![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
2. In the 70-120 kvp range, damage to biologic tissue is most likely the result of:
A. Scattered x-rays B. Characteristic x-rays C. Compton recoil electrons and the photoelectric effect D. Pair Production |
2. In the 70-120 kvp range, damage to biologic tissue is most likely the result of:
A. Scattered x-rays B. Characteristic x-rays C. Compton recoil electrons and the photoelectric effect D. Pair Production Answer: C – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
3. A CT scan is performed on a 90kg adult with 120 kvp, 240 mas, 1.5 Pitch, and a 512x512 matrix. If all parameters remain the same, and the field-of-view is reduced, which one of the following is true?
A. The table speed will change B. The pixel size is smaller C. The child will receive essentially the same radiation dose to the abdomen |
. A CT scan is performed on a 90kg adult with 120 kvp, 240 mas, 1.5 Pitch, and a 512x512 matrix. If all parameters remain the same, and the field-of-view is reduced, which one of the following is true?
A. The table speed will change B. The pixel size is smaller C. The child will receive essentially the same radiation dose to the abdomen Answer: B – If you keep the matrix size the same and decrease the FOV, then the pixel size, which is 1/(2 x matrix in one direction), must become smaller. |
|
|
. Which does not affect Doppler frequency shift?
26. Speed of the moving object 27. Incident beam frequency 28. Beam velocity 29. Size of the moving object 30. Angle between beam and the moving objec |
4. Which does not affect Doppler frequency shift?
26. Speed of the moving object 27. Incident beam frequency 28. Beam velocity 29. Size of the moving object 30. Angle between beam and the moving objec Answer: D – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
5. What is the total dose to a secretary from a source with a dose rate of 6mGy/hour at the secretary's desk and a half life of 10 minutes? The secretary and the source remain at the same distance for 2 hours.
A. 0.7 B. 1.4 C. 2.8 D. 6 E. 12 |
5. What is the total dose to a secretary from a source with a dose rate of 6mGy/hour at the secretary's desk and a half life of 10 minutes? The secretary and the source remain at the same distance for 2 hours.
A. 0.7 B. 1.4 C. 2.8 D. 6 E. 12 Answer: B – Basically we need to find the accumulative dose (Ã) via the MIRD equation. The only tricky thing is to convert the half life to hours (10 min = 0.167hrs) b/c the dose rate is given in hours. Here is the MIRD equation: à = 1.44 * f * Ao * Te à is the accumulative dose f is the fraction of activity per organ, which is 1 if you are calculating whole body dose (all organs added together equals 1) Ao is the original dose rate Te is the effective half life (1.44 * Te is the average half life) à = 1.44 * 1 * 6mGy/hr * 0.1667 hr à = 1.44 mGy |
|
|
6. Which of the following scintillation collimator yields the smallest image with the greatest resolution?
A. multihole parallel B. slant hole C. converging D. diverging E. pinhole |
. Which of the following scintillation collimator yields the smallest image with the greatest resolution?
A. multihole parallel B. slant hole C. converging D. diverging E. pinhole Bad question – best resolution is pinhole; smallest image is diverging. |
|
|
7. Which of the following is true concerning the photoelectric effect in tissues. Most of the energy of the incident photon is:
A. transferred to the nucleus B. transferred to the scattered photon C. given off as Brehmsstrulung radiation D. retained with the incident photon E. absorbed locally |
7. Which of the following is true concerning the photoelectric effect in tissues. Most of the energy of the incident photon is:
A. transferred to the nucleus B. transferred to the scattered photon C. given off as Brehmsstrulung radiation D. retained with the incident photon E. absorbed locally Answer: E – The characteristic xray and the displaced electron are locally absorbed. |
|
|
8. An echo is received from an interface 0.1 ms after pulse transmission. How deep (in cm) is the interface?
A. 1.54 B. 7.7 C. 14.4 D. 15.4 |
. An echo is received from an interface 0.1 ms after pulse transmission. How deep (in cm) is the interface?
A. 1.54 B. 7.7 C. 14.4 D. 15.4 Answer: B – Change the time to microseconds (1ms = 103 microseconds) and plug into the equation depth (cm) = 0.077 x time (us) depth (cm) = 0.077 x 100microseconds = 7.7 cm |
|
|
9. Which of the following is associated with an absorbed radiation threshold of 3 Gy?
A. main erythema B. temporary epilation C. dry desquamation D. radiation dermatitis E. ulceration |
9. Which of the following is associated with an absorbed radiation threshold of 3 Gy?
A. main erythema B. temporary epilation C. dry desquamation D. radiation dermatitis E. ulceration Answer: B |
|
|
10. Which of the following is least likely to affect image quality in teleradiology?
A. data cable transmission rates B. monitor grayscale luminescence C. bit depth D. matrix size E. compression |
10. Which of the following is least likely to affect image quality in teleradiology?
A. data cable transmission rates B. monitor grayscale luminescence C. bit depth D. matrix size E. compression Answer: A – The data cable transmission rates determine how long it takes to transfer an image. The transmission rate has nothing to do with the image quality (higher quality images will take longer to transmit, however). |
|
|
11. Studies of heritable effects of radiation have shown that mutations in germ cells secondary to diagnostic x-rays are:
A. Most likely to be seen in the first generation of offspring B. Most likely to be seen in the second generation of offspring C. Occur by the second generation or will not occur D. Negligible |
11. Studies of heritable effects of radiation have shown that mutations in germ cells secondary to diagnostic x-rays are:
A. Most likely to be seen in the first generation of offspring B. Most likely to be seen in the second generation of offspring C. Occur by the second generation or will not occur D. Negligible Answer: D – on multiple old tests. Heritable effects have been shown in mice and flies, but not in humans. |
|
|
12. Regarding the X-ray interaction with biological soft tissues, which of the following is true:
A. Pair production is the predominate interaction just above the k edge. B. Coherent scatter is common and results from the interaction with the nucleus C. The photoelectric effect predominates at a kVp > 50 D. Compton scatter results from the interaction with outer shell electrons |
12. Regarding the X-ray interaction with biological soft tissues, which of the following is true:
A. Pair production is the predominate interaction just above the k edge. B. Coherent scatter is common and results from the interaction with the nucleus C. The photoelectric effect predominates at a kVp > 50 D. Compton scatter results from the interaction with outer shell electrons Answer: D |
|
|
13. What is the maximum monthly allowable exposure to a fetus in a radiation worker?
A. 1 mSv B. 0.5mSv C. 100mSv D. 1Sv E. 5Sv |
13. What is the maximum monthly allowable exposure to a fetus in a radiation worker?
A. 1 mSv B. 0.5mSv C. 100mSv D. 1Sv E. 5Sv Answer: B – the rates as I memorized it are 50mrem/mo and 500mrem/10mo. |
|
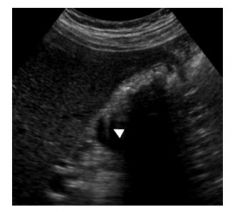
14.What type of ultrasound artifact is depicted in the picture?
|
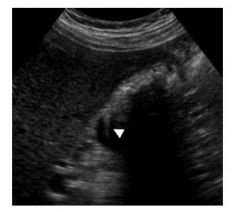
14.What type of ultrasound artifact is depicted in the picture?
A. Reverberation B. Refraction C. Reflection D. Side lobes E. Aliasing Answer: A – ringdown artifact is due to reverberation. |
|
|
15. If the 95% confidence interval for a count is between 120 and 168, then the 68% confidence interval is:
A. 102 to 180 B. 100 to 150 C. 132 to 156 D. 120 to 150 |
15. If the 95% confidence interval for a count is between 120 and 168, then the 68% confidence interval is:
A. 102 to 180 B. 100 to 150 C. 132 to 156 D. 120 to 150 Answer: C – 2 SD (i.e. 95 % CI) is 168-120 = 48, so 1 SD = 24. The count must be the median of the confidence interval, so (168+120)/2 = 144. Therefore, 1 SD is 144 +/- 12. (132 to 156) |
|
|
16) Milliampere-second (mAs) relates to what aspect of electrons?
a) Velocity b) Number c) Flow rate d) Kinetic energy |
16) Milliampere-second (mAs) relates to what aspect of electrons?
a) Velocity b) Number c) Flow rate d) Kinetic energy Answer: B – on multiple old tests. |
|
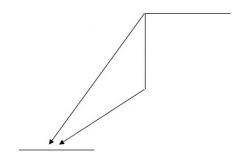
17) This diagram represents what two forms of parent radionuclide decay?
a) electron capture, positron emission b) gamma emission, positron emission c) electron capture, negatron emission d) gamma emission, negatron emission e) electron capture, alpha decay |
17) This diagram represents what two forms of parent radionuclide decay?
a) electron capture, positron emission b) gamma emission, positron emission c) electron capture, negatron emission d) gamma emission, negatron emission e) electron capture, alpha decay Answer: A – if the downward arrows go to the left, it mean Z is less in the daughter than the parent. The opposite is true if it goes right. By the way, a negatron is another word for an electron. |
|
|
18) Reducing workstation flicker can be accomplished by:
a) Data compression b) Lower bandwidth c) Higher refresh rate d) Contrast suppression e) Synchronization |
18) Reducing workstation flicker can be accomplished by:
a) Data compression b) Lower bandwidth c) Higher refresh rate d) Contrast suppression e) Synchronization Answer: C – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
19) Which imaging modality is the highest contributor to medical radiation in the U.S.?
a) CT b) Flouroscopy c) Plain film radiographs d) Nuclear imaging |
19) Which imaging modality is the highest contributor to medical radiation in the U.S.?
a) CT b) Flouroscopy c) Plain film radiographs d) Nuclear imaging Answer: A |
|
|
20) A 25 year old worker receives 2nd and 3rd degree burns over 50% of their body after an explosion at a radiopharmaceutical plant. Effects and treatment should include
a) isolation and treatment in the ER b) determine radioactivity before approaching c) the radiation exposure will cause immediate damage d) shower to wash off possible exposure |
20) A 25 year old worker receives 2nd and 3rd degree burns over 50% of their body after an explosion at a radiopharmaceutical plant. Effects and treatment should include
a) isolation and treatment in the ER b) determine radioactivity before approaching c) the radiation exposure will cause immediate damage d) shower to wash off possible exposure Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
21) What is the reason to use 360-degree rotation of the gamma camera in SPECT rather than a 180-degree rotation?
a. improve the calculation of the linear attenuation coefficients b. increase the number of counts c. blurring of the central pixel d. reduce Compton scatter e. related to intrinsic properties of crystal |
21) What is the reason to use 360-degree rotation of the gamma camera in SPECT rather than a 180-degree rotation?
a. improve the calculation of the linear attenuation coefficients b. increase the number of counts c. blurring of the central pixel d. reduce Compton scatter e. related to intrinsic properties of crystal Answer: A – The number of counts can be the same with 180 degree rotation if the camera moves half as fast. The 360 allows calculation of the LAC via a transmission source. This is a different question than why use 2 cameras instead of one (on multiple tests including 2006). The advantage of 2 cameras is just a faster scan. |
|
|
22) A population is receives 10mGy of absorbed dose each generation. What is the genetic effect after many generations?
A. <0.1% B. 1% C. 10% D. 20% E. 30% |
22) A population is receives 10mGy of absorbed dose each generation. What is the genetic effect after many generations?
A. <0.1% B. 1% C. 10% D. 20% E. 30% Answer: B – I am not sure about this one. I think the reasoning here is that BIER says the mutation doubling dose is 1 Gy. The doubling dose will increase genetic mutations by 100%. Maybe if you give 10 mGy (1/100 Gy) then you get 100%/100 or 1%. Lots of assumptions here! |
|
|
23) A patient swallows during digital subtraction angiography after the acquisition of the mask. What be done to improve the image?
A. logarithmic transformation B. increase frame integration C. obtain a new mask D. frame integration E. Electric shock therapy |
23) A patient swallows during digital subtraction angiography after the acquisition of the mask. What be done to improve the image?
A. logarithmic transformation B. increase frame integration C. obtain a new mask D. frame integration E. Electric shock therapy Answer: C – on multiple old tests. I made up Option D. |
|
|
24) In standard chest radiography what film/screen combination is used?
A. screen in front, single emulsion film B. screen in back, single emulsion film C. screen in front and back and double emulsion film D. screen in front and double emulsion film E. screen in back and double emulsion film |
24) In standard chest radiography what film/screen combination is used?
A. screen in front, single emulsion film B. screen in back, single emulsion film C. screen in front and back and double emulsion film D. screen in front and double emulsion film E. screen in back and double emulsion film Answer: C – makes a film sandwich. The mammo and extremity cassettes are an open faced film sandwich (film on top of screen). Yum... |
|
|
) What is the primary site of radiation-induced pathology in the heart?
A. proximal aorta B. pericardium C. endocardium D. myocardium E. epicardium |
25) What is the primary site of radiation-induced pathology in the heart?
A. proximal aorta B. pericardium C. endocardium D. myocardium E. epicardium Answer: B – No idea why, but this is on several old tests. |
|
|
26. The addition of an intensifying screen in conventional film-screen radiography will:
A. Increase the SNR B. Increase quantum mottle C. Increase spatial resolution D. Increase dose E. Decrease focal spot size |
26. The addition of an intensifying screen in conventional film-screen radiography will:
A. Increase the SNR B. Increase quantum mottle C. Increase spatial resolution D. Increase dose E. Decrease focal spot size Answer: B – anything that reduces the number of photons used to make the image will increase QM. |
|
|
27. A nursing mother should not breast feed for at lease two weeks before therapy with:
A. I-123 Sodium Iodine B. 99m Tc C. 67 Gallium Citrate D. I-131 |
27. A nursing mother should not breast feed for at lease two weeks before therapy with:
A. I-123 Sodium Iodine B. 99m Tc C. 67 Gallium Citrate D. I-131 Answer: D – on multiple old tests. Breast milk concentrates I-131. You want the woman to stop lactating before giving I-131 to decrease dose to breast. You cannot let a baby drink milk with I-131. See Mettler’s appendix as below. Note I rounded some here because these things vary with dose and I can’t memorize all the details. Check for yourself if you need more info: - most Tc products stop 24 hours after dose given then restart. - Ga 67 stop 4 wks - I 131 stop 2 weeks before and don’t restart - I 123 stop 3-5 d - Thalium stop 2 weeks |
|
|
28. In Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA), decrease noise could be achieved by:
A. Reducing the number of frames used in both mask and post contrast images. |
Well we only have one answer choice and it is wrong. Examples of correct answers include frame integration and retaking the mask image if the patient moved.
|
|
|
30. To decrease the patient dose in a single array CT, one could:
A. Increase the pitch. B. Decrease the table movement. C. Increase the exposure time. D. Remove filter |
30. To decrease the patient dose in a single array CT, one could:
A. Increase the pitch. B. Decrease the table movement. C. Increase the exposure time. D. Remove filter Answer: A |
|
|
46. The patient couch movement index in acquiring a scan utilizing a helical CT scanner is
a) proportional to pitch b) is defined in the term pitch as couch motion x collimation/rotation of gantry [sic definitely not the correct formula] c) not useful in dose measurement d) not relevant in helical scanners |
46. The patient couch movement index in acquiring a scan utilizing a helical CT scanner is
a) proportional to pitch b) is defined in the term pitch as couch motion x collimation/rotation of gantry [sic definitely not the correct formula] c) not useful in dose measurement d) not relevant in helical scanners Answer: A |
|
|
47. A woman involved in a traffic accident complained of lower back pain and underwent AP and lateral lumbosacral spine radiography. Two months later she was found to be 18 weeks pregnant. Which of the following is true?
A. The radiographs should not have been obtained. B. A therapeutic abortion should be recommended. C. The cancer incidence to the fetus is < 0.5%. D. The fetus probably received an absorbed dose of 0.1 – 0.15 Gy. E. There is an increased risk of neonatal death. |
47. A woman involved in a traffic accident complained of lower back pain and underwent AP and lateral lumbosacral spine radiography. Two months later she was found to be 18 weeks pregnant. Which of the following is true?
A. The radiographs should not have been obtained. B. A therapeutic abortion should be recommended. C. The cancer incidence to the fetus is < 0.5%. D. The fetus probably received an absorbed dose of 0.1 – 0.15 Gy. E. There is an increased risk of neonatal death. Answer: C – there are questions like this on every old test, and the answer is always “it's going to be okay” or something like that. |
|
|
48. The energy measured of an incident gamma photon in the crystal of a scintillation camera is
A. dependent on the central PMT B. 7 surrounding PMTs C. All the PMTs D. separate caliberation PMT |
48. The energy measured of an incident gamma photon in the crystal of a scintillation camera is
A. dependent on the central PMT B. 7 surrounding PMTs C. All the PMTs D. separate caliberation PMT Answer: C |
|
|
49. The best correlate for deterministic effects is
A. Absorbed dose B. Effective dose C. mAs D. Exposure |
49. The best correlate for deterministic effects is
A. Absorbed dose B. Effective dose C. mAs D. Exposure Answer: A – not that effective dose (Sv) is a risk assessment for fatal cancers and severe genetic defects (stochastic effects). The deterministic effects have thresholds given in Gy (absorbed dose). |
|
|
50. If the probability of attenuation of a monochromatic photon is 75%
after travelling 2mm Pb, what is the HVL? A. 0.5mm B. 1mm C. 2mm D. 4mm |
50. If the probability of attenuation of a monochromatic photon is 75%
after travelling 2mm Pb, what is the HVL? A. 0.5mm B. 1mm C. 2mm D. 4mm Answer: B – 75% is 2 HVLs. |
|
|
71. Regarding the S factor in internal dose calculations, which is FALSE?
A. it can provide an accurate estimate of a patient's dose B. it is dependent on the organ's mass C. it is calculated for individual source to target organ pairs D. it is given in units of Gy/(MBq * Hr) E. it takes into account the entire emission spectrum |
71. Regarding the S factor in internal dose calculations, which is FALSE?
A. it can provide an accurate estimate of a patient's dose B. it is dependent on the organ's mass C. it is calculated for individual source to target organ pairs D. it is given in units of Gy/(MBq * Hr) E. it takes into account the entire emission spectrum Answer: E. It is separate for Beta emission vs Gamma emission. |
|
|
72. In mammography, the following will increase the patient's skin dose:
A. increasing the distance between the patient and image receptor while keeping the source to image distance constant B. increasing the distance between the source and the image receptor while keeping the subject to image distance constant C. decreasing the mAs D. something about the focal spot |
72. In mammography, the following will increase the patient's skin dose:
A. increasing the distance between the patient and image receptor while keeping the source to image distance constant B. increasing the distance between the source and the image receptor while keeping the subject to image distance constant C. decreasing the mAs D. something about the focal spot Answer: A – decreasing the SOD will increase the dose by the inverse square law. |
|
|
73. In mammography, a molybdenum filter is used with a moly target because
A. it increases Compton scatter (?) B. it has a low atomic number C. it transmits a large portion of the K-edge characteristic radiation D. it produces K-edge characteristic radiation |
73. In mammography, a molybdenum filter is used with a moly target because
A. it increases Compton scatter (?) B. it has a low atomic number C. it transmits a large portion of the K-edge characteristic radiation D. it produces K-edge characteristic radiation Answer: C – the anode material can be used to filter the x-ray beam b/c it allows the transmission of characteristic x-rays. The K-edge is always slightly higher than the characteristic x-ray energy because K characteristic x-rays is K-L. |
|
|
74. In CT, detection of a low density 4cm hepatoma will be improved on a non-contrast study with
A. increased slice thickness B. decreased mAs C. something about the couch speed D. something about the ramp filter |
74. In CT, detection of a low density 4cm hepatoma will be improved on a non-contrast study with
A. increased slice thickness B. decreased mAs C. something about the couch speed D. something about the ramp filter Answer: A – improving the SNR will improve contrast. Increasing slice thickness will slightly decrease z-axis spatial resolution, but that should not be a factor in seeing a 4cm mass. |
|
|
75. In conventional linear tomography, a high density point (small round structure) located 2 cm below the imaging plane will appear on the image as:
A. a star B. a line C. an ellipse D. a point E. a rectangle |
75. In conventional linear tomography, a high density point (small round structure) located 2 cm below the imaging plane will appear on the image as:
A. a star B. a line C. an ellipse D. a point E. a rectangle Answer: B – what is tomography? |
|
|
76. CT numbers (Hounsfield units) are related to:
A. Atomic number B. Mass number C. Electrons/gram D. Linear attenuation coefficient E. Pixel size |
76. CT numbers (Hounsfield units) are related to:
A. Atomic number B. Mass number C. Electrons/gram D. Linear attenuation coefficient E. Pixel size Answer: D – remember that Compton effect is determined by electron density (Option C), but almost everything has the same electron density except hydrogen. Therefore electron density cannot be used to differentiate tissues, and C isn't correct. The best answer is D. |
|
|
77. Which of the following is true regarding Technetium 99m?
A. It is produced in a cyclotron B. Its half life is too short for convenient labeling C. Its photon energy is too high for use in conventional scintillation cameras D. It is not available in carrier free state E. Auger electrons and internal conversion electrons do not contribute |
Which of the following is true regarding Technetium 99m?
A. It is produced in a cyclotron B. Its half life is too short for convenient labeling C. Its photon energy is too high for use in conventional scintillation cameras D. It is not available in carrier free state E. Auger electrons and internal conversion electrons do not contribute significantly to patient dose Answer: E – I guess the key word is significantly. Tc-99 is available in a carrier free state (http://jnm.snmjournals.org/cgi/reprint/16/7/639.pdf) which comes up on other questions. |
|
|
78. Using screen-film radiography, to create a film with the optical density within the useful middle range, the exposure should be (in mR):
A. .005 B. .5 C. 50 D. 500 E. 5000 |
78. Using screen-film radiography, to create a film with the optical density within the useful middle range, the exposure should be (in mR):
A. .005 B. .5 C. 50 D. 500 E. 5000 Answer: B – I have seen this one more than once. Just know that most films are less than 1mR exposure (dental films are more b/c of small mass and no screens are used). See the 1st derivative of the H&D curve in the Projection Radiography and Image Quality sections of the Bushberg syllabus. |
|
|
79. The formation of a dicentric is an example of:
A. radiation induced chromosomal aberration B. radiation induced mutation in a germ cell C. cell division D. acentric fragmentation |
Answer: A
|
|
|
80. The terms “twisted cable”, “fiber optic”, and “coaxial” all refer to:
A. local area network structures B. data compression methods C. network transmission media D. data archive media E. image processing algorithms |
80. The terms “twisted cable”, “fiber optic”, and “coaxial” all refer to:
A. local area network structures B. data compression methods C. network transmission media D. data archive media E. image processing algorithms Answer: C |
|
|
81. The time gain compensation (TGC) in ultrasound is used for:
A. attenuation correction B. low frequencies C. multiple reflections D. variations in velocity E. diameter of the transducer |
81. The time gain compensation (TGC) in ultrasound is used for:
A. attenuation correction B. low frequencies C. multiple reflections D. variations in velocity E. diameter of the transducer Answer: A – almost guaranteed to get this question or one like it. |
|
|
81A. The examination with the highest skin dose is:
A. TIPS procedure. B. Intravenous urogram (IVU) C. Barium Enema D. Lateral lumbar spine radiograph E. Abdominal computed tomography scan |
81A. The examination with the highest skin dose is:
A. TIPS procedure. B. Intravenous urogram (IVU) C. Barium Enema D. Lateral lumbar spine radiograph E. Abdominal computed tomography scan Answer: A |
|
|
82. Which of the following has a threshold dose?
A. Leukemia B. Carcinoma of the thyroid C. Reduced lifespan D. Lens opacification E. Genetic mutations |
82. Which of the following has a threshold dose?
A. Leukemia B. Carcinoma of the thyroid C. Reduced lifespan D. Lens opacification E. Genetic mutations Answer: D – cataracts are the classic deterministic effect. |
|
|
83. An anteroposterior abdominal radiograph performed at 80kVp technique and patient thickness of 20cm will yield a posterior exiting exposure to entrance skin dose ratio of:
A. 99% B. 50% C. 20% D. 2% E. 0.2% |
83. An anteroposterior abdominal radiograph performed at 80kVp technique and patient thickness of 20cm will yield a posterior exiting exposure to entrance skin dose ratio of:
A. 99% B. 50% C. 20% D. 2% E. 0.2% Answer: D – The HVL in soft tissue is about 4cm, so the patient would have 5 HVL. So, the ratio of the exiting beam will have the intensity of 1/25 = 0.03. So, 2% is the closest answer... |
|
|
84. In a population of one million people, a whole body dose of low LET 10mSv radiation to each individual will result in an increased number of fatal cancer cases in how many people?
A. 0.4 to 0.8 B. 4 to 8 C. 40 to 80 D. 400 to 800 E. 4000 to 8000 |
84. In a population of one million people, a whole body dose of low LET 10mSv radiation to each individual will result in an increased number of fatal cancer cases in how many people?
A. 0.4 to 0.8 B. 4 to 8 C. 40 to 80 D. 400 to 800 E. 4000 to 8000 Answer: D – remember 6% per Sv... 10mSv x 0.0001 Sv/mSv = 0.01 Sv Sv x 0.06 cases ca/ Sv = 0.0006 cancer risk 0.0006 cancer risk x 1,000,000 people = 600 cancer cases |
|
|
86. After an X ray machine is turned on, a few initial exposures are taken at low kVp and low mAs in order to:
A. Stabilize the filament. B. Saturate the transformer C. Outgas the tube D. Warm up the anode. E. Lubricate the rotor bearings |
86. After an X ray machine is turned on, a few initial exposures are taken at low kVp and low mAs in order to:
A. Stabilize the filament. B. Saturate the transformer C. Outgas the tube D. Warm up the anode. E. Lubricate the rotor bearings Answer: D |
|
|
87. Grid-line artifacts in mammography are usually due to:
A. AEC density is too high. B. High kVp is used in patient with small breasts. C. Low mAs are used in patient with large breasts. D. A molybdenum filter is used in patient with small breasts. E. Inadequate compression of large breasts. |
87. Grid-line artifacts in mammography are usually due to:
A. AEC density is too high. B. High kVp is used in patient with small breasts. C. Low mAs are used in patient with large breasts. D. A molybdenum filter is used in patient with small breasts. E. Inadequate compression of large breasts. Answer: B – this is because with high kVp you use lower mAs, which means short exposure time (the s in mAs). With shorter exposure times, the grid doesn’t have time to move around enough to get blurred out! |
|
|
88. Chemical shift artifacts in MR systems are due to:
A. Difference in resonant frequencies of hydrogen in water and lipids. B. Difference in magnetic susceptibility of water and lipids. C. Gradient nonlinearity. D. Imperfect radio frequency shielding. E. Radio frequency interference. |
88. Chemical shift artifacts in MR systems are due to:
A. Difference in resonant frequencies of hydrogen in water and lipids. B. Difference in magnetic susceptibility of water and lipids. C. Gradient nonlinearity. D. Imperfect radio frequency shielding. E. Radio frequency interference. Answer: A – On every single test! Don't miss easy points. |
|
|
89. At 110 kVp, image contrast is adequately achieved in a single contrast barium enema but not an excretory urogram because:
A. Luminal diameter of bowel is greater than that of the luminal diameter of the ureters. B. Barium has a higher atomic number than that of Iodine. C. Barium has a higher mass attenuation coefficient than Iodine. D. Barium has a K-edge of lower energy than that of Iodine. |
89. At 110 kVp, image contrast is adequately achieved in a single contrast barium enema but not an excretory urogram because:
A. Luminal diameter of bowel is greater than that of the luminal diameter of the ureters. B. Barium has a higher atomic number than that of Iodine. C. Barium has a higher mass attenuation coefficient than Iodine. D. Barium has a K-edge of lower energy than that of Iodine. Answer: A – have seen similar questions before. K edge of Barium and Iodine are similar. |
|
|
90. The acronym ALARA stands for:
A. Absolute Longitudinal Angle Reconstruction Algorithm. B. Average Low Amplification Radiation Attenuation. C. Anode Loaded Auxillary Radiation Apparatus. D. Almost Lethal Acute Radiation Accident. E. As Low As Reasonably Achievable. |
90. The acronym ALARA stands for:
A. Absolute Longitudinal Angle Reconstruction Algorithm. B. Average Low Amplification Radiation Attenuation. C. Anode Loaded Auxillary Radiation Apparatus. D. Almost Lethal Acute Radiation Accident. E. As Low As Reasonably Achievable. Answer: E – more easy points. I think these questions are to see if you studied at all or just showed up to take the test. |
|
|
91. If the field of view in an MR study is decreased, keeping all other variables constant, there will be a decrease in:
a. spatial resolution b. T1 contrast c. T2 contrast d. signal to noise ratio e. wrap around artifact |
91. If the field of view in an MR study is decreased, keeping all other variables constant, there will be a decrease in:
a. spatial resolution b. T1 contrast c. T2 contrast d. signal to noise ratio e. wrap around artifact Answer: D – in general, decreasing the volume of the acquisition decreases the SNR. The exception is decreasing the bandwidth, which does make the slice smaller. However, the imaging takes longer and allows more time for signal to be acquired. Therefore decreasing bandwidth increases SNR. Got it? |
|
|
92. DICOM refers to:
A. software used to access the Internet B. an analog to digital interface card C. a protocol for image transfer D. a method of two way teleradiology communication |
92. DICOM refers to:
A. software used to access the Internet B. an analog to digital interface card C. a protocol for image transfer D. a method of two way teleradiology communication Answer: C . Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine DICOM |
|
|
93. A single “cold” round defect present on an image from a scintillation camera would be caused by a:
A. cracked crystal B. defective PMT C. defective crystal-hydration-detector seal D. software failure E. damaged collimator |
93. A single “cold” round defect present on an image from a scintillation camera would be caused by a:
A. cracked crystal B. defective PMT C. defective crystal-hydration-detector seal D. software failure E. damaged collimator Answer: B – key is a round defect. If all the PMTs show up as cold defects, then the camera is not set at the right energy photopeak. |
|
|
94. Which configuration would cause the highest skin dose: (II=image intensifier)
|
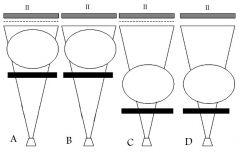
94. Which configuration would cause the highest skin dose: (II=image intensifier)
Answer: C – both the use of a grid and the close source to object distance increase dose. Option B (no grid, high SOD) would give the least dose. |
|
|
95. With a 30 keV beam interacting with soft tissue, contrast is decreased most by:
A. coherent scatter from Thompson interaction B. characteristic x-rays from photoelectric effect C. scatter photons from Compton interaction D. annilation photons from paired production E. recoil electrons from Compton interaction and the photoelectric effect |
95. With a 30 keV beam interacting with soft tissue, contrast is decreased most by:
A. coherent scatter from Thompson interaction B. characteristic x-rays from photoelectric effect C. scatter photons from Compton interaction D. annilation photons from paired production E. recoil electrons from Compton interaction and the photoelectric effect Answer: C |
|
|
96. What is the most likely cause for an area of interest to be underexposed using AEC (automatic exposure control) on a screen film radiograph?
A. Wrong AEC sensor B. Wrong mA C. Wrong focal spot D. Wrong beam filter |
96. What is the most likely cause for an area of interest to be underexposed using AEC (automatic exposure control) on a screen film radiograph?
A. Wrong AEC sensor B. Wrong mA C. Wrong focal spot D. Wrong beam filter Answer: A |
|
|
97. An 800 x 600 CRT monitor is inadequate for
A. digital chest X-rays B. ultrasound C. CT D. MRI |
97. An 800 x 600 CRT monitor is inadequate for
A. digital chest X-rays B. ultrasound C. CT D. MRI Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
98. The main target of radiations-induced cell death is
A. DNA B. RNA C. Mitochondria D. Lysosomes |
98. The main target of radiations-induced cell death is
A. DNA B. RNA C. Mitochondria D. Lysosomes Answer: A |
|
|
99. “Radiation (Absorbed) dose” refers to
A. Amount of energy absorbed per unit mass of target tissue B. Amount of energy absorbed per unit density of target tissue C. Charge liberated per unit mass of target tissue D. Charge liberated per unit density of target tissue |
99. “Radiation (Absorbed) dose” refers to
A. Amount of energy absorbed per unit mass of target tissue B. Amount of energy absorbed per unit density of target tissue C. Charge liberated per unit mass of target tissue D. Charge liberated per unit density of target tissue Answer: A – exposure is a measure of charge, dose is a measure of energy. |
|
|
100. Concerning high level fluoroscopy after 1995, which of the following is false?
A. need an alarm to sound while in this mode B. exposure is less than 20 R/min C. need AEC activated D. need a machine to record cumulative dose E. need to activate it separately from regular fluoroscopy |
100. Concerning high level fluoroscopy after 1995, which of the following is false?
A. need an alarm to sound while in this mode B. exposure is less than 20 R/min C. need AEC activated D. need a machine to record cumulative dose E. need to activate it separately from regular fluoroscopy Answer: D – on multiple old tests. While some machines perform this function, it is not required. |
|
|
101. Compared with convention film/screen radiography, the primary advantage of using computed radiography with a storage phosphor is…
A. Dynamic range B. Improved resolution C. Decreased dose D. Less noise E. Less scatter |
101. Compared with convention film/screen radiography, the primary advantage of using computed radiography with a storage phosphor is…
A. Dynamic range B. Improved resolution C. Decreased dose D. Less noise E. Less scatter Answer: A |
|
|
102. The primary factor determining axial resolution in ultrasound…
A. Pulse length B. Pulse frequency C. Gel coupling D. Blood flow E. Beam width |
102. The primary factor determining axial resolution in ultrasound…
A. Pulse length B. Pulse frequency C. Gel coupling D. Blood flow E. Beam width Answer: A – these questions come up a lot. Know about axial resolution and lateral resolution. See explanations from other old tests. Don't feel like retyping it now. |
|
|
103. In an irradiated person, the factor that best correlates with the risk of developing leukemia is…
A. Absorbed dose to the whole body B. Absorbed dose to the gonads C. Absorbed dose to the bone marrow D. Skin exposure |
103. In an irradiated person, the factor that best correlates with the risk of developing leukemia is…
A. Absorbed dose to the whole body B. Absorbed dose to the gonads C. Absorbed dose to the bone marrow D. Skin exposure Answer: C |
|
|
104. Which of the following has not been reported in a peer reviewed article since 1990 as a result of a fluoroscopically guided interventional procedure?
A. Retarded facial bone growth in pediatric patients B. Skin epilation C. Permanent radiation dermatitis D. Skin necrosis E. Cataract development in the fluoroscopist F. Leprechaun epilation |
104. Which of the following has not been reported in a peer reviewed article since 1990 as a result of a fluoroscopically guided interventional procedure?
A. Retarded facial bone growth in pediatric patients B. Skin epilation C. Permanent radiation dermatitis D. Skin necrosis E. Cataract development in the fluoroscopist F. Leprechaun epilation Answer: A – Fluoroscopy has been associated with all of the above except A (and also F – at least not in a peer reviewed journal). Is it politically correct to put the word 'retarded' in a question? |
|
|
105. If all other parameters are held constant, a 10% increase in which of the following factors will increase the optic density of a film/screen combination the most?
A. Film speed B. Screen speed C. kVp D. Exposure time E. Field size |
105. If all other parameters are held constant, a 10% increase in which of the following factors will increase the optic density of a film/screen combination the most?
A. Film speed B. Screen speed C. kVp D. Exposure time E. Field size Answer: C – OD is a measure of how much of the light from a viewbox gets though to the film, and it is proportional to exposure in mR. Remember the H&D curve? OD is independent of exposure time according to the Law of Reciprocity. However, at the extremes of exposure time the OD drops, which is known as Law of Reciprocity failure. Increasing film or screen speed will usually decrease exposure via AEC, although this question stem states “all other parameters are held constant.” Regardless, increasing speed will not increase exposure. Field size will not increase exposure because although radiation increases due to less collimation, so does volume. Only kVp increases the quantity and quality of the xray beam. So, kVp will have the most effect on the OD. |
|
|
106. The percent uncertainty of a radionuclide count interval is 10% at one second. What is the percent uncertainty for a count interval of 100 seconds.
A. 100% B. 1.0% C. 0.1% D. 3.2% E. 0.5% |
106. The percent uncertainty of a radionuclide count interval is 10% at one second. What is the percent uncertainty for a count interval of 100 seconds.
A. 100% B. 1.0% C. 0.1% D. 3.2% E. 0.5% Answer: B – first solve for the number of counts (N) via the % uncertainty equation: 1/√N = 0.10 N = 100 Then what would the % uncertainty if we had 100 time that number (100 seconds instead of just 1 second): 1/√100x = 1/√(100 x 100) = 1/100 = 1% |
|
|
107. The portion of a sample of radionuclide that is in the desired chemical form is:
A. Pyrogenicity B. Radionuclide purity C. Chemical purity D. Radiochemical purity E. Radionuclide index |
107. The portion of a sample of radionuclide that is in the desired chemical form is:
A. Pyrogenicity B. Radionuclide purity C. Chemical purity D. Radiochemical purity E. Radionuclide index Answer: D |
|
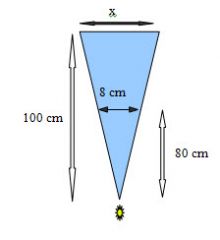
108. An 8 cm object is imaged 80cm from the point source. If the film is 100 cm from the point source, how large dose the object appear on the film? The object is parallel to the film.
A. 8cm B. 10cm C. 12cm D. 20cm E. 30cm |
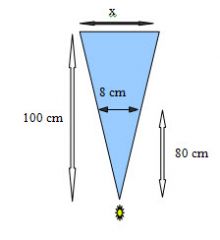
108. An 8 cm object is imaged 80cm from the point source. If the film is 100 cm from the point source, how large dose the object appear on the film? The object is parallel to the film.
A. 8cm B. 10cm C. 12cm D. 20cm E. 30cm Answer: B – Another 'draw the triangle' question. Here is how you do it: Then solve for x: x/100 = 8/80 = 0.1 x = 10 cm |
|
|
109. The in-plane spatial resolution of PET using coincident detection is:
A. independent of the array of photon emission B. nearly independent of the depth within the patient C. relies on the size of the holes in the collimator D. independent of the distance the positron travels before annihilation |
109. The in-plane spatial resolution of PET using coincident detection is:
A. independent of the array of photon emission B. nearly independent of the depth within the patient C. relies on the size of the holes in the collimator D. independent of the distance the positron travels before annihilation Answer: B – know this. It seems to be on almost all the tests. |
|
|
110. Scattered photon in Compton interaction retains the most energy at what angle of deflection from the incident beam.
A. 10 degrees B. 20 degrees C. 90 degrees D. 180 degrees |
110. Scattered photon in Compton interaction retains the most energy at what angle of deflection from the incident beam.
A. 10 degrees B. 20 degrees C. 90 degrees D. 180 degrees Answer: A – Read Nikoloff. |
|
|
111. The focal spot track on the anode of a CT x-ray tube is cooled primarily by:
a. convection in the insulating oil b. dissipation in the housing c. evaporation in the vacuum d. radiation from the anode e. conduction to the anode |
111. The focal spot track on the anode of a CT x-ray tube is cooled primarily by:
a. convection in the insulating oil b. dissipation in the housing c. evaporation in the vacuum d. radiation from the anode e. conduction to the anode Answer: E – this is true. However, the anode itself cools mostly by radiation. Remember, convection doesn't occur in a vacuum. |
|
|
112. What is the activity of a radioactive sample that decays by isomeric transition to a single gamma ray line with internal conversion efficiency of 0.5 (# of internal conversion electrons produced on average for each gamma ray) and the measured number of gamma rays is 1,000 per second:
a. 0.5 kBq b. 0.66 kBq c. 1.0 kBq d. 1.5 kBq e. 2.0 kBq |
112. What is the activity of a radioactive sample that decays by isomeric transition to a single gamma ray line with internal conversion efficiency of 0.5 (# of internal conversion electrons produced on average for each gamma ray) and the measured number of gamma rays is 1,000 per second:
a. 0.5 kBq b. 0.66 kBq c. 1.0 kBq d. 1.5 kBq e. 2.0 kBq Answer: E – basically wants you to figure out how many decays occur from the number of gamma rays detected. For every gamma ray detected, there is an internal conversion electron not detected (0.5 probability of I.T. Gamma ray and 0.5 probability of I.C. Electron). So, there are 2000 decays a second, which equals 2 kBq. |
|
|
113. The decreased intensity of the x-ray beam at the anode side of the tube is caused by:
a. anode wobble b. high anode material atomic number c. unstable filament current d. faulty cathode focusing cup e. absorption in the anode |
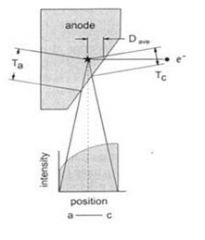
113. The decreased intensity of the x-ray beam at the anode side of the tube is caused by:
a. anode wobble b. high anode material atomic number c. unstable filament current d. faulty cathode focusing cup e. absorption in the anode Answer: E – aka heel effect. The path of the xray on the anode side (Ta) is longer than the cathode side (Tc) so there is a greater chance of attenuation: |
|
|
114. Excluding the lung dose from inhaled radon, the average annual effective dose equivalent from natural occurring radiation to the general public is:
a. 0.07 – 0.2 mSv b. 0.7 – 2.0 mSv c. 7.0 – 20.0 mSv d. 0.07 – 0.2 Sv e. 0.7 – 2.0 Sv |
114. Excluding the lung dose from inhaled radon, the average annual effective dose equivalent from natural occurring radiation to the general public is:
a. 0.07 – 0.2 mSv b. 0.7 – 2.0 mSv c. 7.0 – 20.0 mSv d. 0.07 – 0.2 Sv e. 0.7 – 2.0 Sv Answer: B – depending on where you look this total is about 1 mSv. |
|
|
115. An US beam crossing an interface from fat (1450 m/s) to liver (1550 cm/s) will have:
a. increased frequency b. increased wavelength c. decreased frequency d. decreased wavelength |
115. An US beam crossing an interface from fat (1450 m/s) to liver (1550 cm/s) will have:
a. increased frequency b. increased wavelength c. decreased frequency d. decreased wavelength Answer: B – the frequency of the u/s beam is constant and is a property of the u/s transducer crystal. The speed and wavelength change (in the same direction) with changes in the medium. |
|
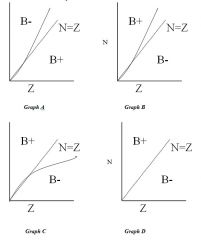
116. The decay in a nucleus is based upon the ratio of protons (Z) to neutrons (N). Which graph best depicts occurrence of Beta minus and Beta plus decay in relation to the number of protons and neutrons:
|
116. The decay in a nucleus is based upon the ratio of protons (Z) to neutrons (N). Which graph best depicts occurrence of Beta minus and Beta plus decay in relation to the number of protons and neutrons:
Graph A Graph B Graph C Graph D Answer: A |
|
|
117. The velocity of ultrasound in biological tissue is related to:
A. The piezoelectric crystal characteristics B. Compressibility of the soft tissues C. The soft tissue interfaces D. Pulse length |
117. The velocity of ultrasound in biological tissue is related to:
A. The piezoelectric crystal characteristics B. Compressibility of the soft tissues C. The soft tissue interfaces D. Pulse length Answer: B |
|
|
118. What aspect of mammography is being tested in this picture (a square block with a compression device on it)?
A. Average glandular dose B. Image quality C. Compression D. Contrast |
118. What aspect of mammography is being tested in this picture (a square block with a compression device on it)?
A. Average glandular dose B. Image quality C. Compression D. Contrast Answer: B – a weekly test. |
|
|
119. In a 10 kg child with a history of reflux, a barium swallow is performed. What is the most practical way to lower patient dose?
A. Remove the copper filter B. Perform continuous fluoroscopy C. Decrease focal spot size D. Disable the grid |
119. In a 10 kg child with a history of reflux, a barium swallow is performed. What is the most practical way to lower patient dose?
A. Remove the copper filter B. Perform continuous fluoroscopy C. Decrease focal spot size D. Disable the grid Answer: D – actually they mean remove the grid. |
|
|
120. An interventionalist declares her pregnancy. The highest average dose recorded on her collier film badge is 4mSv. With regard to her radiation dose to the fetus, what should be performed?
A. Double her lead apron B. Place a film badge on the apron at the level of the fetus C. Place a film badge under the lead apron at the level of the fetus D. No action is required |
120. An interventionalist declares her pregnancy. The highest average dose recorded on her collier film badge is 4mSv. With regard to her radiation dose to the fetus, what should be performed?
A. Double her lead apron B. Place a film badge on the apron at the level of the fetus C. Place a film badge under the lead apron at the level of the fetus D. No action is required Answer: C – I've seen the pregnant x-ray techs do this. |
|
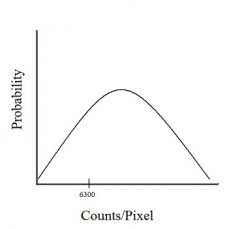
121. What is the percent probability of pixels that have counts above 6300? 6300 is 1 STD below mean.
A. 0.06% B 0.7% C 50% D 85% |
121. What is the percent probability of pixels that have counts above 6300? 6300 is 1 STD below mean.
A. 0.06% B 0.7% C 50% D 85% Answer: D – 1 SD contains the central 67% of values. So 33% is split between the two ends of the graph with 16.5% at each end. They want to know how many above a spot at 1 SD below the mean. That means everything above the bottom 16.5%. 100% - 16.5% = 83.5% or about 85%. |
|
|
122. Define specificity
A. TN/(TN+FP) B. TN/(TN+TN) C. TP/(FP+TP) D. FP/(TP+FP) |
122. Define specificity
A. TN/(TN+FP) B. TN/(TN+TN) C. TP/(FP+TP) D. FP/(TP+FP) Answer: A |
|
|
123. Keeping the source to image distance constant and moving the object towards the source in an X ray system, what will be increased
A scatter B dose C minification D no change |
123. Keeping the source to image distance constant and moving the object towards the source in an X ray system, what will be increased
A scatter B dose C minification D no change Answer: B |
|
|
124. The maximum NCRP guidelines for dose of 500mSv/year is for which scenario
A occupational exposure to ocular lens B occupational exposure to thyroid gland C non occupational exposure to hands D non occupatinal exposure to fetus |
124. The maximum NCRP guidelines for dose of 500mSv/year is for which scenario
A occupational exposure to ocular lens B occupational exposure to thyroid gland C non occupational exposure to hands D non occupatinal exposure to fetus Answer: B – the hardest part of this question is converting the units to whatever you memorized for the limits. I memorized that any organ other than the eye (but including skin & extremities) can get 50 rems/year. 50 rems = 0.5 Sv 0.5 Sv = 500 mSv. |
|
|
125. MQSA requirement for reproducibility of radiographs is
A. daily B. monthly C. semiannually D. quarterly |
125. MQSA requirement for reproducibility of radiographs is
A. daily B. monthly C. semiannually D. quarterly Answer: D – Mammo QC questions are popular. Here is a quick reference chart: Test Timing Processor Density Daily Base + Fog Daily Phantom OD Weekly Repeat analysis Quarterly Reproducibility Quarterly Screen-film contact Semiannually Darkrrom fog Semiannually Compression Semiannually |

