![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
105 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Distance Time Graphs |
Straight = Constant speed. Gradient = Speed. Curved = Acceleration. Flat = Stationary |
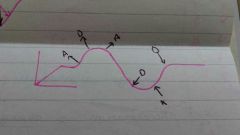
Velocity = Displacement / Time |
|
|
Velocity Time Graphs |
Horizontal = Constant speed. Gradient = Acceleration. Area under line = Distance. |

|
|
|
Velocity |
Speed in certain direction. |
|
|
|
Vector |
Size and Direction |
|
|
|
Scaler |
Size only |
|
|
|
If a car is moving around a circular track, at a constant speed, but is always accelerating. HOW? |
Because the direction is always changing, so the velocity always changes, Acceleration = change in velocity / time |
|
|
|
Change in velocity = |
Final - Initial (v-u) |
|
|
|
Deceleration |
Slowing down, due to braking, negative acceleration. |
|
|
|
Deceleration |
Slowing down, due to braking, negative acceleration. |
|
|
|
Forces can... |
Change shape, motion, or state of rest. |
|
|
|
When 2 objects pull on each other, they exert... |
Equal and opposite force on each other. |
|
|
|
When 2 objects pull on each other, they exert... |
Equal and opposite force on each other. |
|
|
|
Force unit |
Newton (N) |
|
|
|
In order to change speed... |
The resultant force must be NOT zero. |
|
|
|
Resultant force example |

|
|
|
|
Friction |
Driving force - causes motion - caused by friction between two objects |

|
|
|
Force = |
mass x acceleration |
|
|
|
Force = |
mass x acceleration |
|
|
|
Force Diagram |
Size of Arrow = size of force. Direction of Arrow = direction of force. |
|
|
|
Parallelogram of Force |

|
|
|
|
Acceleration is.. |
In the direction of the resultant force |
|
|
|
If velocity increases... |
Resultant force = same direction as velocity. Acceleration = positive |
|
|
|
If Velocity decreases... |
Resultant force = opposite Acceleration = negative |
|
|
|
Bigger resultant force = |
Bigger acceleration |
|
|
|
Cars |
Driving force = engine (motive force) - caused by friction. Resistive force = friction / air resistance |
|
|
|
Thinking distance |
Distance traveled during driver's reaction time. |
|
|
|
Thinking distance = |
Speed x reaction time |
|
|
|
Braking distance |
Distance traveled once brakes are applied |
|
|
|
Braking distance = |
Average speed x braking time |
|
|
|
Affecting Stopping distance |
Tiredness, Drugs, Alcohol - Distraction Faster Car - Both increase with speed Adverse conditions - less friction, more force needed, too much force will mean skidding. Poorly maintained brakes. |
|
|
|
Terminal Velocity |
The velocity it eventually reaches when it is falling in a fluid. The weight of the object is then equal to the frictional force on the object. |
|
|
|
Weight = |
Gravity acting on a mass |
|
|
|
Gravitational field strength... |
Depends on the gravitational field strength at its location. |
|
|
|
On earth |
1Kg = 10 N |
|
|
|
If an object falls with no resistive forces, it will... |
Accelerate at 10m/s^2 |
|
|
|
When an object falls through a fluid... |
Resultant force = weight - frictional force |
|
|
|
Weight = |
Mass x Gravitational field strength |
|
|
|
Weight = |
Mass x Gravitational field strength |
|
|
|
If an object is elastic.. |
It returns to its original shape after removing the original force deforming it. |
|
|
|
Extension = |
Length once weight was added - original |
|
|
|
Method for testing elasticity |

|
|
|
|
When an elastic object is stretched... |
Elastic potential energy is stored. |
|
|
|
When the elastic object is restored... |
Energy transferred to kinetic, or heat as the atoms will vibrate |
|
|
|
Hooke's Law |
The extension of a spring is directly proportional to the force applied, as long as the limit of proportionality is not reached. |
|
|
|
Rubber = |
Low limit of proportionality |
|
|
|
Spring = |
High limit of proportionality |
|
|
|
Energy Transferred = |
Work Done |
|
|
|
Work Done = |
Force x Distance |
|
|
|
Work done to overcome friction ... |
Transferred as heat energy. The energy heat the two objects which causes friction |
|
|
|
Power = |
Useful energy transferred, work done, joules / time taken, seconds |
|
|
|
Gravitational Potential Energy = |
Mass x Gravitational field strength x height raised |
|
|
|
If you raise an object .. |
You transfer Ep to it. |
|
|
|
Kinetic energy = |
1/2 mass x velocity^2 |
|
|
|
Elastic potential energy |
Is stored in an object when work is done on it to change its shape. |
|
|
|
Bungee Jump |
Going up = Ep increase Fall = Ep -- Ek Bungee taught = Ek -- Elastic STOP Elastic -- Ek Ek -- Ep Back on plane Energy is still wasted at heat. |
|
|
|
Centre of Mass |
The point at which all the mass of an object is said to be concentrated. |
|
|
|
To find centre of mass |

|
|
|
|
Pendulum |

|
|
|
|
Amplitude of oscillating object |
Distance from highest point to position of equilibrium. |
|
|
|
Time period of oscillating object |
Time taken for a complete cycle |
|
|
|
Frequency of oscillating object |
Number of complete cycles per second |
|
|
|
Time period = |
1 / Frequency |
|
|
|
Pendulum time period changes due to... |
Length of string |
|
|
|
Pendulum time period changes due to... |
Length of string |
|
|
|
Fairground Swing Boat |
Like a swing, the center of mass of the boat and occupants is higher the the center of mass of the boat when empty. Therefore the oscillations are longer when the boat is empty. |
|
|
|
Moments can be |
Anticlockwise or clockwise |
|
|
|
Moments example |

|
|
|
|
Longer objects... |
Exert a larger turning force than shorter objects. |
|
|
|
Turning effect = |
Moments |
|
|
|
Increase moment |
Increase size of force. Increase distance from effort to pivot. |
|
|
|
Crowbar |

|
|
|
|
Hammer |

|
|
|
|
Moment = |
Force x Distance |
|
|
|
Levers are used as... |
Force multipliers |
|
|
|
For any object moving at constant speed in circular motion... |
The object's velocity is along the tangent, The velocity changes constantly, The change in velocity is towards the center of the circle. |
|
|
|
The velocity of an object moving at a constant speed in circular motion is... |
Always accelerating because the direction always changes. |
|
|
|
Centripetal force |
The resultant force that causes the centripetal acceleration of an object moving round a circle |
|
|
|
Centripetal acceleration |
The acceleration of an object moving round a circle towards the center of the circle. |
|
|
|
Centripetal force... |
Depends on an object's mass, speed and the radius of the circle. |
|
|
|
Resultant force here... |
Centripetal force |
|
|
|
Centripetal force is caused... |

|
|
|
|
Pressure = |
Force / Areaa |
|
|
|
Pressure = |
Force / Areaa |
|
|
|
1 Pascal = |
1N/m^2 |
|
|
|
Pressure in liquid |
Acts equally in all directions |
|
|
|
Pressure in liquid |
Acts equally in all directions |
|
|
|
Hydraulic uses |
Braking systems Jacks ( to lift things) Diggers ( operating arms) Cranes |
|
|
|
Hydraulics work with the fact that... |
More effort of a force occurs on a smaller area |
|
|
|
Liquids are |
Virtually non compressible |
|
|
|
Liquids are |
Virtually non compressible |
|
|
|
If we transfer pressure to a liquid... |
The pressure will be transferred through the whole liquid and out somewhere else. |
|
|
|
If we change the area at the base of the liquid... |
We will change the pressure. |
|
|
|
If we change the area at the base of the liquid... |
We will change the pressure. |
|
|
|
Small SA -- Big SA |
Small force -- Big force. (and vice versa) |
|
|
|
Momentum = |
Mass x velocity. |
|
|
|
Law of conservation of momentum |
In a closed system, the total momentum before an event is equal to the total momentum after an event. |

|
|
|
Explosions |
Momentum is zero |
|
|
|
Explosion Example |

|
|
|
|
Collision |
Momentum is anything |
|
|
|
Impact forces |
Impact time and force |
|
|
|
Acceleration = ∆velocity / time |
Force = mass x acceleration |
Mass x acceleration = mass(final velocity - initial velocity) / time Force = (mass x v velocity) - (mass x u velocity) / time Mass x velocity = momentum Force = ∆P / t |
|
|
Longer impact time... |
Less impact force. |
|
|
|
Car safety |
Seat belts - stretch to increase impact time Air bags - increase impact time |
|
|
|
Car safety |
Seat belts - stretch to increase impact time Air bags - increase impact time |
|
|
|
Other safety |
Crash mats in gyms - cushioned to increase impact time Cycle helmets - padding to increase impact time. |
|

