![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. Changing a complex signal into simpler component frequencies is best performed using:
A. Fourier transformation B. Filled Back projection C. MTF D. Conversion algorithm |
Answer: A – the Fourier transform takes the jumbled combination signal and separates it into its component frequencies to make the picture.
|
|
|
2. An adult is given a dose of 20 mCi of I-131 with a thyroid weight of 40g. His uptake is 20% and the dose to the thyroid is 30 centiGy. If a child is given 10 mCi with a thyroid weight of 10g and his uptake is 40%, what is his thyroid dose?
A. 20 B. 30 C. 40 D. 60 E. 120 |
Answer: E – Understand the relationships involved here. While you cannot calculate the S-factor, you should know that it is proportional to energy deposited divided by the mass of the organ. Take the adult dose of 30 cGy and divide by 2 (kid got half the dose), multiply by 4 (kid has one fourth the thyroid weight), and multiply by 2 (kid has twice the thyroid uptake) to get the answer. Why do you multiply by 4 for the thyroid weight? Well, the child's thyroid is smaller than the adult's (¼ the size), so all the energy from the I-131 is 'crammed' into a smaller mass, which increases the dose (energy/mass).
|
|
|
3. Two brass wires are placed 5 cm apart on a fluoroscopy table. The screen is 36 cm above the table. The brass wires are 9 cm apart on the screen. How far under the table is the x-ray source?
A. 9cm B. 28cm C. 36cm D. 45cm E. 81cm |
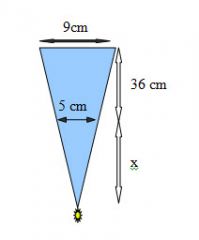
Answer: D - learn to draw these triangles. Here is how:
Then solve for x: x/5 = (36 + x)/ 9 9x = 180 + 5x 4x = 180 x = 45 cm |
|
|
4. Using fluoroscopy, increasing pincushion distortion will occur when
A. Increasing video bandwidth B. Increasing image intensifier distance C. Changing field input phosphor from 4.5 to 9.0 D. Something about changing CsI to ??? |
Answer: C – Pincushion artifact is the relative magnification of the periphery of the image. Vignetting (just fyi) is the relative decrease in brightness of the periphery of the image. Both are caused by the curved input phosphor projecting on the flat output phosphor, and both are improved with decreased FOV.
|
|
|
. A dose calibrator works based on the following detection method:
A. Geigor counter B. Ionization chamber C. Proportional chamber D. Something else |
Answer: B – dose calibrator is an ionization chamber but it is operated in current mode so specific data from individual counts is lost (NOT a spectrometer).
|
|
|
6. Hospital teleradiology project for mammography. How many bits would be required to send 4 images of a 4096 x 4096 matrix study at 2 bytes per pixel?
A. 1 kilobit B. 1 megabit C. 1 gigabit D. 1 terabit E. 1 petabit |
Answer: C – Here is the math:
40962 x 2 bytes x 8bits/byte x 4 images = 1,073,741,1824 = 1 gigabit Remember, 1 gigabyte = 230, or approx 1 billion bytes |
|
|
8. Radiation induced pathology changes to the heart most severely affects the:
A. Proximal aorta B. Pericardium C. Myocardium D. Epicardium E. Endocardium |
Answer: B – Pericardium has the cells with the highest turnover.
|
|
|
9. Regarding a Molybdenum filter and a Molybdenum anode in mammography at 28 kVp, the Moly filter:
A. Prevents scatter radiation from hitting the film B. Transmits high energy bremsstrahlung radiation with little attenuation C. Transmits characteristic x-rays with little attenuation D. Transmits low energy x-rays <10 kev with little attenuation E. Is usually 1 mm thick |
Answer: C - the anode material can be used to filter the xray beam b/c it allows the characteristic xrays through. The K-edge is always slightly higher than the characteristic xrays because the energy of the K characteristic xrays is K-L. The characteristic xrays for Moly are 17.5 and 19.6 keV
|
|
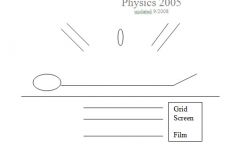
10. The following diagram is for linear tomography of the kidneys through a 40 degree arc. Which of the following is not correct as portrayed in the diagram:
A. The use of the grid is inappropriate B. The screen film unit should follow the x-ray beam C. The anode-cathode direction should be oriented perpendicular, not parallel to the patient D. The x-ray beam should be perpendicular to the screen-film cassette E. The arc is too extreme |
the guy who wrote the question doesnt have the answer. I don't seem to recall being able to use a grid in tomography.
|
|
|
11. For a film-screen system using an automatic exposure control (AEC) to keep the same optical density, which of the following will not affect the amount of noise in the image?
A. Efficiency of converting x-rays into light by the phosphor B. Efficiency of absorbing x-rays by the phosphor C. Matching the wavelength of light with the corresponding wavelength sensitivity of film D. Film screen contact E. Light transmitted by the phosphor |
Answer: B – The absorption efficiency (QDE) does not affect quantum mottle (QM) if the OD is kept constant via an automatic exposure control (AEC). QM is determined by the NUMBER of xray photons absorbed, not the PERCENT. If the QDE is increased, then the AEC will decrease mAs. Less photons reach the detector, but a higher percentage are absorbed. The number of absorbed photons is constant, and the QM is unchanged! One thing to know is that increasing the QDE often means making the phosphor thicker, and spatial resolution suffers when the screen is made thicker.
|
|
|
12. A nuclear medicine technician wants to detect low level I-131 exposure to levels down to 1.5K Bcq (or 1 KBcq?). Which instrument should be used?
A. Ionization exposure meter B. NaI scintillator C. Geiger counter D. Liquid scintillator E. Storage phosphor |
Answer: unsure – If you see the word 'exposure,' think ionization chamber. Exposure means charge in air, and an ionization chamber is an air filled device ideal for measuring exposure. However, at low dose rates, the I.C. may not be sensitive. The NaI well counter can be used for a wipe test for contamination and is sensitive at low radiation levels. Liquid scintillators are good for measuring beta emmisions.
-Effectiveness of contamination control is monitored using Geiger-Mueller survey meters. -Wipe tests should be performed of radionuclide use areas where a small piece of fil- ter paper is wiped on an area and checked in a Nal gamma well counter. |
|
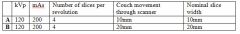
13. There are 2 CT techniques shown below:
kVp mAs Number of slices per revolution Couch movement through scanner Nominal slice width A 120 200 4 10mm 10mm B 120 200 4 20mm 20mm Which of the following will be affected most negatively when technique A is switched to technique B? A. Patient dose B. Patient motion C. Reconstructed image noise D. Spatial resolution in z-axis |
Answer: D – thicker slices but the same dose.
|
|
|
19. The in-plane resolution of a PET scanner using coincidence detection is:
A. Independent of positron range B. Independent of the angular spread of photon emission C. Nearly independent of the depth in the patient D. Primarily dependent on collimator hole size E. Determined by coded aperture |
C. Nearly independent of the depth in the patient
Answer: C – this is on several of the old tests. |
|
|
20. Compression of the breast in mammography does all of the following EXCEPT:
A. Decrease quantum mottle B. Create uniform film optical density C. Decrease dose to the breast D. Increase the amount of tissue imaged at the chest wall E. Increase contrast |
Answer: A – anything that decreases dose will increase quantum mottle. Note about test taking: Options A and C are opposites, so one of them must be false...
|
|
|
21. Compared to the 1000mm SID used in standard radiography, a 600-750mm SID is used in mammography to:
A. Accommodate the focus of a smaller grid ratio B. Decrease the heel effect C. Create uniform geometric resolution D. Decrease geometric magnification E. Increase beam intensity and decrease imaging time |
Answer: E – on multiple old tests.
|
|
|
22. In SPECT, the advantage of using a two-head camera system instead of a one-head camera system is:
A. Increased resolution B. Improved attenuation correction C. Faster reconstruction D. Decreased scan time E. Increased FOV |
Answer: D – the counts are obtained twice as fast with 2 cameras. The same number of counts (or even more counts) can be obtained in less time with 2 cameras.
|
|
|
23. Which of the following increases the effect of radiation cell killing:
A. Tobacco smoke B. Hypothermia C. Diagnostic ultrasound D. Tetracycline E. Actinomycin |
Answer: E – just something to memorize. Note, oxygen also increases the effects of radiation (via free radicals). Tobacco smoke decreases oxygen levels, although probably not by enough to make any difference...
|
|
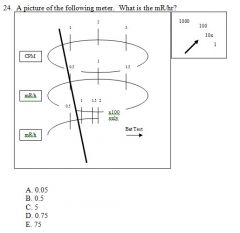
|
A. 0.05
B. 0.5 C. 5 D. 0.75 E. 75 Answer: C |
|
|
25. A radioactive sample is imaged for 4 minutes. The count is 400. The 95% confidence interval of the count rate is plus or minus:
A. 10 B. 20 C. 40 D. 80 E. 160 |
Answer: B – The question asks for a 95% CI, which is 2 SD.
√ (400/4) = 10cts So 2 SD = 20 |
|
|
26. The regulatory board which is responsible for enforcing radiation dose limits of occupational exposures is:
A. National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements (NRCP) B. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) C. International Commission on Radiological Protection (IRCP) D. United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR) E. Conference of Radiation Control Program Directors (CRCPD) |
B. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC)
|
|
|
27. The most effective room shielding from the exposure of β particles from diagnostic examinations produced from β-emission decay is:
A. Lead B. Tungsten C. Titanium D. Steel E. Plastic |
Answer: E – any of the options will block the electrons, but you want something with a low mass number to avoid creation of Bremsstrahlung radiation (you don't want to turn the shield into an 'anode').
|
|
|
28. When compared to spin echo magnetic resonance sequences, echo planar technique has the advantage of:
A. Obtained in 100 ms B. Increased magnetic susceptibility artifact C. Improved spatial resolution D. Higher Signal-to-Noise Ratio E. Decreased Phase-encoding errors |
Answer: A – Just think about those fuzzy T2 images (low SNR) that the techs get on patients who are moving are labeled EPI (echo planar imaging).
|
|
|
29. In digital imaging, DICOM stands for:
A. An analog-to-digital interface B. A software program for accessing the internet C. A network used to share images and patient health information D. A standard protocol for accessing images over the network E. Two-way tele-radiology communication. |
Answer: D
|
|
|
30. Houndsfield units in CT may have the following values:
A. -500 to 500, normalized to 500 for water B. -1000 to >1000, normalized to 0 for water C. -500 to 500, normalized to 0 for water D. -1000 to 1000, normalized to 500 for water E. 0 to 1000, normalized to 0 for water |
Answer: B – I hope I get this question
|
|
|
31. A breast feeding woman needs to receive I-131 for therapeutic treatment. To most effectively minimize the absorption of radiation to her breast glandular tissue and to keep the infant’s exposure to less than 1 mSV, the best recommendation is for her to stop breast-feeding:
A. Permanently, starting 2 weeks before to stop lactation B. Permanently, starting 6 hours before to empty the remaining milk in her ducts C. Temporarily, until 5 days with no breast milk pumping D. Temporarily, until 5 days after while maintaining breast-milk pumping every 6 hours |
Answer: A – on multiple old test but not always worded so obviously. I-131 concentrates in the breast milk. Bottom line is you don't want the mom lactating b/c the breast will get a big radiation dose from the I-131. You obviously don't want the baby to drink the radioactive milk (This isn't Russia. What? Too soon?)
|
|
|
32. The units for dose-area product are:
A. Gy cm-2 B. Sv cm-2 C. Gy cm D. Sv cm2 E. Gy cm2 |
Answer: E – remember rem (and Sv) is radiology equivalent in man, and has to do with risk of cancer in people. Rad (and Gy) is a more general dose term.
|
|
|
33. The acronym CAD refers to:
A. A method of image transfer B. A method of image data compression C. A data storage device D. A digital diagnostic aid E. Method of image display |
Answer: D – used in mammography (and by lawyers).
|
|
|
34. The term “use factor” in radiation protection refers to:
A. Hours/wk that an xray unit is in use B. Roetgens/wk that an xray unit produces C. mA/wk that an xray unit generates D. Fraction of time that xray unit is in use per week E. Fraction of time that xray unit is directed toward a specific area per week |
E
use factor term used in designing x-ray shielding that accounts for the fraction of time an x- ray beam is pointing in any given direction |
|
|
35. The ability of a dose calibrator to accurately determine the activity of samples at a range of activities refers to the:
A. Linearity B. Uniformity C. Sensitivity D. Resolution E. Registration |
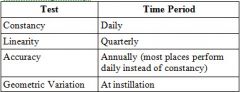
Answer: A – measured by letting Tc-99m decay or by putting lead sleaves over the radiation. Measured quarterly. See chart:
|
|
|
36. The term “radiation exposure” refers to:
A. Energy deposited in a unit volume B. Energy deposited in a unit mass C. Charge deposited in a unit air D. Disintegrations per unit time E. Biological effectiveness |
Answer: C – exposure is charge/air. Dose is energy/mass.
|
|
|
37. 500mSv/year is the regulated permitted dose to which of the following:
A. A conceptus B. A radiation worker C. The lens of a radiation worker D. The hands of a radiation worker E. The hands of a member of the general public |

Answer: D – 500mSv (50rem) is the limit for all organs (except the lens) and extremities of radiation workers. Just memorize this chart:
|
|
|
38. If an image is blurred and then multiplied by a factor K and then subtracted from the original image, the subtracted (new) image will have the follow characteristic:
New image = original image – K x blurred image A. Edge enhancement B. Has the same appearance as an image taken with a low frequency filter C. Increased signal to noise D. Increased smoothing E. Enhances low frequency contrast |
Answer: A – Options B, D, and E say the same thing and can be eliminated as options (they can't all be right). A and C are opposite b/c edge enhancement has high noise (low SNR).
Here is a tangent about filters: Edge enhancement in SPECT and CT. Edge enhancement in CT (aka bone windows) has better spatial resolution but increased noise. The difference is due to the filter used in the processing of the image. Edge enhancement uses a high pass ramp filter , which leave many of the high spatial frequencies (small objects). The high spatial frequencies contain spatial data such as the edge of the vessel or bone, which is why it is called edge enhancement. However, high spatial frequencies also contain 'all those little dots' that you see on bone windows that give the image a grainy appearance (noise). Clear as mud? See the graph below if you aren't sure the terms high and low pass. |
|
|
39. Visualization of US waves through bone is not possible because bone_____ the US waves.
A. Reflects B. Absorbs C. Refracts D. Scatters E. Transmits |
Answer: A and B are both true, but I think B is the best answer. Bone is the classic example of a substance the absorbs ultrasound waves. Lung (air) is the classic example of substance that reflects ultrasound waves. This question is on multiple old tests.
|
|
|
40. What is the minimum dose that will cause a detectable abnormality to the peripheral lymphocytes?
A. 2.5 Gy B. 0.25 Gy C. 0.025 Gy D. 0.0025 Gy |
Answer: B – on multiple old tests.
|
|
|
41. Tc99 is eluted from Mo99. When will Tc99 and Mo99 be in equilibrium? (Tc99 half life = 6 hrs, Mo99 half life = 2.8 days)
A. 6 hrs B. 24 hrs C. 2.8 days D. 11.2 days E. 28 days |
Answer: B – in general it take ~4 daughter half lives to reach equilibrium.
|
|
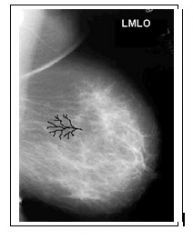
42. What is the cause of the black line artifact on this otherwise unremarkable mammogram?
A. Deteriorated screen B. Deteriorated cassette C. Deteriorated filter D. Cracked compression paddle E. Static electricity |
Answer: E
|
|
|
43. What is the MTF (modulation transfer function) of an image intensifier system whose components have individual MTFs of 1.0, 0.8, 0.5, 0.4?
A. 1.0 B. 0.4 C. 0.28 D. 0.16 |
Answer: D – MTF components multiply. The system is always lower (worse) than the lowest component.
|
|
|
44. During a photoelectric interaction, an M-shell electron fills the resultant K-shell vacancy. The resultant characteristic X-ray that is formed ejects a different M-shell electron. Let Ek and Em represent the binding energies of K- and M-shell electrons, respectively. What is the kinetic energy of the ejected M-shell electron?
A. Ek - 2Em B. Ek + 2Em C. Em - 2Ek D. Em + 2Ek E. 2Ek - Em |
Answer: A – the energy of the characteristic xray is Ek-Em and the energy of the ejected M electron is the characteristic xray minus Em . This gives a total energy of Ek-2Em
|
|
|
45. LSO and BGO are PET detectors. LSO has a shorter window for coincidence detection because:
A. LSO has a higher density than BGO. B. LSO has a higher average atomic number than BGO. C. LSO has a higher electron density than BGO. D. LSO has a shorter decay time than BGO. E. LSO has a higher percent resolution than BGO. |
Answer: D – this is an advantage of LSO
Actually the term is recovery time. |
|
|
46. A woman underwent a radiographic examination and received a dose of 0.2 Gy within day 10 of pregnancy. What is most likely to happen to the fetus?
A. intrauterine demise B. general growth retardation C. mental retardation and microcephaly D. congenital organ malformations |
Answer: A – this early in pregnancy there is an 'all or nothing' response, and since 'nothing' wasn't an option...
|
|
|
47. What is the pixel resolution of CT?
A. 0.005 mm B. 0.05 mm C. 0.5 mm D. 5 mm |
Answer: C – this is just a number to memorize.
|
|
|
51. The most radiosensitive cells in the cell cycle are in what phase:
A. G1 B. M C. G2 D. S |
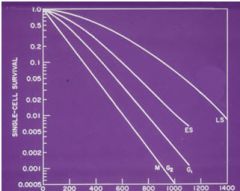
B –The relative sensitivity is M>G2>G1>S per Bushberg. Here is a cell survival chart of Chinese hamster cells based on cell cycle.
|
|
|
52. Which group of people were shown to have increased incidence of lung cancer?
A. Patients treated for ankylosing spondylitis B. Marshall island inhabitants C. Uranium workers D. Dial painters who work with radium E. Patients who underwent fluoroscopy repeatedly for treatment of tuberculosis |
Answer: C – see below:
Uranium miners lung cancer Marshall island thyroid (benign and malignant tumors increased) XRT Tb breast XRT tinea capitis thyroid and brain XRT for AS leukemia Dial painters bone cancer Hiroshima darn near every kind of cancer! 3 mile island negligible |
|
|
50. Which of the following is true regarding radioactive decay?
A. The number of daughter cells is always equal to the number of parent cells B. The number of daughter cells forming is constant C. The number of parent cells decaying is constant D. The fraction of parent cells decaying is constant E. Activity is constant |
D. The fraction of parent cells decaying is constant
|
|
|
51. A major difference between computed radiography (CR) and traditional screen-film is?
A. CR resolution is not dependent on the detector thickness B. CR contrast is independent of kVp C. There is increased dynamic range D. CR contrast is dependent on the area of the detector E. There is increased noise with increased kVp |
Answer: C – on multiple old tests.
|
|
|
52. Which of the following is true for a screen used to evaluate for hair-line fractures of the hand versus the screens used for a standard PA and lateral CXR?
A. Increased absorption efficiency B. Increased conversion efficiency C. Increased quantum module D. Thinner phosphor layer E. Higher speed film |
Answer: D – uses a single phosphor (like mammo), which is a slower system and requires more radiation (lowers quantum mottle) than chest radiography.
|
|
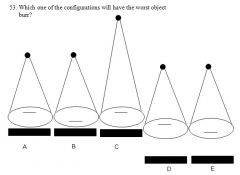
|
Answer: D – largest OID.
|
|
|
54. mAs refers to what with regard to electrons?
A. Number B. Velocity C. Flow D. Kinetic energy E. Potential energy |
Answer: A – on multiple old tests.
|
|
55. Standing at which site will give the radiologist the most scatter radiation?
|
Answer: A – kind of a funny picture, just know that back scatter (from under the table) is the worse than forward scatter.
|
|
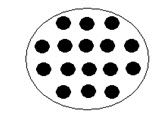
56. This artifact is caused by:
A. Poor PMT contact to the NaI crystal B. Collimator shift C. Improper Energy and window settings D. Edge packing |
Answer: C – it is highly unlikely that all the PMT would be broken.
|
|
|
57. What dose-response curve is used to generate recommendations for occupational exposure limits?
A. Linear threshold B. Linear non-threshold C. Quadratic threshold D. Quadratic non-threshold E. Exponential non-threshold |
57. What dose-response curve is used to generate recommendations for occupational exposure limits?
A. Linear threshold B. Linear non-threshold C. Quadratic threshold D. Quadratic non-threshold E. Exponential non-threshold Answer: B – is used b/c it overestimates risk. On multiple old tests. |
|
|
58. Decreased x-ray intensity at the anode side of the anode is caused by:
A. Focal uncapping at the cathode B. Absorption within the anode C. Unfocused radiation scatter D. Anode wobble |
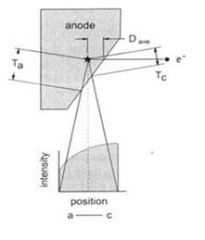
58. Decreased x-ray intensity at the anode side of the anode is caused by:
A. Focal uncapping at the cathode B. Absorption within the anode C. Unfocused radiation scatter D. Anode wobble Answer: B – a.k.a. Heel effect. The path of the xray on the anode side (Ta) is longer than the cathode side (Tc) so there is a greater chance of attenuation: |
|
|
59. F-18 is a more difficult radioisotope to handle safely relative to T99m because of its:
A. Beta emissions B. Increased photon penetration C. Volatile nature and increased risk of inhalation D. Longer half life E. Increased quality factor |
Answer: B – F-18 is a positron emitter, therefore the xray photon emission is 511 keV.
|
|
|
60. Switching to a medium-strength collimator from a low energy collimator for T99m results in:
A. Decreased sensitivity B. Decreased focal length C. Decreased uniformity D. Decreased intrinsic resolution |
60. Switching to a medium-strength collimator from a low energy collimator for T99m results in:
A. Decreased sensitivity B. Decreased focal length C. Decreased uniformity D. Decreased intrinsic resolution Answer: A – would also increase spatial resolution. |
|
|
61. Which statement regarding radiation-induced skin injury is FALSE:
A. The effect is deterministic B. The threshold for transient erythema is approximately 2 Gy C. It can be caused by standard fluoroscopy equipment D. The threshold for hair loss is approximately 1 Gy |
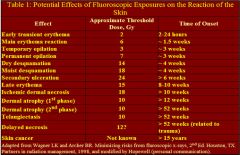
61. Which statement regarding radiation-induced skin injury is FALSE:
A. The effect is deterministic B. The threshold for transient erythema is approximately 2 Gy C. It can be caused by standard fluoroscopy equipment D. The threshold for hair loss is approximately 1 Gy Answer: D – hair loss occurs at about 3 Gy. Here is that chart on skin reactions to radiation again: |
|
|
62. A dark streak seen on a CT image directly between two bone structures which pass through the slice is most likely due to:
A. Aliasing B. Beam hardening C. Metallic implant D. Partial volume effect E. A single faulty detector |
62. A dark streak seen on a CT image directly between two bone structures which pass through the slice is most likely due to:
A. Aliasing B. Beam hardening C. Metallic implant D. Partial volume effect E. A single faulty detector Answer: B |
|
|
63. A pencil chamber is used to measure:
A. Thyroid uptake in nuclear medicine B. Lymph node radioactivity in lymphoscintigraphy C. Fan beam profile in bone densitometry D. Transmission data for attenuation correction in SPECT E. Radiation doses in X-ray computed tomography |
63. A pencil chamber is used to measure:
A. Thyroid uptake in nuclear medicine B. Lymph node radioactivity in lymphoscintigraphy C. Fan beam profile in bone densitometry D. Transmission data for attenuation correction in SPECT E. Radiation doses in X-ray computed tomography Answer: E – the CT phantoms have holes for the pencil chambers. Manufacturers specify CT doses by the CT dose index (CTDI), which is the inte- gral of the axial dose profile for a single CT slice divided by the slice thickness. -The CTDI can be measured using a pencil-type ionization chamber in phantoms that simulate heads (16 cm diameter acrylic) and bodies (32 cm diameter acrylic). |
|
|
64. Which of the following organ systems was most frequently affected by in utero radiation exposure resulting from the atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki?
A. Skeletal B. Digestive C. Pulmonary D. CNS E. Genitourinary |
64. Which of the following organ systems was most frequently affected by in utero radiation exposure resulting from the atomic bombs dropped on Hiroshima and Nagasaki?
A. Skeletal B. Digestive C. Pulmonary D. CNS E. Genitourinary Answer: D – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
65. Axial spatial resolution of an ultrasound unit is degraded by an increase in:
A. Frequency B. Pulse length C. Time-gain compensation D. Length of the Fresnel zone E. The beam width in the Fresnel zone |
65. Axial spatial resolution of an ultrasound unit is degraded by an increase in:
A. Frequency B. Pulse length C. Time-gain compensation D. Length of the Fresnel zone E. The beam width in the Fresnel zone Answer: B – the smallest discrete objections resolved in the axial direction (direction of the beam) must be >½ the SPL. Increasing the SPL will worsen axial resolution. Axial resolution is independent of depth. |
|
|
66. The intense signal around the eye in the MR image shown below is an artifact most likely caused by: [Provided was an axial image through the brain at the level of the orbits; the image was pretty fuzzy, but the CSF was dark, and I think it was a FLAIR sequence. There was bright signal involving the entire left orbit and adjacent superficial muscles. The right orbit was normal/dark.]
A. Flow B. Motion C. Chemical shift D. Magnetic susceptibility E. Inappropriately short TR |
66. The intense signal around the eye in the MR image shown below is an artifact most likely caused by: [Provided was an axial image through the brain at the level of the orbits; the image was pretty fuzzy, but the CSF was dark, and I think it was a FLAIR sequence. There was bright signal involving the entire left orbit and adjacent superficial muscles. The right orbit was normal/dark.]
A. Flow B. Motion C. Chemical shift D. Magnetic susceptibility E. Inappropriately short TR Answer: D according to the Mallenkrot people, but susceptibility artifacts are dark, not bright. Who knows for sure. Bad news if you can't tell for sure what sequence it is... Probably chemical shift artifact. think about MRI orbits and why we use fat suppression. |
|
|
67. Which of the following actions would most likely increase patient dose in standard fluoroscopy?
A. Adding a copper filter to the beam B. Moving the image intensifier away from the patient C. Opening up the aperture of the image intensifier D. Using pulsed mode instead of continuous mode E. Removing the grid from the image intensifier |
67. Which of the following actions would most likely increase patient dose in standard fluoroscopy?
A. Adding a copper filter to the beam B. Moving the image intensifier away from the patient C. Opening up the aperture of the image intensifier D. Using pulsed mode instead of continuous mode E. Removing the grid from the image intensifier Answer: B – this is why you want to bring the II down as far as possible, especially with kids. |
|
|
68. In xray computed tomographic imaging, quantum mottle increases with an increase of:
A. Patient size B. Current C. Scan time D. kVp |
68. In xray computed tomographic imaging, quantum mottle increases with an increase of:
A. Patient size B. Current C. Scan time D. kVp Answer: A – less photons get through the patient, so there is more quantum mottle. |
|
|
69. Keeping all other factors constant, increasing the tube-to-image distance will have what effect on patient exposure:
A. Increase exposure dose B. Decrease exposure dose C. Exposure dose unchanged but depth dose increased D. No effect |
69. Keeping all other factors constant, increasing the tube-to-image distance will have what effect on patient exposure:
A. Increase exposure dose B. Decrease exposure dose C. Exposure dose unchanged but depth dose increased D. No effect Answer: A – kind of tricky wording. If you keep the SOD (aka “all other factors”) the same, increasing the distance to the film will mean more radiation is needed to keep the OD constant. |
|
|
70. For a low-contrast 4cm-diameter hepatoma on a non-contrast enhanced CT scan, contrast will be increased by:
A. Increasing slice thickness B. Increasing cutoff frequency of ramp filter C. Decreasing mAs D. Decreasing scan time E. Decreasing kVP |
70. For a low-contrast 4cm-diameter hepatoma on a non-contrast enhanced CT scan, contrast will be increased by:
A. Increasing slice thickness B. Increasing cutoff frequency of ramp filter C. Decreasing mAs D. Decreasing scan time E. Decreasing kVP Answer: A – This question is on the 2003 test. Anything that decreases noise will improve contrast. |
|
|
. Regarding NCRP Report Number 116, an annual limit of 500mSv is permitted for:
A. Occupational exposure to thyroid B. Occupational exposure to the lens of eye C. Non-occupational exposure to the gonads D. Non-occupational exposure to the hands E. Patient gonad dose |
71. Regarding NCRP Report Number 116, an annual limit of 500mSv is permitted for:
A. Occupational exposure to thyroid B. Occupational exposure to the lens of eye C. Non-occupational exposure to the gonads D. Non-occupational exposure to the hands E. Patient gonad dose Answer: A – almost the exact same question as #37. 500mSv (50rem) is the limit for all organs (except lens) for occupational workers. |
|
|
72. A 12:1 grid would be most appropriate for:
A. Screen/film breast mammography B. High kVp Chest radiography C. Extremity radiography D. Magnification angiography E. Portable Chest radiograph |
72. A 12:1 grid would be most appropriate for:
A. Screen/film breast mammography B. High kVp Chest radiography C. Extremity radiography D. Magnification angiography E. Portable Chest radiograph Answer: B – 12:1 in chest xray, 10:1 and 8:1 in flouro, 5:1 in mammography |
|
|
73. In the photoelectric effect, almost all of the energy of the incident x-ray:
A. Is transferred to the nucleus B. Is emitted as a scattered photon C. Is absorbed locally D. Results in Bremstralung radiation E. Is retained in the incident photon |
73. In the photoelectric effect, almost all of the energy of the incident x-ray:
A. Is transferred to the nucleus B. Is emitted as a scattered photon C. Is absorbed locally D. Results in Bremstralung radiation E. Is retained in the incident photon Answer: C – the emitted electron and the resulting characteristic xray do not travel very far before being absorbed. photoelectric effect a photon is absorbed by an atom and a photoelectron is emitted |
|
|
74. In quality control for SPECT imaging, images of a point air source are obtained at various viewing angles for:
A. Center of rotation correction B. Image uniformity C. Intensity correction D. Image uniformity at various angles E. Spatial linearity at various angles |
74. In quality control for SPECT imaging, images of a point air source are obtained at various viewing angles for:
A. Center of rotation correction B. Image uniformity C. Intensity correction D. Image uniformity at various angles E. Spatial linearity at various angles Answer: A – COR uses a point source. On multiple old tests. |
|
|
75. Xray computed tomography and SPECT are similar in which of the following ways:
A. Both use projections to reconstruct the image B. Both rely on a rotating source of photons to create the image C. Both have mechanisms to correct for beam hardening D. Both use an energy peak window to decrease scatter E. Both rely on attenuation of photons to create an image |
75. Xray computed tomography and SPECT are similar in which of the following ways:
A. Both use projections to reconstruct the image B. Both rely on a rotating source of photons to create the image C. Both have mechanisms to correct for beam hardening D. Both use an energy peak window to decrease scatter E. Both rely on attenuation of photons to create an image Answer: A - on multiple old tests. |
|
|
76. A patient is exposed to I-131 for Graves disease and is found to be four weeks pregnant. Which of the following is true?
A. Fetal demise is likely B. The fetus will almost definitely not have hypothyroidism C. There is a 5% increased chance the child will develop leukemia D. There is a 10% increased chance the child will develop a solid tumor other than leukemia. |
76. A patient is exposed to I-131 for Graves disease and is found to be four weeks pregnant. Which of the following is true?
A. Fetal demise is likely B. The fetus will almost definitely not have hypothyroidism C. There is a 5% increased chance the child will develop leukemia D. There is a 10% increased chance the child will develop a solid tumor other than leukemia. Answer: B – Sources vary on the exact dates, but the fetal thyroid does not take up iodine until somewhere between 8 and 12 weeks. If the fetal thyroid doesn’t take up the radioactive iodine, it won't be damaged. |
|
|
77. Linear regression analysis of two variables show a correlation coefficient of -0.95. Which of the following is true?
A. No causal relationship exists between them B. One variable will increase as the other decreases. C. A non linear relationship exists between them. D. The regression line passes through the origin E. A causal and statistically significant relationship has been established. |
77. Linear regression analysis of two variables show a correlation coefficient of -0.95. Which of the following is true?
A. No causal relationship exists between them B. One variable will increase as the other decreases. C. A non linear relationship exists between them. D. The regression line passes through the origin E. A causal and statistically significant relationship has been established. Answer: B – the higher the correlation coefficient, the more tightly the two variables are associated. The sign (+ or -) of the coefficient determines directionality. |
|
|
78. A patient in the emergency department arrested and underwent CPR. An AP supine radiograph of the chest was obtained, and the nurse bagging the patient was concerned about her exposure. She was standing one meter from the patient’s chest. Her dose was most likely:
A. 3nGy B. 0.5 microGy C. 0.01mGy D. 0.3 mGy E. 1 mGy |
78. A patient in the emergency department arrested and underwent CPR. An AP supine radiograph of the chest was obtained, and the nurse bagging the patient was concerned about her exposure. She was standing one meter from the patient’s chest. Her dose was most likely:
A. 3nGy B. 0.5 microGy C. 0.01mGy D. 0.3 mGy E. 1 mGy Answer: B – Scatter radiation at 1 meter is 0.1% (need to know this rule of thumb). CXR is about 5mrad (0.005rad = 0.05 mGy), so the answer should be about 0.5 microGy (0.0005 mGy). |
|
|
79. In digital subtraction angiography, which of the following is true regarding increased noise due to quantum mottle?
A. The noise is greater in the mask than the subtracted image. B. The noise is greater in the subtracted image than the mask. C. The noise is reduced by prolonging the time between the mask and the subtracted image D. The noise is increased if the exposure time per frame is prolonged. E. The noise is unaffected by kVp and mAs |
79. In digital subtraction angiography, which of the following is true regarding increased noise due to quantum mottle?
A. The noise is greater in the mask than the subtracted image. B. The noise is greater in the subtracted image than the mask. C. The noise is reduced by prolonging the time between the mask and the subtracted image D. The noise is increased if the exposure time per frame is prolonged. E. The noise is unaffected by kVp and mAs Answer: B – on multiple old tests. The subtracted image has 1.4x the noise of the mask. |
|
|
80. MI and TI displayed during the acquisition of ultrasound images describe:
A. Impedance and specular reflection B. Motion and temporal resolving time C. Receiver and transmitter gain D. Frequency and depth of focus E. Cavitation and heat |
80. MI and TI displayed during the acquisition of ultrasound images describe:
A. Impedance and specular reflection B. Motion and temporal resolving time C. Receiver and transmitter gain D. Frequency and depth of focus E. Cavitation and heat Answer: E – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
81. Cumulated dose is expressed in units of:
A. Millicuries and Bq B. Millicurie-hours and Bq-seconds C. Microcurie-hours per gram and Bq-seconds per kilogram D. Microcurie per gram and Bq per kilogram E. Microcurie per cubic cm and Bq per cubic meter |
Answer: B – The cumulated dose is NOT corrected for mass (C, D, & E wrong). Cumulated dose is the dose to the entire body. Cumulated dose = 1.44 X A0 X T e
|
|
|
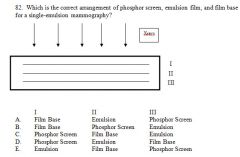
82. Which is the correct arrangement of phosphor screen, emulsion film, and film base for a single-emulsion mammography?
I II III A. Film Base Emulsion Phosphor Screen B. Film Base Phosphor Screen Emulsion C. Phosphor Screen Film Base Emulsion D. Phosphor Screen Emulsion Film Base E. Emulsion Film Base Phosphor Screen Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
83. Which of the following best defines the magnetic properties of Gadolinium?
A. Paramagnetic B. Diamagnetic C. Ferromagnetic D. Supraparamagnetic E. Orthomagnetic |
83. Which of the following best defines the magnetic properties of Gadolinium?
A. Paramagnetic B. Diamagnetic C. Ferromagnetic D. Supraparamagnetic E. Orthomagnetic Answer: A – Gad is paramagnetic and shortens T1. There are other questions about calcium, which is diamagnetic. |
|
|
84. Which of the following is best to increase signal-to-noise ratio in digital subtraction angiography?
A. Windowing B. Veiling glare C. Log Transformation D. Hybrid Subtraction E. Frame Integration |
84. Which of the following is best to increase signal-to-noise ratio in digital subtraction angiography?
A. Windowing B. Veiling glare C. Log Transformation D. Hybrid Subtraction E. Frame Integration Answer: E – frame integration adds multiple frames together with the goal of lowering noise (thereby increasing SNR). |
|
|
85. Which chemical group gives the greatest protective effect from spurious ionizing radiation such as x-rays?
A. Methyl B. Hydroxyl C. Carboxyl D. Sulfahydryl E. Phosphoryl |
In organic chemistry, a thiol is an organosulfur compound that contains a sulfur-hydrogen bond (S-H). Thiols are the sulfur analogue of an alcohol. The SH functional group is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group. Thiols are often referred to as mercaptans.
|
|
|
86. Which of the following TR and TE times generate both proton density and T2 weighted images in dual sequence, dual spin echo MR?
A. TR1 = 1000 TR2 = 4000 TE = 80 B. TE = 80 TR = 4000 C. TE1 = 20 TE2 = 40 TR = 1000 D. TE1 = 20 TE2 = 50 TR = 10000 E. TE1 = 20 TE2 = 80 TR = 4000 |
86. Which of the following TR and TE times generate both proton density and T2 weighted images in dual sequence, dual spin echo MR?
A. TR1 = 1000 TR2 = 4000 TE = 80 B. TE = 80 TR = 4000 C. TE1 = 20 TE2 = 40 TR = 1000 D. TE1 = 20 TE2 = 50 TR = 10000 E. TE1 = 20 TE2 = 80 TR = 4000 Answer: E – you need a long TR for both PD and T2. You need a short TE for PD and a long TE for T2. |
|
|
87. Ultrasound phased arrays sweep the ultrasound beam through a pie-shaped wedge or sector by selectively changing the angle of each of the transducer elements. Which of the following sentences describes the process most accurately?
A. Electronically altering the transducer elements by introducing delays B. Electronically altering the transducer elements by changing the amplitude C. Physically rocking the transducer elements D. Mechanically rocking the transducer elements E. Rotating the transducer elements within the transducer |
87. Ultrasound phased arrays sweep the ultrasound beam through a pie-shaped wedge or sector by selectively changing the angle of each of the transducer elements. Which of the following sentences describes the process most accurately?
A. Electronically altering the transducer elements by introducing delays B. Electronically altering the transducer elements by changing the amplitude C. Physically rocking the transducer elements D. Mechanically rocking the transducer elements E. Rotating the transducer elements within the transducer Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
88. What are the effects from an acute dose of 3 Gy?
A. Main Erythema B. Transient Epilation C. Desquamation D. Ulceration E. Radiodermatitis |
88. What are the effects from an acute dose of 3 Gy?
A. Main Erythema B. Transient Epilation C. Desquamation D. Ulceration E. Radiodermatitis Answer: B – see the chart on #61 for more details. |
|
|
89. Which of the following is true regarding an upright PA view of the chest in a dedicated chest unit?
A. The patient is positioned so that he is facing the tube. B. An air gap is used to decrease the scatter. C. A higher kVp is usually used to widen the latitude. D. Exposure time is between 0.25 and 0.50 seconds. |
89. Which of the following is true regarding an upright PA view of the chest in a dedicated chest unit?
A. The patient is positioned so that he is facing the tube. B. An air gap is used to decrease the scatter. C. A higher kVp is usually used to widen the latitude. D. Exposure time is between 0.25 and 0.50 seconds. Answer: C – a higher kVp lowers the photoelectric effect and lowers contrast, which widens latitude. |
|
|
90. Which of the following cannot occur during isomeric transition?
A. Beta particle B. Gamma ray C. Auger electron D. Internal conversion electron E. Characteristic X-rays |
90. Which of the following cannot occur during isomeric transition?
A. Beta particle B. Gamma ray C. Auger electron D. Internal conversion electron E. Characteristic X-rays Answer: A – beta particle is an electron from the nucleus. |
|
|
91. Which of the following results in the highest dose to the patient per image?
A. Digital subtraction angiography B. Digital angiography C. Cinecardiography D. Fluoroscopy with last image hold E. Pulsed fluoroscopy |
91. Which of the following results in the highest dose to the patient per image?
A. Digital subtraction angiography B. Digital angiography C. Cinecardiography D. Fluoroscopy with last image hold E. Pulsed fluoroscopy Answer: A – you need 2 images to make a single DSA image. |
|
|
92. In converting microcurie to mega becquerel, the microcurie should be:
A. Divided by 0.693 B. Multiplied by 0.693 C. Divided by 3.7 D. Multiplied by 37 E. Multiplied by 100 |
Answer: D – 1mCi = 37Mbq
|
|
|
94. Which of the following is true regarding sublethal damage due to radiation?
A. Repair occurs in split-dose experiments B. Repair is facilitated at high doses C. It occurs in the cell wall D. It is generally irreversible |
94. Which of the following is true regarding sublethal damage due to radiation?
A. Repair occurs in split-dose experiments B. Repair is facilitated at high doses C. It occurs in the cell wall D. It is generally irreversible Answer: A |
|
|
95. Which of the following results in the highest increase in lifetime risk of cancer?
A. Two-view chest x-ray B. Head CT C. Nuclear medicine bone scan D. Nuclear medicine lung perfusion scan E. Lateral view of the lumbar spine |
95. Which of the following results in the highest increase in lifetime risk of cancer?
A. Two-view chest x-ray B. Head CT C. Nuclear medicine bone scan D. Nuclear medicine lung perfusion scan E. Lateral view of the lumbar spine Answer: D The common bone scan with 600 MBq of technetium-99m-MDP has an effective dose of approximately 3.5 mSv The common VQ scan using tech MAA and xenon is 500 – 900 MBq |
|
|
96. A sample of a radioactive substance has a half-life of 100 seconds and an activity of 1 MBq. How many radioactive nuclei are in the sample?
A. 1.44 x1010 B. 1.44 x 108 C. 0.69 x 1010 D. 0.69 X 108 |
96. A sample of a radioactive substance has a half-life of 100 seconds and an activity of 1 MBq. How many radioactive nuclei are in the sample?
A. 1.44 x1010 B. 1.44 x 108 C. 0.69 x 1010 D. 0.69 X 108 Answer: B. Specific activity = λ X N = (0.693 / T ½) X N Then, find the decay constant: λ = 0.693/half-life = 0.693/100 sec = 0.00693 sec-1 Then solve for the # atoms: 106 sec-1 = 6.93 x 10-3 sec-1 x #atoms # atoms = 0.144 x 109 = 1.44 x 108 |
|
|
97. If all other variables are held constant, increasing which of the following will decrease the dose to the patient in a helical CT?
A. kVp B. mA C. Pitch D. FOV E. Increment of reconstruction of slices |
97. If all other variables are held constant, increasing which of the following will decrease the dose to the patient in a helical CT?
A. kVp B. mA C. Pitch D. FOV E. Increment of reconstruction of slices Answer: C |
|
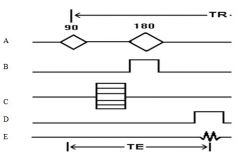
98. The following diagram corresponds with a spin echo pulse sequence. Which letter demonstrates the phase encoding gradient?
|
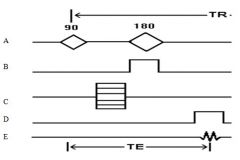
98. The following diagram corresponds with a spin echo pulse sequence. Which letter demonstrates the phase encoding gradient?
Answer: C – just know this stuff. |
|
|
99. A barium enema involves both fluoroscopy and spot imaging. The spot imaging is performed at:
A. kVp = 70 in order to match k-edge of barium B. kVp = 70 in order to decrease noise C. kVp = 100 in order to improve imaging latitude D. kVp = 120 in order to match k-edge of barium |
99. A barium enema involves both fluoroscopy and spot imaging. The spot imaging is performed at:
A. kVp = 70 in order to match k-edge of barium B. kVp = 70 in order to decrease noise C. kVp = 100 in order to improve imaging latitude D. kVp = 120 in order to match k-edge of barium Answer: C, I think – The techs tell me the kVp is about 95 for Barium work. If the mean beam energy is 1/3 to 1/2 of the kvp and the k edge of barium is around 37 then 100 would be a safe answer. |
|
|
100. A look-up table (LUT) is primarily used to:
A. Set kVp B. Determine patient exposure levels C. Improve edge enhancement D. Something about using a histogram E. Something about grayscale |
100. A look-up table (LUT) is primarily used to:
A. Set kVp B. Determine patient exposure levels C. Improve edge enhancement D. Something about using a histogram E. Something about grayscale Answer: E lookup table used to assign (transform) digital data into image brightness values |
|
|
101. When imaging using high dose fluoroscopy:
A. The kVp is set at 110 B. Exposure rates greater than the legal limit of 10 R/minute are allowed C. The machine must record cumulative dose D. commonly used in pediatric barium studies |
101. When imaging using high dose fluoroscopy:
A. The kVp is set at 110 B. Exposure rates greater than the legal limit of 10 R/minute are allowed C. The machine must record cumulative dose D. commonly used in pediatric barium studies Answer: B – exposure rate can be up to 20R/min. Some machines do record the cumulative dose, but it is not mandatory. High dose flouro is mostly cardiac and neuro interventional usage. |
|
|
102. There has recently been a terrorist attack using nuclear warfare. Upon presenting to the scene of its victims, a health care worker’s first duty should be:
A. To identify the contaminated patients B. To segregate the contaminated patients from other patients and health care workers C. To prevent spread of radioactive material D. To perform basic life support and assess medical needs of victims |
102. There has recently been a terrorist attack using nuclear warfare. Upon presenting to the scene of its victims, a health care worker’s first duty should be:
A. To identify the contaminated patients B. To segregate the contaminated patients from other patients and health care workers C. To prevent spread of radioactive material D. To perform basic life support and assess medical needs of victims Answer: D -- Bushberg states that critical medical care should not be delayed to treat internal or external contamination. Concerns regarding contamination to staff or ED should not delay care. Only patients with serious injuries/conditions should be treated in the ED. People who are only contaminated should not be sent to the ED. He states that emergency doses to save a life are 50 rem. Send in older people first (less cancer risk). Info is suppose to be on http://hps.org/hsc/responsemed.html “Emergency Department Management of Radiation Casualties.” |
|
|
103. Which of the following is felt to have a threshold dose in humans?
A. Lymphoma induction B. Thyroid Cancer C. Lens opacification D. Some other solid cancer |
103. Which of the following is felt to have a threshold dose in humans?
A. Lymphoma induction B. Thyroid Cancer C. Lens opacification D. Some other solid cancer Answer: C – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
104. As an ultrasound beam travels from fat (velocity 1440 m/sec) to liver (velocity
1550 m/sec) what other change is observed? A. Increase in wavelength B. Decrease in wavelength C. Increase in frequency D. Decrease in frequency |
104. As an ultrasound beam travels from fat (velocity 1440 m/sec) to liver (velocity
1550 m/sec) what other change is observed? A. Increase in wavelength B. Decrease in wavelength C. Increase in frequency D. Decrease in frequency Answer: A – the frequency is constant, so increasing speed causes an increase in wavelength since speed = frequency x wavelength. |
|
|
105. Which range best represents a pulse height analyzer that is centered at the Kpeak of Tc99m with a window setting of 20%?
A. 112 - 168 B. 112 - 140 C. 126 - 154 D. 130 - 150 E. 128 - 156 |
105. Which range best represents a pulse height analyzer that is centered at the Kpeak of Tc99m with a window setting of 20%?
A. 112 - 168 B. 112 - 140 C. 126 - 154 D. 130 - 150 E. 128 - 156 Answer: C – you have to know that the photopeak of Tc99m is 140 keV. So 20% is +/- 14 for a total range of 28 keV. |
|
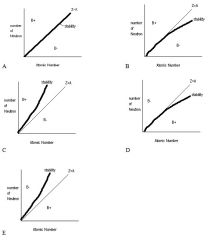
106. What graph below best illustrates the relationship between nucleon stability as a function of atomic number and number of neutrons, and the tendency for β+ and β- decay?
|
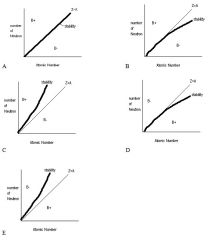
106. What graph below best illustrates the relationship between nucleon stability as a function of atomic number and number of neutrons, and the tendency for β+ and β- decay?
A B C D E Answer: E |
|
|
107. What best describes phase contrast MR angiography?
A. Uses alternating phase gradients B. Uses resonance suppression of background non-flow structures C. It is the algorithm for constructing a 3D image using a data set D. Utilizes tagged blood outside of the field of view E. Utilizes flow artifact of the blood vessel |
107. What best describes phase contrast MR angiography?
A. Uses alternating phase gradients B. Uses resonance suppression of background non-flow structures C. It is the algorithm for constructing a 3D image using a data set D. Utilizes tagged blood outside of the field of view E. Utilizes flow artifact of the blood vessel Answer: A – check out this webpage for some more info: http://www.e-mri.org/mr-angiography-flow/phase-contrast-mra.html |
|
|
108. A dose of 2mCi/ml of Tc-99m is prepared at 8am. At 5 p.m. the same day, how many mL of sample should be obtained for a dose of 2 mCi?
A. 2.3 B. 2.8 C. 3.3 D. 3.8 E. 4.3 |
108. A dose of 2mCi/ml of Tc-99m is prepared at 8am. At 5 p.m. the same day, how many mL of sample should be obtained for a dose of 2 mCi?
A. 2.3 B. 2.8 C. 3.3 D. 3.8 E. 4.3 Answer: B – A little bit of a long math problem, but not too bad if you break it down into steps. First find the decay constant (λ): λ = 0.693/T1/2 = 0.693/6hr = 0.116 hr-1 Then plug it into the decay equation: A = Ao e-λt A = 2mCi/ml * e-(0.116)(9) A = 0.7 mCi/ml In order to get 2 mCi, solve the following equation for volulme (V): 2mCi = 07mCi/ml * V V = 2.8 ml |
|
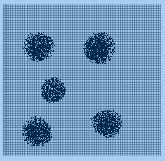
109. Below is the film result of a quality control test in mammography. What do the dark circular blotches represent?
A. Dented grid B. Poor film-screen contact C. Film non-uniformity D. Poor grid motion |
109. Below is the film result of a quality control test in mammography. What do the dark circular blotches represent?
A. Dented grid B. Poor film-screen contact C. Film non-uniformity D. Poor grid motion Answer: B probably – Kind of a bad question, but I think the picture may be demonstrating a 40 mesh Cu screen, which is used to look for poor film-screen contact. If there is poor-film screen contact, then there will be artifacts present. |
|
|
110. The CRT with resolution of 1078 x 780 is not appropriate for the following modality:
A. CT B. MRI C. US D. Digital chest E. Nuclear |
110. The CRT with resolution of 1078 x 780 is not appropriate for the following modality:
A. CT B. MRI C. US D. Digital chest E. Nuclear Answer: D – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
111. In scintillation camera with low energy (LEAP), all purpose collimator, the external spatial resolution is:
A. Best at the surface of the collimator B. Independent of the distance from the surface of the collimator C. Improved when using shorter collimator length (thickness) with the same hole size D. Equals to half the diameter of the collimator hole (in mm) E. Measured using bar phantom and a point source with activity at a distance greater than 3 m |
111. In scintillation camera with low energy (LEAP), all purpose collimator, the external spatial resolution is:
A. Best at the surface of the collimator B. Independent of the distance from the surface of the collimator C. Improved when using shorter collimator length (thickness) with the same hole size D. Equals to half the diameter of the collimator hole (in mm) E. Measured using bar phantom and a point source with activity at a distance greater than 3 m Answer: A – this question is on almost every test. Nucs collimator questions are popular. |
|
|
112. As an radiation protective agent, KI:
A. Is only effective in protecting the thyroid gland from radioiodine B. Repairs DNA breaks C. Acts at cellular level to lengthen M phase D. Is a powerful antioxidant |
112. As an radiation protective agent, KI:
A. Is only effective in protecting the thyroid gland from radioiodine B. Repairs DNA breaks C. Acts at cellular level to lengthen M phase D. Is a powerful antioxidant Answer: A – KI is not a cure all. Only works by saturating the thyroid, so it won't take up the radioactive iodine. |
|
|
113. In MR, chemical shift (i.e. in fat and water) is due to differences in:
A. T1 B. T2 C. Atomic number D. Resonant frequency |
113. In MR, chemical shift (i.e. in fat and water) is due to differences in:
A. T1 B. T2 C. Atomic number D. Resonant frequency Answer: D – on muliple old tests (I think every one). |
|
|
114. The penetration (depth) of a 5 MHz ultrasound transducer is increased by decreasing the noise by a factor of 100. If the attenuation coefficient is 0.5 dB/cm per MHz, the penetration is increased by how many (cm)?
A. 2 B. 4 C. 8 D. 12 E. 16 Answer: Data incomplete, however this is the equation to be used. This is given in Bushberg. Penetration = 70 / (2 X α X ν) α = Linear attenuation ν = Transducer frequency |
114. The penetration (depth) of a 5 MHz ultrasound transducer is increased by decreasing the noise by a factor of 100. If the attenuation coefficient is 0.5 dB/cm per MHz, the penetration is increased by how many (cm)?
A. 2 B. 4 C. 8 D. 12 E. 16 Answer: Data incomplete, however this is the equation to be used. This is given in Bushberg. Penetration = 70 / (2 X α X ν) α = Linear attenuation ν = Transducer frequency |
|
|
115. In a certain MR sequence, the scan time is 12 minutes. If the matrix size is decreased from 256 x 256 to 128 x 128, what is the new scan time (in minutes)?
A. 1 B. 3 C. 8 D. 6 |
115. In a certain MR sequence, the scan time is 12 minutes. If the matrix size is decreased from 256 x 256 to 128 x 128, what is the new scan time (in minutes)?
A. 1 B. 3 C. 8 D. 6 E. 12 Answer: D – time = TR * Nex * #phase encode steps (just one side of the matrix size) |
|
|
116. Contrast of a radiographic image can be improved by:
A. Increasing kVp B. Increasing mAs C. Collimating the beam more tightly D. Switching over to lower grid ratio E. Switching over to a screen/film combination with a lower gradient |
116. Contrast of a radiographic image can be improved by:
A. Increasing kVp B. Increasing mAs C. Collimating the beam more tightly D. Switching over to lower grid ratio E. Switching over to a screen/film combination with a lower gradient Answer: C – scatter reduces contrast. |
|
|
117. Regarding Apoptosis which of the following is true:
A. Apoptosis is more likely than mitotic death after irradiation with 1.5 Gy B. Apoptotic death peaks at 2-14 days after irradiation C. Cell death by apoptosis D. Apoptosis occurs step-wise in four distinct phases E. Apoptosis is the primary affect following irradiation of lymphoma |
117. Regarding Apoptosis which of the following is true:
A. Apoptosis is more likely than mitotic death after irradiation with 1.5 Gy B. Apoptotic death peaks at 2-14 days after irradiation C. Cell death by apoptosis D. Apoptosis occurs step-wise in four distinct phases E. Apoptosis is the primary affect following irradiation of lymphoma We think this is B. Apoptosis is programed cell death, sort of like a self destruct button for cells. |
|
|
118. For patient couch-motion during data acquisition for helical (spiral) CT:
A. It is performed using a slip ring B. Is a factor in determining pitch C. Couch motion accelerates to the middle of the scan and then decelerates D. It occurs in a set of distinct intermittent table movements under automated computer control E. It is related as the integral unit per 360° of tube rotation |
118. For patient couch-motion during data acquisition for helical (spiral) CT:
A. It is performed using a slip ring B. Is a factor in determining pitch C. Couch motion accelerates to the middle of the scan and then decelerates D. It occurs in a set of distinct intermittent table movements under automated computer control E. It is related as the integral unit per 360° of tube rotation Answer: B – remember Pitch = (table travel per 360 rotation)/(beam width) |
|
|
119. Using the same film-screen combination but using an increased film speed would result in increased:
A. Patient dose B. Quantum Mottle C. Contrast D. Spatial Resolution |
119. Using the same film-screen combination but using an increased film speed would result in increased:
A. Patient dose B. Quantum Mottle C. Contrast D. Spatial Resolution Answer: B – anything that lowers dose increase QM. A faster system lowers dose. |
|
|
120. Regarding positron imaging which of the following is true:
A. Detects gamma rays accompanying Beta decay B. Detects annihilation photons from pair production C. Detects annihilation photons from positron decay D. Detects Auger electron production resulting from Compton interactions E. Detects characteristic x-rays from positron decay |
120. Regarding positron imaging which of the following is true:
A. Detects gamma rays accompanying Beta decay B. Detects annihilation photons from pair production C. Detects annihilation photons from positron decay D. Detects Auger electron production resulting from Compton interactions E. Detects characteristic x-rays from positron decay Answer: C – read every option carefully. I almost always miss this recall b/c I pick B and move on... (B is obviously wrong b/c there is no pair production in diagnostic imaging range). |
|
|
. A radiologist finds out she is pregnant. Her film badge worn on her collar reads 4mGy exposure over the last month. What is the appropriate action?
A. Assign her to separate duties B. Have her wear a double lead apron C. Have her place the film badge under the apron at the level of the uterus D. Provide her with a second film badge to wear under the apron at the level of the uterus E. No action necessary |
121. A radiologist finds out she is pregnant. Her film badge worn on her collar reads 4mGy exposure over the last month. What is the appropriate action?
A. Assign her to separate duties B. Have her wear a double lead apron C. Have her place the film badge under the apron at the level of the uterus D. Provide her with a second film badge to wear under the apron at the level of the uterus E. No action necessary Answer: D |
|
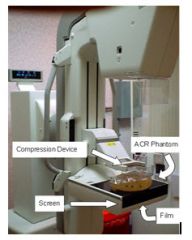
122. What weekly mammographic quality assurance factor is being tested below?
A. Collimation B. Compression C. Average Glandular Dose D. Image Quality E. Screen-film contact |
122. What weekly mammographic quality assurance factor is being tested below?
A. Collimation B. Compression C. Average Glandular Dose D. Image Quality E. Screen-film contact Answer: D – a big clue here is the word “weekly” |
|
|
123. If two films with an optical density of 1 are placed back-to-back what would the resulting optical transmission be?
A. 0.01 B. 1 C. 2 D. 10 E. 50 |
123. If two films with an optical density of 1 are placed back-to-back what would the resulting optical transmission be?
A. 0.01 B. 1 C. 2 D. 10 E. 50 Answer: A – tricky question. The OD will be 2, but the transmittance follows the equation: OD = log (1/T) 2 = log (1/T) 102 = 1/T T = 0.01 |
|
|
124. In compensating for attenuation of ultrasound with depth of the patient, the operator adjusts which of the following:
A. Centering device B. Zoom control C. Transmission output D. Time gain compensation E. Suppression control |
124. In compensating for attenuation of ultrasound with depth of the patient, the operator adjusts which of the following:
A. Centering device B. Zoom control C. Transmission output D. Time gain compensation E. Suppression control Answer: D – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
125. If the patient absorbs 98% of the primary x-ray beam and the screen-cassette absorbs 50%, what percent of the primary beam exits the cassette (ignore inverse square effects):
A. 0 B. 0.5 C. 1 D. 2 E. 5 |
125. If the patient absorbs 98% of the primary x-ray beam and the screen-cassette absorbs 50%, what percent of the primary beam exits the cassette (ignore inverse square effects):
A. 0 B. 0.5 C. 1 D. 2 E. 5 Answer: C – 2% exits the patient, and half of this is absorbed by the cassette. |
|
|
127. Which of the following values expresses the results of a bone density scan in terms of the standard deviation above or below the mean for a “normal” young adult of the same sex?
A. T score B. Z score C. DEXA value D. QCT value E. BMD value |
127. Which of the following values expresses the results of a bone density scan in terms of the standard deviation above or below the mean for a “normal” young adult of the same sex?
A. T score B. Z score C. DEXA value D. QCT value E. BMD value Answer: A – the T-score is based on a Thirty year old T-score The T-score shows the amount of bone you have compared to a young adult (at the age of 35) of the same gender with peak bone mass T-scores are based on a statistical measure called the standard deviation, which reflects differences from the average score. The Z-score Z-scores are calculated in the same way, but the comparisons are made to someone of your age, sex, race, height, and weight. Physicians may also measure a patient’s Z-score with a bone mineral density test. The Z-score is not used to confirm a diagnosis of osteoporosis because a favorable BMD measurement (compared to the average BMD measurement for the patient’s age group) does not mean the patient is not at risk for osteoporosis. |
|
|
128. For a given iodine concentration used in neuroangiography, blood vessel subject contrast is:
A. Dependent on tube mA B. Higher at 120 kVp than 70 kVp C. Higher in vessels in the head, farther away from the image receptor D. Higher with increased image intensifier veiling glare E. Increased with increasing blood vessel diameter |
128. For a given iodine concentration used in neuroangiography, blood vessel subject contrast is:
A. Dependent on tube mA B. Higher at 120 kVp than 70 kVp C. Higher in vessels in the head, farther away from the image receptor D. Higher with increased image intensifier veiling glare E. Increased with increasing blood vessel diameter Answer: E – contrast is defendant on kVp, not mA (A is wrong). The lower kVp the more contrast b/c of more photoelectric effect (B is wrong). Increased distance to the II and veiling glare both decrease contrast (C and D are wrong). The bigger the vessel, the more photoelectric effect from the iodine and therefore more contrast. |
|
|
129. I-131 decays to stable Xe-131 via beta minus emission. If I-131 is absorbed by the thyroid, which of the following deposits the most energy in the gland?
A. Beta minus particle B. Neutron C. Gamma ray D. Characteristic x-ray from Xe-131 E. Anti-neutrino |
129. I-131 decays to stable Xe-131 via beta minus emission. If I-131 is absorbed by the thyroid, which of the following deposits the most energy in the gland?
A. Beta minus particle B. Neutron C. Gamma ray D. Characteristic x-ray from Xe-131 E. Anti-neutrino Answer: A – in other words, electrons. |
|
|
130. Which of the following physical characteristics primarily determines the radiographic subject contrast of nonionic iodinated contrast when used in angiography?
A. Atomic number (Z) B. Molecular bond energy (eV) C. Physical density (g/cm3) D. Electron density (electrons/g) E. Atomic mass (A) |
130. Which of the following physical characteristics primarily determines the radiographic subject contrast of nonionic iodinated contrast when used in angiography?
A. Atomic number (Z) B. Molecular bond energy (eV) C. Physical density (g/cm3) D. Electron density (electrons/g) E. Atomic mass (A) Answer: A – the photoelectric effect is determined by Z3/E3 |

