![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What happens to a ray of light when it goes from air to a more dense medium?
|
It's speed and wavelength change
Frequency does not change in a new medium |
|
|
Which type of electromagnetic wave is more readily absorbed:
long wavelengths or short wavelengths? Would IR be absorbed at more than visible light? |
Shorter wavelengths are more readily absorbed (hence an xray has high frequency and is absorbed by bone)
IR has a longer wavelength than visible light, so visible light is absorbed more. |
|
|
If a sound is reduced by an intensity of 20dB's, what factor of intensity does it decrease by?
|

intensity
|
|
|
For a block on an incline plane, what is the force parallel to the incline (pulling the block down
|
F = mg sin (θ)
|
|
|
If a block on an incline plane at angle θ is not moving, what is the μs (static coff)?
|
μs ≥ tan θ
|
|
|
What is constant while in uniform circular motion:
Speed? Velocity? |
Speed is constant
Velocity is changing direction, hence no constant |
|
|
Give eqn for centripetal acceleration
|
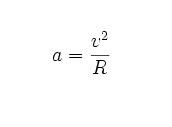
centripetal acceleration
|
|
|
Define centripetal force
|
Sum of Ft in string and gravity, not a new force
|
|
|
Give eqn for rotational momentum
|

rotational momentum
|
|
|
Give eqn for torque relating it to rotational acceleration
|
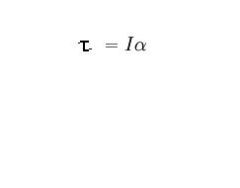
rotational acceleration
|
|
|
What is impulse (J)?
|
Change in momentum
|
|
|
What are the 3 different types of heat transfer?
|
Conduction: vibration of atoms transfered to neighbors
Convection: heat transfers to air, air becomes less dense, carries heat upwards Radiation: sun rays travel across empty space to heat earth |
|
|
What is the density of water?
|
1g/cm^3
|
|
|
How does each density react to changes in temp and pressure?
Give 2 eqns pertanint |
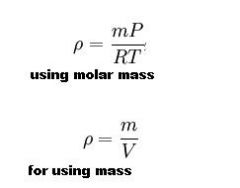
Solids and liquids don't change much, thus their specific gravity doesn't change much
Gases however follow the eqns above |
|
|
Give eqn for flow rate (Q)
|
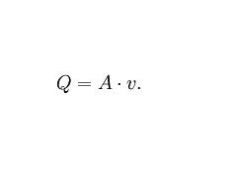
Flow rate
|
|
|
Describe the force that drives capillary action up a tube? Give eqn of the force
|

Surface tension. Force that resists changes surface distortion
|
|
|
Can a magnetic field do work?
Can it change speed and direction? |
No, it is always perpendicular to v
It can change speed and direction |
|
|
What is the 1st harmonic of a wave with wavelength X in a closed tube?
|
1/2 wavelength.
|
|
|
What is the definition of n (like in Snell's Law) in optics?
|
n = c / v speed
its the speed of light / v of light in medium |

