![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Kinematics Equations |
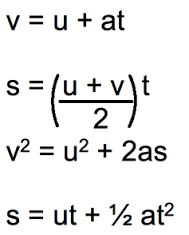
S=Distance (m) U=Initial Velocity (ms^-1) V=Final Velocity A=Acceleration (ms^-2) T=Time (s) |
|
|
Equation for weight |
W=mg F=mg M=Mass (Kg) g=Gravitational field strength (ms^-1) W/F=Force/ Weight (N) |
|
|
Newton's second law |
F=ma F=Force (N) M=Mass (Kg) a=Acceleration (ms^-2) |
|
|
Moments equation |
Moment=Fx F=Force (N) x=Distance from pivot (m) |
|
|
Work done equation |
W=Fs W=Work done (J) F=Force (N) s=Distance (m) |
|
|
Kinetic Energy |
Ek=1/2 mv^2 Ek=Kinetic energy (J) m=Mass (Kg) V=Velocity (ms^-1) |
|
|
Gravitational Potential Energy |
Eg=mgh Eg=Gravitational potential energy (J) m=Mass (Kg) g=Gravitational field strength (ms^-1) h=Height (m) |
|
|
Power (non circuit) |
P=E/t P=W/t P=Power (w) E/W=Energy/ Work done (J) t=Time (s) |
|
|
Potential difference |
V=W / Q V=Potential difference (V) W=Work done (J) Q=Charge (C) |
|
|
Resistance (ohm's Law) |
R=V / I R=Resistance (Ω) V=Potential Difference (V) I=Current (A) |
|
|
Current equation |
I=Q / t I=Current (A) Q=Charge (C) t=Time (s) |
|
|
Resistivity |
R=pl / A R=Resistance (Ω) p=Resistivity (Ωm) l=Length (m) A=Cross section (m^2) |
|
|
Current (drift velocity) |
I=nqvA I=Current (A) n=Density of charge carriers (m^-3) q=Charge on carrier (C) V=Drift velocity (ms^-1) A=Area of cross section (m^2) |
|
|
Power (circuit) |
P=VI P=Power (w) V=potential difference (V) I=Current (A) |
|
|
Density |
p=m/v p=Density (KgM^-3) m=Mass (Kg) v=Volume (m^3) |
|
|
Stokes' Law |
F=6πrηv F=Frictional force/Drag (N) r=Radius (m) η=Viscosity (mPa s) v=Velocity (ms^-1) |
|
|
Hooke's law |
F=kx F=Force (N) k=Spring constant (Nm^-1) x=Extension (m) |
|
|
Pressure |
p=F/A p=Pressure (Pa) F=Force (N) A=Area (m^2) |
|
|
Stress |
δ = F / A δ=Stress (Pa) F=Force (N) A=Area (m^-2) |
|
|
Strain |
ε = Δx / x ε=Strain Δx=Change in length (m) x=Original length (m) |
|
|
Young modulus |
E = Stress/Strain E=Young modulus (Pa) |
|
|
Elastic energy |
E = 1/2 FΔx E=Elastic energy (J) F=Force (N) Δx=Change in length (m) |
|
|
Wave speed |
v=fλ v=Velocity (ms^-1) f=Frequency (Hz) λ=Wavelength (m) |
|
|
Speed of a transverse wave on a string |
V = (T / μ)^1/2 V=Velocity (ms^-1) T=Tension (N) μ=mass/unit length |
|
|
Intensity of radiation |
I = P / A I=Intensity (Wm^-2) P=Power (W) A=Area (m^-2) |
|
|
Power of a lens |
P = 1/f P=Power (D) f=Focal point (m) P = P1 + P2 + P3 +... |
|
|
Thin lens equation |
1/f = 1/u + 1/v f=Focal point (m) u=image distance (m) v=object distance (m) |
|
|
Magnification |
= Image height / Object height |
|
|
Diffraction grating |
nλ = dsinx n=Order λ=Wavelength (m) d=Distance between grating (1/period) x=Angle between beam and n |
|
|
Refractive index |
n1sinx1 = n2sinx2 n1=Refractive index 1 x1=Incidence angle n2=Refractive index 2 x2=Reflection angle |
|
|
Critical angle |
sinC = 1/n c=Critical angle n=Refractive index |
|
|
Photon model |
E = hf E=Energy h=Planck's constant f=Frequency (Hz) |
|
|
Einstein's photoelectric equation |
hf = Φ + Ek Ek=Kinetic energy (J) Φ=Threshold frequency (Hz) |
|
|
De Broglie waveform |
λ = h / p λ = Wavelength h=Planck's Constant p=Momentum |

