![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
161 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define sound energy |
Sound energy: vibrations of particle matters (solid liquid gas) that moves in waves and can be heard |
|
|
Vibrations: repeating back and forth movement |
When any object vibrates, it causes movement of other particles near it These particles bump into the particles close to them, which makes them vibrate, too, causing them to bump into even more particles.
|
|
|
True or false: Sound waves is a form of kinetic energy |
TRUE! Sound waves is a form of kinetic energy, not potential energy |
|
|
True or False: sound wave is a form of mechanical energy |
True. Since sound waves belong to kinetic energy, it also belongs to mechanical energy |
|
|
Why do our ears hear sound ? |
Our ears heard sound because they are in range (near) the vibrations! |
|
|
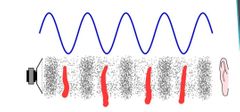
Vibration of air molecules result in compressions of air molecules |
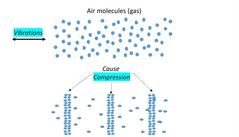
|
|
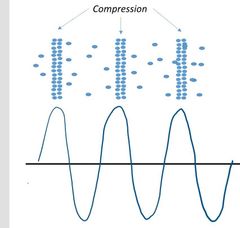
Visualization of sound as a wave function |
As you can see, the dark bands represent the compressions of sound wave , which also represent as highest points in the wave known as crest
Dark bands = compressions = crests |
|
|
True or False: sound is controlled by the characteristics of the waves and the materials they travel through |
True! Sound is controlled by the type of waves (short or long waves) and the medium it goes through
Example: sounds travel in water |
|

Short sound |

Sustained sound |
|
|
True or false: sounds are waves that are passing along like dominoes by vibrating and bumping into each other |
True! |
|
|
Higher density of material = higher speed or higher velocity that sound is traveling . More molecules packing or grouping together (e.g solid) = faster sound speed |
Density: Rock (solid) > water (liquid)> air (gas) > plasma > vacuum (in space)
Sounds will travel faster in rock than in water. Sound will travel faster in water than in air . Sound will not travel at all in vacuum cuz no molecules |
|
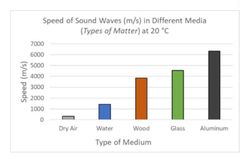
As you can see sounds travel fastest in aluminum (solid). Base on the graph of sound-s speed: Aluminum > glass > wood > water > dry air |
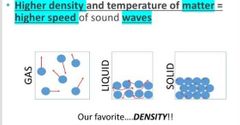
Higher temperature will also lead to higher speed or velocity of sound traveling ! |
|
|
True or false: lower temperature result in faster speed of sound wave |
FALSE! Higher temperature will result in higher sound speed. Lower temperature results in slower sound speed.
Ex: sound travels faster in boiling water than in room temperature water! |
|
|
Sound can only move through a medium (matter). If there are no particles of matter present (like in a vacuum as in outer space) there is no sound. Ex: astronauts make no sounds in space! Space = vacuum = no molecules = no sound! |

Tree falls in forest = have molecules in air and in the ground = have sound Astronaut in space =vacuum= no molecule= no sound even if he claps |
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
What is wavelength? |
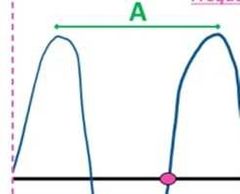
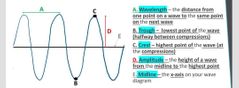
Wavelength is the distance from one point on a wave to the same point on the next wave
It can be between two crests (like in this picture denoting segment A), or between two troughs, or anywhere in between crest or trough |
|
|
What is a trough ? |
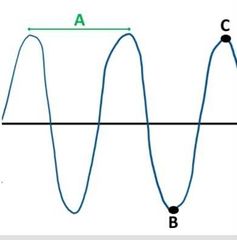
Trough: lowest point of the wave . In this picture point B is a trough
Also, trough is found halfway between compressions
Trough = lowest pressure |
|
Halfway between compressions is known as a ________ |
A trough = halfway between compressions, as shown with red vertical lines
|
|
|
Region with lowest pressure is known as a ____ |
Trough: region with lowest pressure |
|
|
Lowest point on a wave function known as a ____ |
Trough: a lowest point on a wave function |
|
|
Remember: trough = lowest point on the wave fuction = region of lowest pressure = halfway between compressions |
Trough = lowest point = lowest pressure = halfway (1/2) between compressions |
|

What is a crest? |
A crest is the highest point of the wave or wave function as at point C
A crest is also a region of highest pressure
A crest is also where a compression is located (or where a compression is at) |
|
|
Highest point in the wave function known as a ____ |
Crest: highest point in the wave function |
|
|
A region of highest pressure is known as a ____ |
Crest: a region of highest pressure |
|
|
This can be found at region of compression |
CREST can be found at region of compression |
|
|
Crest = highest point on wave function = higher pressure region = where compression can be found |
Crest = highest point = highest pressure = compressions |
|
|
What is amplitude? |
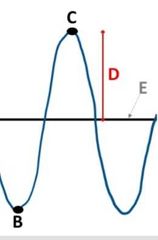
Amplitude: the height of a wave from the midline to the highest point or tobthe loeest point, as shown with D's height
Amplitude = half way (1/2) from crest to trough , or half distance from crest to trough
|
|
|
the height of a wave from the midline to the highest point is known as a _____ |
Amplitude: the height of a wave from the midline to the highest point |
|
|
What is a midline? |
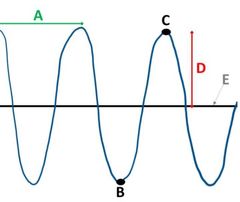
Midline is the x-axis on the wave function or diagram . In the picture, E is the midline |
|
|
Define frequency |
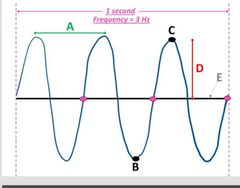
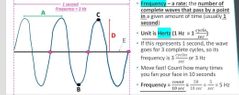
Frequency is a rate: the number of complete waves that pass by a point in a given amount of time (usually 1 second) Frequency unit is Hertz 1 Hertz = 1 cycle per sec (cycle/sec) In this wave function, the frequency is 3Hz because there are 3 completed cycle in 1 sec |
|
|
True or False: 4 Hertz means there are 4 completed cycles in 1 sec |
True. 4 Hertz means there are 4 completed cycles in 1 sec |
|
|
If there are 6 completed cycles passed in 2 secs on a wave function, what is its frequency? |
Frequency is counted as completed cycles in 1 sec. Since there are 6 cycles in 2 sec, half of 2 sec is 1 sec which mean half of 6 is 3. The frequency is 3 Hertz |
|
|
If there are 5 completed cycles passed in 0.5 secs on a wave function, what is its frequency? |
Frequency is counted as completed cycles in 1 sec. Since there are 5 cycles in 0.5 sec, twice of 0.5 sec is 1 sec which mean twice of 5 is 10. The frequency is 10 Hertz |
|
|
What is frequency's unit ? |
Hertz, or # of cycles per 1 sec |
|
|
The numbers of completed cycles per 1 second is known as ? |
Hertz, or frequency |
|
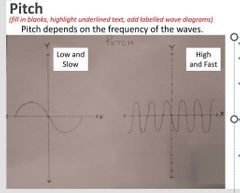
What is a pitch ? |

|
|
|
True or False: The faster the wave the slower the pitch |
False! The faster the wave the faster the pitch |
|
|
True or false: The smaller the pitch, the smaller the frequency |
True! |
|
|
True or False: The higher the frequency, the higher the pitch |
True Also: Faster wave = higher pitch = higher frequency |
|
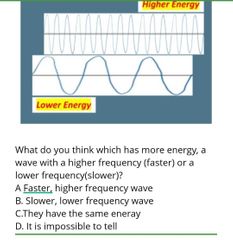
|
Answer: A . Faster high frequency wave has more energy |
|
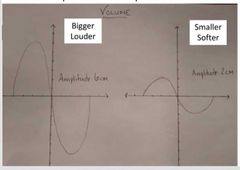
What is a volume ? |
Volume is how LOUD a sound is or how SOFT a sound is Volume is related to amplitude (goes in the same direction) Higher volume means higher amplitude means LOUD sound Lower volume means lower amplitude means SOFTER sound Volume = amplitude =loud/soft sound = larger/smaller wave |
|
|
Remember: Faster or slower wave is DIFFERENT than larger wave or smaller wave |
Fast or slow wave = frequency = pitch (faster/slower)
Larger or smaller wave = amplitude = volume (soft/loud)
|
|
|
________ controls the amplitude of the wave? |
Volume controls the amplitude of the wave |
|
|
True or false: Softer sound means larger amplitude look |
False. Softer sound = smaller volume = smaller amplitude |
|
|
True or false: LOUD sound means larger amplitude |
True |
|
|
Remember, amplitude has NOTHING to do with pitch. It has to do with Volume
Larger amplitude = loud volume = larger sound
Smaller amplitude = soft volume = smaller sound
Soft= smaller Loud = larger |
Frequency has NOTHING to do with VOLUME. It has to do with pitch Larger frequency = higher pitch = faster wave= Smaller frequency = lower pitch = slower wave |
|
Light energy (LE): aka Electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of energy made of photons(massless) that are travel in waves, some of which are visible
|
Photons: massless particles that travel in waves
Photons are NOT protons |
|
|
Type of light waves: 1) long wavelengths: travel slowly Ex: radio wavelength:100km long (100,000m) 2) short wavelengths: travel fast Ex: gamma wavelength: 1x10^-12m (0.000000000001m) |
All wavelengths of light made up of electromagnetic spectrum |
|
|
Gamma waves are examples of _____ |
Gamma waves are examples of very short wavelengths |
|
|
Radio wavelengths are example of ____ |
Radio wavelengths are example of very long wavelengths |
|
|
True or False: electromagnetic spectrum consist of certain wavelengths (very short or very long) |
False! electromagnetic spectrum consist of ALL wavelengths |
|
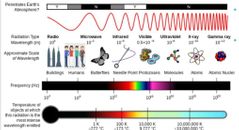
Different types of wavelengths and examples |
As you can see,
The ones with very long wavelengths tend to be a) very slow travel b) lower energy c) slow frequency and d) very cool temperature
The one with with very short wavelengths a) travel fast b)high energy c) high frequency and d) very hot temperatures
|
|
|
Can light travel in space ? |
Yes. Light or light wave can travel in space AND in vacuum because they (photons) do not require matter to move Sound wave cannot travel in vacuum or space because they require matters to vibrate |
|

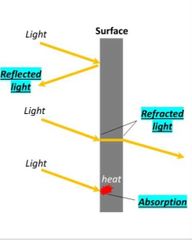
3 ways of light: Reflection, Refraction, and Absorption (RRA acronym) |
|
|
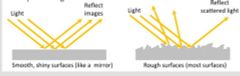
What is reflection? |
Reflection occurs when light rays bounced off a surface that they cannot travel through
Reflection depends on how smooth the surface:
A. Smooth surface: Examples: aluminum foil, mirrors, still water B.rough surface: scattered lights, not complete images. Ex: most surfaces are rough surface, mountains |
|
|
Does rough surfaces reflect images? |

NO, rough surfaces SCATTERED images |
|
|
Does smooth surface reflect images? |
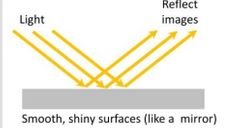
Yes, smooth surface reflect and does not scattered images. |
|
|
When a light ray bounded off a surface it is called a____ |

When a light ray bounded off a surface it is called a reflection
Smooth (still water) vs rough surface (moving water) |
|
|
Mirror, aluminum foils, and still water are examples of ? |
Mirror, aluminum foils, and still water are examples of smooth surfaces |
|
|
Most surfaces, moving water, and mountains are examples of ? |

Most surfaces, moving water, and mountains are examples of rough surfaces |
|
|
What is refraction ? |
Refraction: the bending of light when it passes into new medium |
|
|
True or False: Light waves change speed when they travel through different medium or different phases of matter |
True. Light waves change speed when they travel through different medium or different phases of matter Examples: a straw in a glass of soda, glass prism |
|
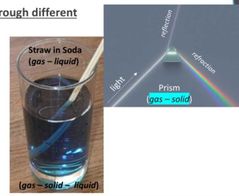
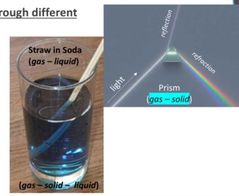
What happen with refraction in a straw in a glass of soda ? |
Light waves bend as they travel through the air (gas), soda (liquid), and glass (solid) resulting in refraction. That is why the straw looks distorted! |
|
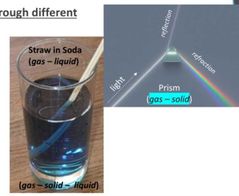
What happen to refraction when light travel to a prism? |
Glass Prism: Triangular piece of glass or plastic. Light waves is splitted into different wavelengths of visible light travel at different speeds through the solid and create a rainbow of colors when they exit |
|
|
Light enters the prism and got splitted into different colors at the other end. This process is called____ |
Refraction |
|
|
The straws looks bend when it enters the water. This process is called ____ |
Refraction |
|

What is absorption? |
Absorption occurs when an object takes in light waves
Photons with certain wavelengths are absorbed until the matter |
|
|
Can atoms absorbs the light ? |

Yes, they can abosrppted the light and become excited and vibrate
Wavelength can only be absorbed if they they match the distance between electron shells in the atoms or molecules just like elevator |
|
|
Processes of atom absorbing lights:
Normal atom --> light absorbed into atoms --> excited atom ---> atom returns to normal and emitting lights |
As atoms or particles absorbing light, vibrations increases and temperature increases |
|
|
True or False: temperature and vibration of the object increases when it absorbs light. |
True. Temperature and vibrating of the object increases when it absorbs light.
|
|
|
Thermal radiation: light energy can be transformed into heat or thermal energy
|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
What are visible light? |
Visible light = Visible spectrum = white light= broken into rainbow colors via a prism
Visible light: also known as white light. It is what our eyes see: white lights.
White light are broken into rainbow colors |
|
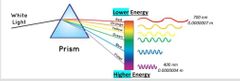
Visible light = White light = Visible spectrum |
As you can see from the picture, white lights enter the prism and is being splitted into rainbow colors (ranging from low energy light colors to high energy light colors) |
|
|
Example of visible lights and questions |

|
|
|
What are rainbows? |
Rainbows are made when light is being refracted and reflected |
|
|
Does light travel faster or slower in higher density material? |
Light travel slower in higher density materials Less dense (air): light travels faster More dense (water): light travels slower |
|
|
How are rainbows formed ? |

|
|
|
What make objects appear as different colors ? |
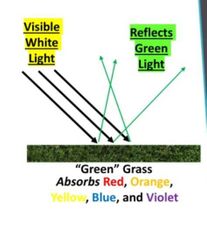
Objects appear as different color due to absorption and reflection. The wavelengths of light that are not absorbed are reflected off an object are what we see
|
|
|
The colors we see are the light wavelengths that are reflected and not absorbed of an object
|

|
|
|
True or false : The "green" grass that we see is due to the grass absorbed all colors of lights (wavelengths) except green color. That green color is reflected |
True . The color of object is due to that object absorbed ALL the wavelengths of colors except the color on its object. That color is being Reflected |
|
|
Why does wearing dark-colored clothing on sunny day make us feel warmer than wearing light-colored clothing? |
Because dark-colored cloth absorbs the light energy and makes us feel warmer Light-colored cloth reflects the light energy and makes us feel cooler |
|

In the sun is about 10-15C (18-26F) warmer than the shade
Black color in the sun is about 5C(10F) warmer than the white color in the sun |
Transformation of light energy into thermal energy (TE) or heat depends on how much is absorbed or reflected
|
|
|
True or False: Black objects absorbed all wavelengths of visible light and white objects reflected all wavelengths of visible light. |

True !
When you wear a black shirt, you'll get warmer because all wavelengths of light are being absorbed
When you wear white shirt, it'll get cooler because all wavelengths are reflected |
|
|
True or False : Black object = all light absorption = cooler temperature White object = all light reflection = hotter temperature |
True Black object = all light absorption = cooler temperatureWhite object = all light reflection = hotter temperature |
|
|
True or False: Black color means all light are reflected |
False. Black color means all light are absorbed |
|
|
True or False: Black color means lower temperature |
True because black color reflects all the light, hence lowering the overall temperature |
|

|

|
|
|
What is thermal energy(TE) ? |
Thermal energy is a type of energy measured as heat and produced when atoms and molecules vibrate and move
Temperature is just a measurement of how fast molecules are moving, so temperature is a measure of how much thermal energy or heat that a substance has.
Thermal energy can move from one substance or object to another |
|
|
True or false: Thermal energy always moves from warmer to colder ) |
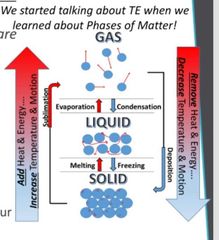
True. If you hold an ice cube on your warm hand, the heat from your hand will move to the ice cube and melt it |
|
|
Add heat and energy to the system will increase temperature and motion and lead to change of phase from solid to liquid to gas |
Remove heat and energy from the system will decrease temperature and motion and lead to change of phase from gas to liquid to solid |
|

|

|
|
|
What is radiation ? |
Radiation is the energy that is sent out and can move through space as infrared electromagnetic wave (EM)
Radiation = EM = sunlight |
|
|
Atoms and molecules give off electromagnetic (EM) wave at their vibration frequencies = infrared radiation (IR) |
Absorbed EM waves, including IR, makes particles vibrate more, increasing their heat |
|
|
Conduction vs convection vs radiation |

|
|
|
True or False : Faster vibration = higher frequency = higher energy = higher temperature = higher heat |
True. Faster vibration = higher frequency = higher energy = higher temperature = higher heat |
|
|
True or False: Short wavelengths = high energy Long wavelengths = low energy |

True : Short wavelengths = high energy . Long wavelengths = low energy |
|
|
Short wavelengths = higher energy = higher temperature = higher frequency = higher or faster vibrations = higher heat
Examples: ultraviolet (below violet range), x-ray, gamma ray |
Long wavelengths = lower energy = lower temperature = lower frequency = lower or slower vibrations = lower heat Examples: radio wave, microwave, infrared wave (below the red range) |
|
|
Visible light = Visible color spectrum = Visible spectrum = white light
Among all colors, four colors are important : White, black, red, and violet |
White color = reflect all colors = cooler temperature
Black color = absorb all colors = hotter temperature
Violet color = reflected only violet color and absorb ALL other color = highest energy of visible colors = shortest wavelength of visible colors
Red color = reflected only red color and absorbed All other colors= lowest energy of visible colors = longest wavelength of visible colors |
|
|
Describe the process of sunlight excite atoms and molecules |
An analogy of sunlight to atoms is that it like to make every at the party (atoms and molecules' electrons) excited . Sunlight in the form of electromagnetic radiation or EM waves reach atoms and molecules. Atoms and molecules' electrons become excited . Once electrons excited, they become higher-energy state. Then, they released the light in the form of heat and become normal state (non-excited) again. |
|
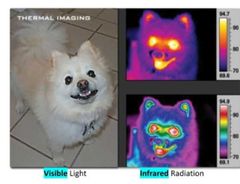
True or false: Anything greater than -268 C( it is in celcius, not farenheit unit) will emit infrared waves |
True. Anything greater than -268 C( it is in celcius, not farenheit unit) will emit infrared waves
Night-vision goggles and infrared cameras can see infrared energy , allow us to see object's energy |
|
|
Any living thing will emit heat in the form of infrared waves above -268⁰C |
Absolutely zero (-273⁰C or 0⁰ Kelvin) is the theoretical temperature that molecules or atoms stop vibrating or stop moving . As you see, -273⁰C is pretty close to -268C. Infrared waves = vibrating or moving |
|

|
Thermal energy: solar power, greenhouse effect, absorption of energy |
|
|
Convection : involves density , warm air rises and cold air sinks
Warm air rises because it has less density than cold air
Density = mass ÷ volume |

Remember that convection happens because warm liquids and gases are less dense than cold liquids and gases |
|

Examples of convection : buoyancy, cloud formation, pressure systems, storms, plate tectonic, tectonic plates movement |

Example of radiations: sunlight, black color's absorption vs white color's reflection , greenhouse gas effect (carbon dioxidegas trapping), global warming,solar power, light energy absorption |
|

|

|
|
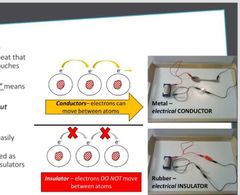
Conduction: must involve when one substance "touching" or contacting another |

|
|
|
Conductor vs insulator |
Conduct: can conduct or transfer electricity or electrons . Example : metal group , copper, water Insulator : cannot transfer electricity . Example: rubber, wood ,ceramic |
|
|
True or False : Heat always move from high temperature (warmer) to low temperature (colder) |
True. Heat always move from high temperature (warmer) to low temperature (colder)
Example: ice cube melt on your hand because the heat from your hand transfer to the ice cube and melt it |
|

Thermal conduction: Heat moves when two substances at different temperatures are physically touching |
When we talk about heat, we talk about vibrations of atoms and molecules |
|
|
True or false: higher density materials are better heat conductors |
True. Higher density materials are much better heat conductors. Examples of high density materials: granite, metal Examples of heat insulator materials : plastic, wood, rubber |
|

Convection (density) vs conduction (contact) vs radiation (em waves) |
Convection: warm air rises . Ex: smokes and heat rises above from the bonfire
Conduction: physically touching. Ex: pot directly sits on a stove, or pushing marshmallows inside the bonfire
Radiation: Heat transfer without touching. Ex: sunlight's heat from the sun warming the skin, one sits nearby bonfire can feel the radiated heat |
|

Answer: point A is A. Electrical Energy . |

Point B is Light Energy . A small portion of the energy will escape as heat as a form of Thermal Energy |
|

MELTSCN: mechanical, electrical, light, thermal, sound, chemical , nuclear
Energy transformation: change energy from one type to another |
Law of conservation of energy: energy can be transformed but it cannot be create or destroyed .
When we study energy , we think about 1) energy transformation, 2)how energy moves and 2) how the 3 phases of matter effects energy movement |
|
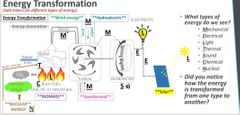
Energy transformation |

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|
Rotation vs Axis |
The Earth rotates on its axis Rotate: spin around Axis: immagrinary line around on which an object spins |
|
|
Direct vs indirect sunlight |
Direct sunlight = zero angle sunlight striking the Earth
Indirect sunlight = sunlight striking the earth at an angle |
|
|
Orbit vs revolution |

|
|
|
1 revolution of the Earth around the sun =?? Days |
1 revolution of the Earth around the sun = 365 days |
|
|
What is an Orbit? |
Orbit is when an object revolves around another object Ex: moon orbiting the Earth The Earth orbiting the sun |
|
|
True or false: season is caused by the Earth's tilting and also by its revolution around the sun |
TRUE Season is caused by the Earth's tilting and also by its revolution around the sun
ROTATION does not cause seasonal change since rotation=short term . 1 rotation = 1 day
Seasonal = long term |
|
|
1 Rotation of the Earth vs 1 revolution of the Earth |
1 rotation of the Earth = 1 days 2 roration of the Earth = 2 days 1 revolution of the Earth = 365 days or 365 rotations! |
|

|
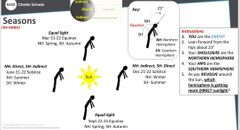
|
|
|
What is equinox? |
Equinox = equal light= equal length of days and night Equinox only occurs during Spring (starting Mar 21-22 DADDY'S BIRTHDAY) and Autumn (starting Sep 22-23
In the Northern Hemisphere, Spring occurs during March 21-22. In the Southern Hemisphere, Autumn occurs during March 21-22
In the Northern Hemisphere, Autumn occurs during September 22-23. In the Southern Hemisphere, Spring occurs during Sept 22-23
|
|
|
What is solstice ? |
Solstice: unequal lights, either longest or shortest days Summer solstice: longest day, shortest night . More DIRECT sunlight shinning because Earth tilted toward the sun (Jun 21-22) Winter solstice: shortest day, longest night. Less sunlight (more INDIRECT sunlight) because the Earth tilted away from the sun (Dec 21-22) |
|
|
Indirect sunlight = what season? |
Indirect sunlight = WINTER = winter solstice= nights are longer than days, starting Dec 21-22 in Northern Hemisphere
In Northern Hemisphere, Dec 21-22 is winter so therefore the Southern Hemisphere it will be summer |
|
|
True or False: Indirect sunlight means the earth tilted toward the sun
|
FALSE. Indirect sunlight means the earth tilted away from the sun |
|
|
Direct sunlight = what season? |
Direct sunlight = summer solstice =summer season = days are longer than nights= starting June 21-22 in the Northern Hemisphere
In Northern Hemisphere, June 21-22 is summer so therefore the Southern Hemisphere it will be in the winter
|
|
|
True or False: direct sunlight means the earth tilted toward the sun |
True |
|
|
True or False : If the Northern Hemisphere is receiving indirect sunlight then the southern hemisphere is receiving direct sunlight |
True ! If the Northern Hemisphere is receiving indirect sunlight (winter) then the southern hemisphere is receiving direct sunlight (summer) |
|
|
True or False : If the Northern Hemisphere is titled toward the sun then the southern hemisphere tilted away from the sun! |
True ! If the Northern Hemisphere is titled toward the sun(summer or summer solstice) then the southern hemisphere tilted away from the sun (winter or winter solstice)! |
|
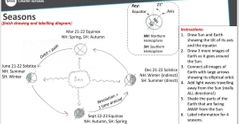
|
Need to remember the shade and labels as well as the important months ! |
|

|

|
|
|
True or False: The moon's gravity is responsible for high and low tides on earth |
TRUE! |
|
|
Moon's fact: 1. It is the only Earth's natural satellite 2. Stabilizing Earth's climate and wobble 3.has different phases (waxing crescent, waxing glibbons etc) 4. Its gravity creates high n low tides on the Earth
|

|
|

|

|
|
|
True or False: The sun is a huge ball of hot gas that constantly undergoes nuclear fusion and gives off radiation |

True ! |
|

Amplitude refers to the heigh Definition: distance from midline to the crest Amplitude = Sound |
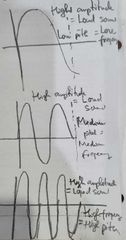
Frequency refers to the numbers of complete waves passed in 1 second Frequency = Pitch |
|
|
Wind energy is an example of what kind of energy transformation ? |
Wind energy path: mechanical (wind) --> mechanical(spinning turbine)--> electrical (spinning magnets) |
|
|
Geothermal is an example of what kind of energy transformation ? |
Geothermal energy path: mechanical (steam) --> mechanical(spinning turbine)--> electrical (spinning magnets) |
|
|
Hydroelectric is an example of what kind of energy transformation ? |
Hydroelectric energy path: mechanical (water) --> mechanical(spinning turbine)--> electrical (spinning magnets) |
|
|
Biomass is an example of what kind of energy transformation ? |
Biomass energy path: chemical (composted) --> light (spinningfire due to coal,gas,fuel)--> mechanical (steam)---> mechanical (spinning turbine)---> electrical (spinning magnets) |
|
|
Dvd player energy transformation path |
Dvd: electrical --> mechanical --> sound and light wave |
|
|
A black shirt sitting in the sun energy transformation |
Light energy to thermal energy via absorption process |
|
|
A balling rolling downhill is an example of what kind of energy transformation ? |
Mechanical (potential)---> mechanical (kinetic) |
|
|
Raking leaves is example of what kind of energy transformation |
Mechanical energy to sound energy |
|
|
A lamp or light bulb is an example of what kind of energy transformation ? |
Electrical --> light energy AND thermal energy |
|
|
A wind-up music box is example of what kind energy transformation ? |
Mechanical energy to sound energy |
|
|
A radio is example of what kind of energy transformation |
Electrical(plug in) to mechanical (know tunning) to light energy (radio wave) to sound energy |
|
|
Plucking guitar string is an example of what kind of energy transformation |
Mechanical energy to mechanical energy to sound energy |
|
|
Difference between orbit and revolution |
Orbit does not mention the number and revolution does! Both orbit and revolution mean a planet or moon that goes around another object due to Gravitational force |
|
|
Orbit: a planet or moon's path that travel on as it goes around another object in space Notice it does not mention the number |
Revolution: it refers to planet or moon travelling around another object one time Notice it mentions the number! |
|
|
Revolution vs Rotation |
Both mention number in description Rotation also refers to spinning or moving around an axis or imaginary line Revolution does not mention imaginary line |
|
|
True or False: season is affected by Earth's tilted axis and Earth's revolution |
True! Season is affected by Earth's tilted axis and Earth's revolution Season is not affected by rotation! |
|
|
Remember the diagram of seasons, soldiers and equinoxes |
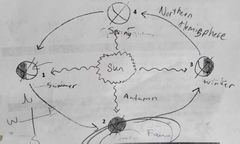
|
|
|
Acronym for all planets from closet to the sun to furtherest from the sun: My Very Eager Mother Just Served Us Noodles: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars,Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune |
Rocky Planets: My Very Eager Mother (MERCURY, VENUS, EARTH, MARS) GAS GIANTS: Just Served Us Noodles (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ) |

