![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
TRANSVERSE WAVES |
-Oscillations are perpendicular to the wave direction. -Surface of water, em waves, waves on a stretched string, s-waves. |
|
|
LONGITUDINAL WAVES |
-Oscillations are parallel to direction of energy transfer. -Sound waves and p-waves -Creates compressions and rare fractions when travelling through medium. |
|
|
DISPLACEMENT |
Symbol-s Unit-m -Distance from equilibrium position in a particular direction |
|
|
AMPLITUDE |
Symbol-A Unit-m -Maximum displacement from the equilibrium position. |
|
|
PERIOD |
Symbol-T Unit-s -Time taken for one complete oscillation of a wave. |
|
|
WAVELENGTH |
Symbol-lamda Unit-m -Minimum distance from one point to another in phase on adjacent waves. -Distance from one peak to another peak. |
|
|
FREQUENCY |
Symbol- f Unit- hz -number of wavelengths passing a given point per unit time. |
|
|
WAVE SPEED |
Symbol- V Unit- ms-1 -Distance travelled by the wave per unit time. |
|
|
OSCILLOSCOPE |
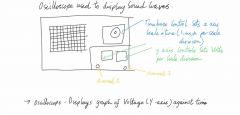
Back (Definition) |
|
|
INTENSITY & DISTANCE |
-Inverse square relationship. -If Distance doubles, intensity decreases by a factor of 4 (2)^2 |
|
|
INTENSITY AND AMPLITUDE |
-Intensity is directly proportional to the square of the amplitude. -Double the amplitude and the intensity will quadruple. |
|
|
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE |
-Transverse wave. - Electric and magnetic fields oscillating at right angles to each other. -Can be reflected, refracted and diffracted. -Travel at speed of light in a vacuum. |
|
|
EM WAVELENGTHS AND USES |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
REFLECTION |
-Wave changes direction at a boundary between two points. -Direction taken by the wave is a ray, it shows the direction of energy transfer. -Waves are reflected, wavelength and frequency do not change. |
|
|
LAW OF REFLECTION |
-Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. |
|
|
REFRACTION |
-Change in wave speed and sometimes direction as the wave passes through one medium to another. -wave slows down, refracts towards normal. -Wave speeds up, refracts away from the normal. -Shallow to deep, slows down, refracts towards normal. |
|
|
REFRACTION PART 2 |
-Refraction has an affect on wavelength but not frequency. -when wave slows down wavelength decreases and frequency remains unchanged. |
|
|
DIFFRACTION |
-Wave spreads out when passing through a gap or travel around an obstacle. - Diffraction dependant on wavelength and gap or obstacle size. -Most significant when gap or obstacle size similar to the wavelength size. |
|
|
POLARISATION |
-Particles oscillate in one direction, wave confined to a single plane. -Longitudinal waves cannot be plane polarised as they are already in one plane. The oscillations are parallel to the direction of travel of the wave. |
|
|
POLARISING FILTER |
-Transmits light polarised in one direction and absorbs light polarised in the perpendicular direction. -metal grille acts as polarising filter for microwaves. Absorbs the vertical component of the oscillations and transmits the horizontal component. |
|
|
INVESTIGATING POLARISATION OF LIGHT |
-If two polarising filters are rotated with respect to each other, the amount of transmitted light varies as the angle between the two filters is changed. -Transmitted intensity 0 when planes of the two polarising filters are perpendicular to each other and maximum when planes of two polarising filters are parallel to one another. -when unpolarised light falls onto plane polarising filter the transmitted intensity is half the incident intensity. |
|
|
EM WAVELENGTHS AND USES |

Back (Definition) |

