![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Y axis |
The vertical axis runs up and down. Measures velocity ( speed) and depth |
|
|
|
X-axis |
The horizontal axis, or X axis run side to side. X Measures time |

|
|
|
Unrelated |
Two items that are not associated |
|
|
|
Directly related |
Two items that are associated or affiliated however the relationship between them does not have to be specified |
|
|
|
Directly proportional |
Two items that are associated such that when one item increases the other increases |
|
|
|
Inversely related |
Two items are associated such that when one item increases the other decreases. |
|
|
|
Inversely proportional |
Two Items are associated such that when one item increases the other decreases |

|
|
|
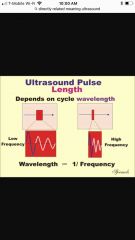
Reciprocal relationship |
When two numbers with a reciprocal relationship or multiplied together the result is one (period and frequency are reciprocals. |
Ex: 2 and 1/2 10 and 1/10 |
|
|
Sound |
Is a longitudinal mechanical wave in which particles in the medium move |
Is a mechanical wave in which particles in the medium move |
|
|
Acoustic propagation properties |
The effects of the medium upon the sound wave. (How sound is traveling) |

|
|
|
Biological effects |
The effects of the sound waves upon the biological tissue through which it passes. Over long periods of time possible tissue. |
|
|
|
Acoustic variables |
Sound waves pressure, density, distance |

|
|
|
Acoustic parameters |
Used to describe a wave there are seven |

|
|
|
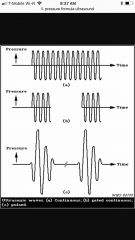
Pressure |
A force within an area measured and PasCala (Pa) |
|
|
|
Density |
Concentration of mass in a volume (Weight) Unit kg/cm 3 (cubed) |

|
|
|
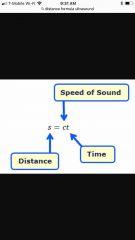
Distance |
Measures of particle motion Cm, feet, mile, mm |
|
|
|
Transverse waves |
Particles move in a direction that is perpendicular (at right angles) |
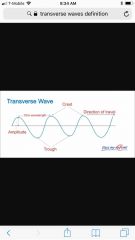
|
|
|
Longitudinal wave |
Particles that move in the same direction that the wave propagates. Sound is a longitudinal wave. |
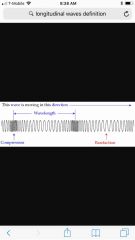
S |
|
|
In-Phase |
A pair of waves in phase when their peak i.e. maximum value, occurs at the same time and at the same location. |
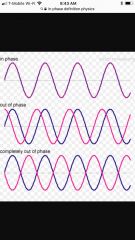
|
|
|
Out-of-phase |
In contrast, when two waves are at their peak at different times they are out of step. |
|
|
|
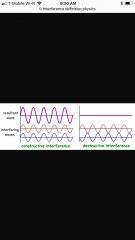
Interference |
When I way loses its individual Characteristics at that moment and combine to form a single wave when waves meet |
|
|
|
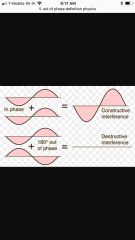
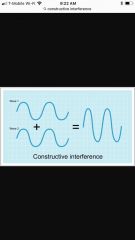
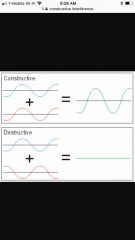
Constructive interference |
InSync waves, positive waves |
|
|
|
Distractive Interference |
Waves are not in sync, not positive |
|

