![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Force of gravity equation |
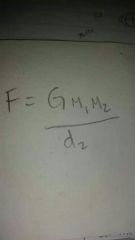
|
|
|
Solar tides |
Are about half as high as lunar tides |
|
|
Spring tides |
Full & New moons Earth, moon and sun in alignment Higher high tides Lower low tides Moon and sun tug on earth |
|
|
Neap tides |
Lower high tides Higher low tides Lesser variation low-high 1st and 3rd quarter moons |
|
|
Relativity |
All measurements are relative to the motion of the observer |
|
|
Einstein's gravity |
Local curvature of space-time governs how masses accelerate. Mass governs the local curvature of space-time |
|
|
Newton discovered |
Gravity is universal |
|
|
Universal gravitational constant |
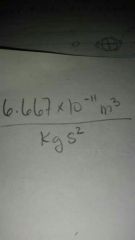
|
|
|
Gravitational force b/w Earth and an object |
Weight mg |
|
|
Force of gravity when distance is doubled |
1/4 (Gm1m2)/(d^2) |
|
|
When is weight equal to more than mg? 0? |
=to more than mg: support force+acceleration 0=no support force |
|
|
Ocean tides are caused by |
Differences in gravitational pull b/w moon and earth on opposite sides of earth. Moon pulls on one side more than the other |
|
|
Magnitude of gravitational field at Earth's center |
0 Gravitational forces cancel in every direction |
|
|
Einstein viewed the curving of a planet |
As the pth along the curved space (due to gravity) around the planet. |
|
|
If Earth shrank with no change in mass |
Your weight at Earth's surface would increase. Be closer to center of earth. |

