
|
Small hydrophilic substances cross cap wall by
|
water filled clefts (exceptionally small in brain; big in liver/intestine)
|
|
|
Large hydrophilic susbstances cross cap wall by
|
pinocytosis
|
|
|
Starling eqn?
|
Jv = Kf (Pc -Pi) - (pc -pi)
|
|
|
Jv positive correlates with
|
Filtration; net fluid movement OUT of cap
|
|
|
Jv negative correlates with
|
Absorption; net fluid movement INTO cap
|
|
|
Which 2 forces promote filtration?
|
Pc, pi
|
|
|
Which 2 forces promote absorption?
|
Pi, pc
|
|
|
Why is lymph flow unidirectional?
|
one-way flap valves
|
|
|
What force aids lymphatic flow?
|
Skeletal muscle contraction
|
|
|
How do burns induce edema?
|
Incr Kf (constant)
|
|
|
What else does this?
|
Infl (Histamine, cytokines)
|
|
|
Mech of EDRF?
|
EDRF -> incr cGMP -> SM relaxation
|
|
|
What's the most popular EDRF?
|
NO
|
|
|
3 organs that exert autoregulation of blood flow
|
heart, brain, kidney
|
|
|
What is active hyperemia?
|
Incr blood flow b/c of metabolic activity
|
|
|
What is reactive hyperemia?
|
Incr blood flow after pd of occlusion
|
|
|
Myogenic mech of local ctrl?
|
Vasc SM contracts when it is stretched
|
|
|
Metabolic mech of local ctrl?
|
Vasodilating metabolites: CO2, H, K, lactate, adenosine
|
|
|
What 2 chemicals cause vasodilation and venous constriction?
|
Histamine, bradykinin
|
|
|
What causes arteriolar constriction, implicating it in migraines?
|
5HT
|
|
|
Which PG are vasodilators?
|
PGI2, PGE2
|
|
|
Which PG are vasoconstrictors?
|
PGF2, TXA2
|
|
|
Coronary flow is primarily regulated by
|
metabolic factors
|
|
|
The most important of which are
|
hypoxia, adenosine
|
|
|
How does reactive hyperemia help coronary flow?
|
Vessels compressed in systole -> fill during diastole
|
|
|
Cerebral flow is primarily regulated by
|
metabolic factors
|
|
|
The most important of which is
|
CO2
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle is regulated by 2
|
Sympathetics, metabolic factors
|
|
|
Main metabolic factors?
|
latate, adenosine, K
|
|
|
Skin is regulated primarily by
|
sympathetics
|
|
|
What is the main fxn?
|
Temperature control
|
|
|
Mech of ortho hypotension? 6
|
Venous pooling -> dec venous return -> dec SV -> dec CO -> dec BP -> baroreceptor
|
|
|
Norm P wave
|
0.08-0.1 s = 2-2.5 little boxes
|
|
|
Norm QRS
|
0.06-0.1s = 1.5-2.5 little boxes
|
|
|
Norm PR
|
0.12-0.2s = 3-5 little boxes
|
|
|
Norm QTc
|
<0.44s = <11 little boxes
|
|
|
QTc eqn?
|
QT/√RR
|

