![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are constituent parts of an atom? |
Proton, neutron, electrons exist in discrete energy shells. |
|
|
|
Why were neutrinos hypothesized? |
Beta decay was at first only thought to contain an electron but that would mean energy was not conserved, so neutrinos were hypothesized to exist. |
|
|
|
What holds the nucleus together? |
The strong nuclear force only affects the protons and neutrons. It does not differentiate between proton to proton or neutron to neutron. It binds the two particles together - at seperations of less than 0.5fm, it is highly repulsive, at seperations of 0.5fm to 3fm it is highly attractive, any larger than 3fm it has no range. |
|
|
|
What are the two decay types and how do they happen? |
In beta decay, a neutron turns proton, a neutrino and electron. This tends to happen in neutron rich nuclei. In alpha decay, a proton turns into a neutron. This happens in proton rich nuclei, and an alpha particle is released. |
|
|
|
What are the four fundamental forces and what are their interaction particles? |
Gravity - Gravitons Electromagnetic - Virtual Photons (Charged particles only) Weak force - W+, W- (All particles) Strong Force - pi+, pi-, pi0 (hadrons only) |
|
|
|
What did einstien prove? |
Einstien discovered that photons must come in quanta (ie packets). |
|
|
|
Describe the process of ahnnilation. |
When a particle and it's antiparticle meet and their rest mass is turned into high energy photons. |
|
|
|
What is pair production? |
When a particle and antiparticle is made from a single photon, normally happens near a nucleus. |
|
|
|
Draw a feynman diagram for B- decay, B+ decay, and electron capture. |
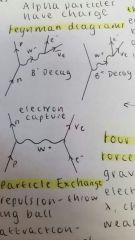
|
|
|
|
Describe two simple models of particle exchange. |
Attraction - throw a boomerang on skateboards. Repulsion - throw a ball on skateboards. |
Boomerang, ball |
|
|
How do we classify particles? |
Matter / \ Lepton Hadron / \ Baryon Meson |
|
|
|
What is a lepton? |
A lepton is a fundamental particle that does not feel the strong nuclear force. It can interact via the weak force and electromagnetic if charged. These particles are stable with the exception of the muon and the tau. |
|
|
|
What is a hadron? |
A hadron is a particle that feels the strong nuclear force. It is made of smaller particles called quarks. Hadrons decay via the weak interaction and interact via the strong interaction - the strong interaction is where strange particles are made. This group is further subdivided into the baryons and mesons. |
|
|
|
What is a baryon? |
A baryon is a particle that is made of three quarks or three antiquarks. These are the types of hadrons that contain protons in their decay products. The proton is the only stable baryon. |
|
|
|
What is a meson? |
A meson does not include any protons in their decay products. A general rule of thumb is that all mesons are unstable. Mesons can interact via the strong nuclear force. |
|
|
|
What do you know about kaons? |
Kaons are the heaviest and the most unstable. They have a short half life and decay into pions. |
|
|
|
What do you know about pions? |
The lightest and decay into high energy photons, found via cosmic rays. |
|
|
|
How is a particle made to be strange? |
Strange particles are made via the strong interaction and decay via the weak. Strangeness is conserved in strong interactions. |
|
|
|
Describe the photoelectric effect. |
When electromagnetic radiation is incident on metal, the electrons inside it absorbs the energy. It then escapes the metal. |
|
|
|
Why does wave theory not agree with photoelectric effect? |
- Intensity should increase the Ek of electrons but it doesn't and only increases the number of electrons emitted per second. - All forms of light should emit electrons eventually, no matter the frequency. |
|
|
|
What observations can be made from the photoelectric effect? |
- No electrons are emmitted when below threshold frequency. - All energies vary up to Ek max. - Intensity is proportional number of electrons are emitted per second. |
|
|
|
What is ionisation? |
Ionisatiom energy is defined as the energy required to fully excite an electron from ground state. |
|
|
|
What is the electron volt? |
The KE energy carried by an electron after it is accelerated theough a pd of one volt. |
|
|
|
What is line spectra is evidence of? |
Is evidence of absorption and excitation of an atom as emission only shows certain energies. |
|
|
|
How do you get absorption spectra? |
Pass light through a cool gas and then seperate it with a prism. Black background with colored lines. |
|
|
|
How does fluorescent tubing work? |
A tube coated in phosphor is filled with mercury gas at low pressure, it contains a bimetallic starter strip at one end that accelerates electrons through an electric field. |
|
|
|
Excitation is a major process of fluorescent tubing. Why? |
The electrons collide with mercury atoms and excite them. The atoms dexcite and emit photons which are absorbed by the coating and remitted as visible light photons. |
|

