![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
The ______ of all 7 parameters are required to completely characterize a sound wave? |
Values |
|
|
|
What are the 7 parameters and how are they organized? |

Back (Definition) |
They describe sound waves |
|
|
Source of the sound wave? |
Transducer |
|
|
|
The medium is? |
(Human) tissue |
|
|
|
Time it takes a wave to vibrate a single cycle, OR the time from start of cycle to start of next cycle. |
Period (units: time) (Determined by: source) (NOT adjustable=transducer specific) |
|
|
|
Typical values of PERIOD? |
0.06 to 0.5 (µs) Or 6 X 10^-8 to 5 X 10^-7 seconds Or 0.00000006 to 0.0000005 seconds |
|
|

This graph is an example of a? |
Period (start to start next cycle) |
|
|
|
The number of cycles that occur in 1 second=? |
Frequency (Units=hertz) (Determined by: source) (NOT adjustable) 1 cycle/second = 1 hertz (1,000 cycles/second= 1kHz) |
|
|
|
What is the typical value range for FREQUENCY? |
2 MHz to 15 MHz Or 2 million to 15 million per second |
|
|
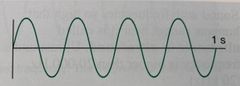
What is this wave’s frequency? |
4 per second Or 4 Hz |
|
|
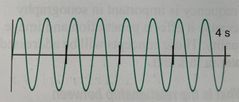
What is the frequency of this wave? |
8/4 per second Or 2 Hz |
|
|
|
What frequency is below the threshold of human hearing? |
< 20 Hz |
|
|
|
Sound waves with frequencies below human hearing are called? |
Infrasonic Or Infrasound |
|
|
|
What is the range of audible sound? |
20 Hz to 20,000 Hz |
|
|
|
What aspects of diagnostic sonography does frequency affect? |
Penetration And image quality |
|
|
|
How are frequency and period related? |
They are inversely related and reciprocal (+)frequency (-)period (-) frequency (+)period If one doesn’t change the other doesn’t change |
|
|
|
What is the frequency used for ultrasound? |
> 20 kHz |
|
|
|
Period X Frequency= ? |
1 (reciprocal relationship) |
|
|
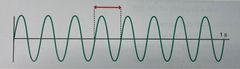
What are the frequency and period of this wave form? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Hertz means_______ per second? |
Events per second: In our examples the “event(s)” is the number of completed cycle(s) |
|
|
|
Which three (3/7) parameters describe (the BIGness) size, magnitude, or strength of a sound wave? |
Amplitude, power, and intensity |
|
|
|
Which parameter is the “BIGness” of the wave? The difference between the maximum (OR minimum) value and the average or undisturbed value of an acoustic variable? |
Amplitude (Units: any units or decibels (dB)) (Determined by: source wave and characteristics of the medium as sound propagates through body) (Adjustable: yes controls on machine) |
Pressure (pascals) Density (g/cm^3) Particle motion (distance) |
|
|
What are the typical values for Amplitude? |
Pressure amplitude= 1 million pascals to 3 million pascals OR 1 MPa to 3 MPa |
|
|
|
The difference between maximum and minimum values of an acoustic variable? |
Peak-to-peak amplitude = 2 X amplitude |
|
|
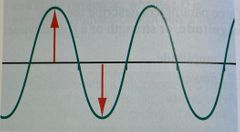
The red arrows are indicating what parameter? |
Amplitude |
|
|
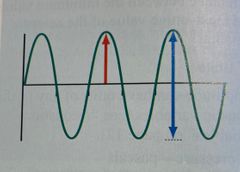
The blue arrow is indicating which parameter? |
Peak-to-peak amplitude |
|
|
|
What parameter is the rate of energy transfer or the rate at which work is performed? |
Power (Units= watts) (Determined by: source wave and then decreases as sound propagates through (medium) body) (Adjustable: controls on machine) |
|
|
|
Typical range of Power? |
0.004 to 0.090 watts Or 4 to 90 milliwatts Depending on setting/ technique |
|
|
|
Power is proportional to? |
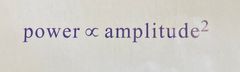
Increase Amp by factor 3 Increase Power by factor 9 3x3=9 Decrease Amp by factor 1/2 Decrease Pow by factor 1/4 1/2 x 1/2 = 1/4 |
|
|
|
What is the concentration of energy in a soundbeam? (How the power of the wave is distributed over area which power is supplied.) |
Intensity (Units: watts/ cm^2 Aka Power/beam area) (Determined by: source wave and the medium, changes as sound propagates) (Adjustable: controls (power) and amplitude on machine) |
|
|
|
What is the typical range of values for intensity? |
0.01 to 300 W/cm^2 |
|
|
|
What is the equation to solve for intensity of a sound beam? |
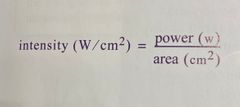
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Intensity is proportional to what parameter? |
Power |
|
|
|
Like power intensity is proportional to which parameter squared? |
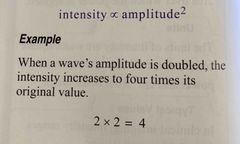
Anplitude^2 |
|
|
|
The length/distance of one complete cycle? |
Wavelength (Units: length (mm)) (Determined by: Source and Medium)*** (NOT adjustable) |
Only parameter that is determined by source and medium. |
|
|
What is the typical range for wavelength? |
0.1 to 0.8 mm |
|
|
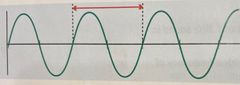
The red line is an example of? |
Wavelength |
|
|
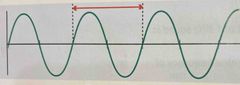
Difference between wavelength and Period of a wave? |
Wavelength=distance Period= time |
|
|
|
Wavelength is inversely proportional to which parameter within a specific medium? |
Frequency Decrease Wavelength Increase Frequency |
|
|
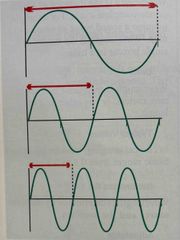
These graphs demonstrate the relationship between? |
Wavelength and frequency |
|
|
|
What is the wavelength of 1MHz of sound in soft tissue? |
1.54 mm |
|
|
|
What is the equation to determine wavelength in soft tissue? |
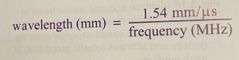
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
In soft tissue, sound with frequency of 2 MHz has a wavelength of? |
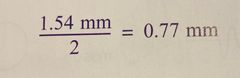
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
In soft tissue, sound with frequency of 2 MHz has a wavelength of? |
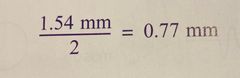
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What role does wavelength play in ultrasound imaging? |
Image quality High frequency= shorter wavelengths=greater detail images |
|
|
|
What is the rate at which a sound wave travels through a medium? |
Propagation Speed (Units: distance) (Determined by: medium only) (NOT adjustable: all sound travels at the same speed through a specific medium) |
|
|
|
Do waves with different frequencies have different propagation speeds? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is the typical range for propitiation speeds in tissue? |
500 m/s to 4,000 m/s |
|
|
|
What is the propagation speed of sound in soft tissue? |
1,540 m/s Or 1.54 mm/micro second Or 1.54 km/s Or 1 mile per second! |
|
|
|
500 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Lungs |
|
|
|
500 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Lungs |
|
|
|
1,450 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Fat |
|
|
|
500 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Lungs |
|
|
|
1,450 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Fat |
|
|
|
1,540 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Soft tissue (average) |
|
|
|
500 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Lungs |
|
|
|
1,450 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Fat |
|
|
|
1,540 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Soft tissue (average) |
|
|
|
1,560 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Liver and Blood |
|
|
|
500 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Lungs |
|
|
|
1,450 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Fat |
|
|
|
1,540 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Soft tissue (average) |
|
|
|
1,560 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Liver and Blood |
|
|
|
1,600 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Muscle |
|
|
|
500 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Lungs |
|
|
|
1,450 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Fat |
|
|
|
1,540 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Soft tissue (average) |
|
|
|
1,560 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Liver and Blood |
|
|
|
1,600 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Muscle |
|
|
|
1,700 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Tendon |
|
|
|
500 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Lungs |
|
|
|
1,450 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Fat |
|
|
|
1,540 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Soft tissue (average) |
|
|
|
1,560 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Liver and Blood |
|
|
|
1,600 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Muscle |
|
|
|
1,700 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Tendon |
|
|
|
3,500 m/s is the speed of sound through what biological media? |
Bone (materials that are stiff but not dense have the fastest speed) |
|
|
|
What is the propagation speed of air? (Not stiff) |
330 m/s |
|
|
|
What is the propagation speed of Water? |
1,480 m/s |
|
|
|
What is the range of propagations speeds for metal? |
2,000 to 7,000 m/s |
|
|
|
Sound travels fastest in ____. Slower in _____. Slowest in _____. |
Fastest solids Slower liquids Slowest gases |
|
|
|
What is the equation for propagation speed? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What 2 characteristics of a medium determine propagation speed? |
Stiffness and Density > |
|
|
|
Characteristic describing the ability of an object to resist compression and retain(?) shape? |
Stiffness Aka Bulk Modulus |
|
|
|
Stiffness and speed are ______ related? |
Directly related (More stiffness= more speed) |
|
|
|
What is the opposite of stiffness ? |
Compressibility And Elasticity |
|
|
|
What characteristic describes the relative weight of a material? |
Density |
|
|
|
What characteristic describes the relative weight of a material? |
Density |
|
|
|
Density and propagation speed are ______ related? |
Inversely (If two media are equally stiff, the denser medium will have a lower speed) |
|
|
|
Which characteristic of a medium has the greatest influence on propagation speed? |
Stiffness (Air =330 m/s) |
|
|
|
Materials that are _____ but not _____ will have the fastest speed? (Bone) |
Stiff not dense |
|
|
|
Materials that are not ____ and very ____ will have the slowest speed? |
Not stiff Very dense |
|
|
|
How is is speed related to stiffness and density? |

Back (Definition) |
Directly Vs inversely related |

