![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What does the term quantum mean |
A quantity that only exists in integer multiples |
|
|
What are some experiential observations that cannot be explained by classical physics, but can be explained using quantum theory |
Black body radiation curves (ultraviolet catastrophe) The formation of emission and absorption spectra The photoelectric effect |
|
|
Summarise the Bohr model of the atom |
Electrons can only occupy certain discrete orbits While in these orbits no energy is emitted Electrons can jump between orbits Electrons emit a photon of they jump down an energy level Electrons absorb a photon is they go up a level The energy of the emmited/absorbed photon is equal to the difference between the energy levels |
|
|
What are the certain wavelengths of light emitted by an atom called |
Line spectrum |
|
|
What is the word particles used to describe |
A localised phenomena that transports energy and mass |
|
|
What is the word wave used to describe |
A delocalised phenomena that carry energy but no mass |
|
|
What is Heisenberg's uncertainty principle |
It is impossible to determine accurately both position and speed and direction of a quantum particle at the same instant |
|
|
Explain the helical motion of a particle |
The component of velocity perpendicular to the feild causes a centripetal force, which produces a uniform circular motion. The component of velocity parallel to the feild is constant, so no unbalanced force in that direction. |
|
|
What are cosmic rays |
High energy particles originating from outer space |
|
|
What is solar wind |
A stream of plasma released from the upper atmosphere of the sun. It consists mainly of protons and electrons |
|
|
What is simple harmonic motion |
When an object is displaced from its equilibrium or rest position, and the unbalanced force is proportional to the displacement of the object and acts in the opposite direction, the motion is said to be simple harmonic |
|
|
What is wave motion |
In wave motion only energy is transferred. There is no net mass transport |
|
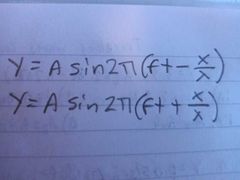
When would you use each one |
Top- for finding displacement for wave traveling left to right Bottom- same for right to left |
|
|
What is the intensity of a wave |
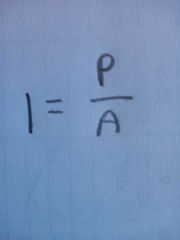
Intensity of a wave is the energy per second per unit area |
|
|
What is the wave energy directly proportional to? |
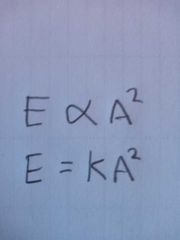
The wave energy (or intensity) is directly proportional to is amplitude squared |
|
|
What is phase difference |
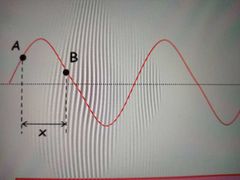
Phase difference is the separation between two points on a wave, expressed as an angle in radians |
|
|
What is the phase difference and separation of two points that are in phase |
Phase difference- 0 Separation- π, 2π, 3π.... |
|
|
What is the equation for phase difference |
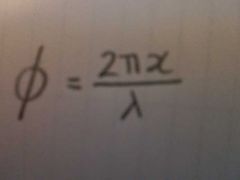
|
|
|
What is the phase difference and separation of two waves completely out of phase |
Phase difference- π rad Separation- 1/2 wavelength |
|
|
How are the Auroroe formed |
They are caused by solar wind particles which penetrate the Earth's upper atmosphere. These particles strike nitrogen and oxygen molecules causing their electrons to be excited into higher energy levels and then emit light when the electrons drop back down to their previous levels. |
|
|
What happens when cosmic rays reach earth |
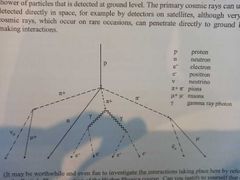
They interact with particles in the earth's atmosphere, producing a chain of reactions resulting in the production of a large number of particles known as a cosmic air shower |
|
|
What is dampening |
The rate which energy is lost, or the amplitude of oscillations decreases. |
|
|
What is underdamping |

If the frictional force is small it continues to oscillate for a while, the amplitude decreases slowly |
|
|
What is critical dampening |
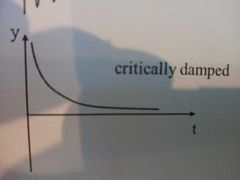
The value of frictional resistance which is just sufficient to prevent any oscillation past the rest position |
|
|
What is overdamping |
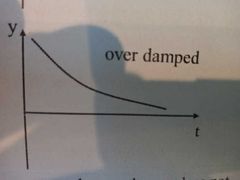
Systems with a very large resistance produce no oscillations and take a long time to come to rest |
|
|
How are stationary waves formed |
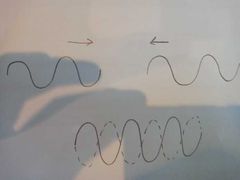
By the interference between two waves of the same frequency and amplitude, traveling in opposite directions. |
|
|
What are nodes and antinodes |
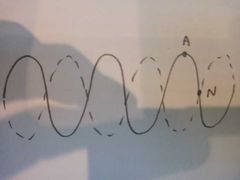
Nodes are positions that always have zero amplitude Antinodes are points of maximum amplitude |
|
|
What is interference by division of amplitude |
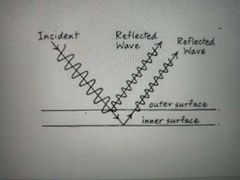
The splitting of one wave into two by producing a reflected wave and a transmitted wave at the surface between media of different refractive index |
|
|
What happens to light reflected off a medium of greater refractive index |
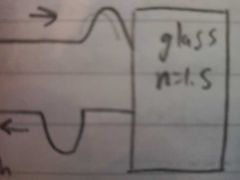
A phase change of π occurs when light is reflected from a higher refractive index medium |
|
|
What happens to light reflected off a medium of lower refractive index |
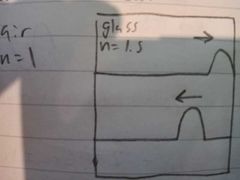
No phase change occurs |
|
|
For destructive interference to occur what must the opd be? |
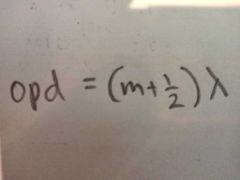
A half number of wavelengths |
|
|
For constructive interference to occur what must the opd be? |
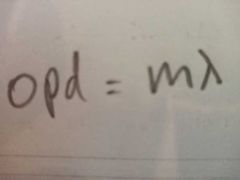
A whole number a wavelengths |
|
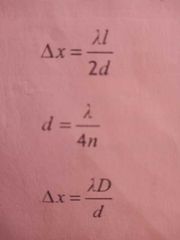
|
Top- wedge fringes Middle-non-reflective coating Bottom- youngs double slit |
|
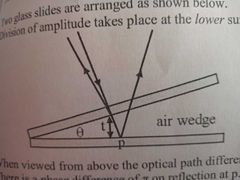
Wedge Fringes |

|
|
|
Non-reflective coating |
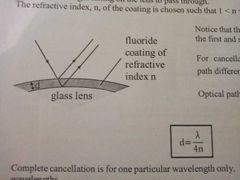
|
|
|
Experimental evidence of particle like behaviour of electrons |
An electron has mass and can be accelerated, this can be seen in a cathode ray tube. Photoelectric effect |
|
|
Experimental evidence for wave like behaviour of electrons |
Electrons can diffract and produce interference patterns |
|
|
What are the conditions for two waves to be coherent |
They have the same frequency and wavelength, and there is a constant phase difference |
|
|
Destructive interference between two overlapping coherent waves is when: |
The phase difference is π The crests of each wave are half a wavelength apart A crest is superimposed on a trough |
|
|
Constructive interference between two overlapping coherent waves is when: |
The phase difference is zero The crests of each wave are superimposed on one another |
|
|
What is the optical path difference for interference by division of amplitude when 1- phase change in only one of the waves 2- phase change in neither or both waves |
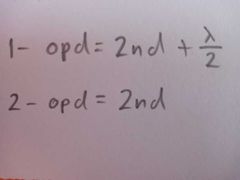
|

