![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many rads for a 2 minute upper GI
|
5-15 rads (question answer is 6 roetgens)
|
|
|
Normal amount of mA for flouro
|
0.5 – 5 mA
Usually 1 – 3 mA |
|
|
Normal amount of mA for spot films
|
100 mA or higher
|
|
|
If the tube is operated above 125 kVp, what size Al eq is required
|
3mm
|
|
|
Source to table top distance
|
Cannot be less than 12” and should be 18”
Mobiles are required to be at least 12” Fixed units, 15” |
|
|
protection of the table top
|
Less than 1 mm Al eq at 100 kVp
|
|
|
The primary protective barrier
|
The II is the primary barrier and must have 2 mm Pb eq for systems operating above 125 kVp
|
|
|
Lead equivalent of the bucky slot cover
|
Automatically covered, 0.25 mm Pb eq
(protects penis) |
|
|
Lead equivalent of protective curtains
|
0.25 mm Pb eq
|
|
|
Amount of scatter at 1 ft
|
Scatter at 1 foot can reach 500 mrad/hr
|
|
|
Amount of exposure rate
|
Cannot exceed 5 rad/minutes
|
|
|
types of artifacts
|
Distortion
Size, shape, pincushion Lag Vignetting Less bright at the edges than center of image Magnification tubes, Multi-mode Variable FoV |
|
|
Photospot camera dose
|
½ to 1/3 dose of convent. Cass
|
|
|
Cine camera dose
|
Per frame basis 10 x the dose than fluoro
|
|
|
dosage with change of II FOV
|

|
|
|
Advantages of medium/high frequency generator
|
Relatively high mA
Higher effective kVp Near constant potential Less ripple |
|
|
How many photons/ray from input screen
|
1 X Ray photon creates 3,000 light photons
|
|
|
What percent of light rays are converted into electrons
|
only 10 to 20% of light photons are converted into photoelectrons
|
|
|
brightness gain
|
BG is the product of minification gain and flux(electronic) gain
|
|
|
flux gain
|
Caused by the conversion efficiency of the output phosphor and the acceleration of the electrons across the II
|
|
|
How much is the flux gain
|
Flux gain is usually between 50 and 150.
|
|
|
What is minification gain
|
Minification Gain
Input phosphor dia.2/output phosphor dia2 |
|
|
How much does brightness gain deplete annually
|
Brightness gain will deteriorate 10% annually
|
|
|
What percent of the light goes to the video camera
|
10% of the output light goes to the vidicon (video camera) the remainder goes to the photospot device
|
|
|
ABC
|
Increase mA increase brightness; direct relationship
Increase kVp 10% double brightness |
|
|
Places where brightness is sensed for the abc
|
II photocathode current
Television camera signal sensing Lens coupled phototube sensing |
|
|
types of abc settings
|
Variable mA, preset kVp
Set the kVp and the unit adjusts mA Variable mA with kVp following If the mA range is exceeded the unit will automatically adjust the kVp to compensate Variable kVp, preset mA Set the mA and the unit adjusts kVp Variable kVp, variable mA |
|
|
horizontal resolution
|
Bandwidth or bandpass
Increase frequency bandwidth increase horizontal resolution |
|
|
vertical resolution
|
Determined by number of scan lines
Kell factor Ratio of vertical resolution and scan lines |
|
|
cinefluoroscopy
|
Synchronization
Camera shutters open at the same rate as x-ray pulses |
|
|
pulsed flouroscopy
|
Variable frame rates are possible with a corresponding decrease in patient dose
|
|
|
Spot film
|
Dose 20 – 50 X higher per frame than fluoro because of higher mA
|
|
|
Boost fluoro
|
10-20 mA usual 40 mA potentially
Increase patient dose 2-10 times reg. Fluoro 10-50 rads per minute Limited to 20 rad/minute unless recording the image |
|
|
Rads per minute with boost
|
10-50
|
|
|
What is the limit
|
Limited to 20 rad/minute unless recording the image
|
|
|
collimation
|
A border needs to be visible when the II is 14 inches above the tabletop and the collimator is fully opened
|
|
|
filtration
|
2.5 mm Al eq < 125 kVp
3.0 mm Al eq at 125 kVp and above |
|
|
exposure rate
|
Exposure rate should be less than 2.2 rads/min at 80 kVp
|
|
|
exposure rate
|
Limited to 5 rads per minute
If the unit has ABC/ABS then 10 rads/minute is allowed However, if the unit has ‘boost’ then the limit is 5rads/minute |
|
|
inspection
|
ABC/ABS units have to be checked by a physicist annually
Also have to have weekly fluoro checks of mA and kVp No ABS 3 year check by physicist |
|
|
increased distance from II
|
TPD increases from 12 to 18 inches
Pt. Dose decreases by 30% |
|
|
gonad shielding
|
0.5 mm Pb eq
97% effective at 100 kVp and 3 mm Al filtration |
|
|
scatter radiation at different angles
|
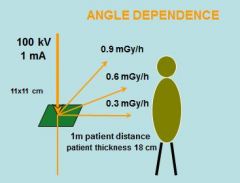
45 degrees is the worst
|
|
|
scatter radiation at different distance
|
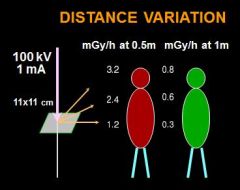
|
|
|
ssd for mobile equipment
|
SSD has to be at least 12 inches
|
|
|
immediate notification
|
Total dose 25 rems
Eye dose 75 rems Skin or extremity dose of 250 rems |
|
|
24h notice if
|
Total dose 5 rems
Eye dose 15 rems Skin or extremity 50 rems |
|
|
somatic effects of radiatin
|
Somatic dose indicators
Injuries to superficial tissue Induction of cancer Cataracts, fertility issues, life-span shortening Injuries to developing fetus Based on dose at specific locations or points |
|
|
genetic
|
50 rads temp male sterility
30 rads temp female sterility |
|
|
high bone marrow exposure
|
BE, UGI, abdominal angio
|
|
|
radiation effects
|
25 rads or less demonstrate no effects
|
|
|
embryologic effects
|
As little as 10 rads demonstrates effects in animal models
50 rads can cause spontaneous abortion |
|
|
bone marrow coverage
|
Aprons cover 80% of the bone marrow
|
|
|
film badge detector
|
10 mrad to 700 rads
+- 25% accuracy |
|
|
maximum dose over 18
|
Whole body - head, trunk, arms above the elbow, and legs above the knee
5 Rem |
|
|
maximum dose over 18
|
Skin and extremities
50 rem |
|
|
maximum dose over 18
|
Lens
15 Rem |
|
|
maximum dose under 18
|
Occupational dose for people under 18 y/o 10% of adult dose
|
|
|
occupational exposure
|
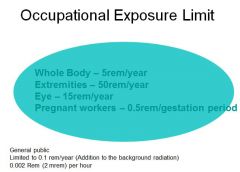
|
|
|
At 80kVp the intensity of X-ray at the the table top should not exceed
|
2.2R/min
|
|
|
Doubling the distance from the Xray tube to the II will
|
decrease the output to 1/4
|
|
|
The normal viewing distance for binocular vision is
|
4-8 inches
|
|
|
Scatter radiation exposure at 1 hr
|
500mR/hour
|
|
|
magnification is switch to 6 inch field of view
|
exposure rate has increased by 150%
|
|
|
300ergs for 3 grams is
|
1 rads
|
|
|
Gonadal shield
|
.5 pb equiv
|
|
|
What film size in spot film has the greatest dose
|
105
|
|
|
time it takes to recognize an object
|
0.2sec
|
|
|
flourescent material and minification will result in
|
brighter image at the output phosphorus
|
|
|
What is a virtual line
|
image created by actual intersection of light rays
|
|
|
plumicon TV
|
least exposure
|
|
|
electronic intensification
|
electrons are moved at high speed from the photocathode to the output intenisfier
|
|
|
What happens to a centrally located image on the input window
|
If the center of the image intensifier has better resolution and less geometic distortion it follows that
a sma'' 'mage 'ntensifier, that encompasses only the central, more accurate'y focused e'ectrons, produces a better-qua,,ty ,mage than a ,arge un,t |
|
|
Cause of increased radiation with magnification
|
Concurently, the collimator must
automatically reduce the X-ray ield to the useable input phosphor area. The 6-inch mode has a reduced miniication gain with ewer photoeectrons incident on the output phosphor. A dimmer image J is the result With automatic bightness control (ABC) the mA is automaically increased when the y\V\V v( unit is used in the 6-inch node o compensate for the decreased bightness. Thus, paient dose also increases |
|
|
Moving from 9 to 6 will
|
more than double the dose
|
|
|
What controls the mottle
|
mA
|
|
|
Does a smaller tv have better resolution
|
yes
|
|
|
Last image hold decreases flouro by 80%
|
yes
|
|
|
The speed of any given camera sysem depends on the abifty of its lens o concentrate light on a
given area and is denoted by the lens* "f-number. |
as F decreases less light needed by worse quality
|
|
|
High level fluoroscopy refers to a "special activation' capability of a luoroscopy system to provide
significantly higher tube currents, from 10 to 20 mA, and in some instances to even 40 mA. The coresponding entance dose rate o the patient is 2 o 10 times higher than conventional luoroscopy, from 10 to 50 rads per minute at the tabletop |
yes
|
|
|
maximum tabletop dose rate o 20 rads per minute when acquiring
images without recording devices such as videotape. |
yes
|
|
|
During digital flouroscopy, how does the under-table x-ray tube operate?
|
it operates in the radiographic mode. Tube current is measured in hundreds of mA instead of less than 5 mA, as in image-intensifying fluoroscopy.
|
|
|
If the flouro has AEC the max exposure rate is
|
10R/min
|
|
|
The linear nonthreshold curve
|
the most conservative type of dose effect cuvrve and also the curve upon which radiation protection guides and regulatory requirements are based on
|
|
|
Several hundred rads will result in cataractses
|
yes
|
|
|
risk to fetus for malformation is significantly increased if
|
above 15 rads
|
|
|
high radiation area
|
greater than 100mrem
|
|
|
radiation area
|
greater than 5mrem
|
|
|
cardiac catheterization bone marrow dose
|
110 mrads
|
|
|
dosage a pt would recieve for 5 minutes of flouro
|
10-30
|
|
|
dose to fetus from 5 R
|
100milirad
|
|
|
Cine with 33 mm film at 30frame sec exposure rate
|
10-20 R/min
|
|
|
5 rems to the skin of the whole body
|
notify state within 24h
|
|
|
If an occupational worker is exposed to 2 Rems in a calendar quater
|
notify within 30 days
|
|
|
red bone marrow
|
most sensitive tissue
|
|
|
0.25 pb
|
decrease exposure by 97%
|
|
|
stray radiation from x-ray tube
|
leakage radiation
|
|
|
material in TLD
|
lithium flouride
|
|
|
5 rems a year
|
occupational 18 and over
|
|
|
special procedure examination or pregnant
|
can wear a 2nd device
|

