![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. PET detects:
A. Positron particles B. Gamma rays C. Beta particles D. Annihilation photons |
1. PET detects:
A. Positron particles B. Gamma rays C. Beta particles D. Annihilation photons Answer: D |
|
|
2. Risk of malignancy in women is greatest at what age:
A. <10 B. 10-20 C. 20-30 D. 30-40 E. 40-50 |
2. Risk of malignancy in women is greatest at what age:
A. <10 B. 10-20 C. 20-30 D. 30-40 E. 40-50 Answer: E – Risk of malignancy in general is higher as you age, but younger women are more at risk for cancer due to the effects (stochastic) of radiation. |
|
|
3. Fat attenuates 3 dB/cm and you use a 5MHz transducer. If the lesion is 5 cm deep, what is the reduction in intensity at the transducer?
A. 10 B. 13 C. 100 D. 130 E. 1000 |
3. Fat attenuates 3 dB/cm and you use a 5MHz transducer. If the lesion is 5 cm deep, what is the reduction in intensity at the transducer?
A. 10 B. 13 C. 100 D. 130 E. 1000 Answer: E – 5cm there and 5cm back equals 10cm. 10cm x 3dB/cm = 30dB. Plug into equation: dB = 10 log I/I 30 = 10 log I/I 3 = log I/I I/I = 103 = 1000 A short cut is to divide the dB loss by ten and raise 10 to that number. |
|
|
4. The Larmour frequency of a proton with spin (1/2) is 100MHz when put in a magnetic field of 4T. What is the gyromagnetic ratio?
A. 25 B. 100 C. 200 D. 4000 |
4. The Larmour frequency of a proton with spin (1/2) is 100MHz when put in a magnetic field of 4T. What is the gyromagnetic ratio?
A. 25 B. 100 C. 200 D. 4000 Answer: A – 100MHz/4T = 25 MHz/T Any free system with a constant gyromagnetic ratio, such as a rigid system of charges, a nucleus, or an electron, when placed in an external magnetic field B (measured in teslas) that is not aligned with its magnetic moment, will precess at a frequency f (measured in hertz), that is proportional to the external field: . For this reason, values of γ/(2π), in units of hertz per tesla (Hz/T), are often quoted instead of γ. |
|
|
5. With DICOM which of the following is correct?
.A. Increasing bandwidth allows faster transmission B. Refresh rate less than 5% |
5. With DICOM which of the following is correct?
.A. Increasing bandwidth allows faster transmission B. Refresh rate less than 5% Answer: Probably A. |
|
|
6. If an object transmits 5% of light, what is OD?
A. 1 B. 1.3 C. 2 D. 3 E. 4 |
6. If an object transmits 5% of light, what is OD?
A. 1 B. 1.3 C. 2 D. 3 E. 4 Answer: B – OD = log (I/Io). Transmittance is Io/I. So OD = log (1/T). OD = log (1/0.05) OD = log 20 = 1.3 |
|
|
7. If you switch from parallel to pinhole collimation you increase
A. Resolution B. Contrast C. Radiation D. Sensitivity |
7. If you switch from parallel to pinhole collimation you increase
A. Resolution B. Contrast C. Radiation D. Sensitivity Answer: A |
|
|
8. What is the MTF of a system given that the four components of the system are 1.0, 0.5, 0.8, and 0.7?
A. 1.0 B. 0.50 C. 0.28 D. 0.14 |
8. What is the MTF of a system given that the four components of the system are 1.0, 0.5, 0.8, and 0.7?
A. 1.0 B. 0.50 C. 0.28 D. 0.14 Answer: C – Remember MTFs multiply. ODs add. |
|
|
. Most tissue damage caused by ionizing radiation is through
A. Electrons B. Neutrons C. Protons D. Pi Mesons |
9. Most tissue damage caused by ionizing radiation is through
A. Electrons B. Neutrons C. Protons D. Pi Mesons Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
10. If a 10 microcurie dose of an agent is needed at 1:30 PM for a test, what dose should be prepared at 8 AM if the half life is 110 minutes?
a. 150 b. 95 c. 80 d. 20 |
10. If a 10 microcurie dose of an agent is needed at 1:30 PM for a test, what dose should be prepared at 8 AM if the half life is 110 minutes?
a. 150 b. 95 c. 80 d. 20 Answer: C – Here is how you do this one: Decay contant (λ) = 0.693/110min = 0.0063 min--1 10mCi = N e-(0.0063/min)(330min) N = ~80mCi |
|
|
12. A pregnant technologist should be monitored/restricted to assure that the fetal dose is for the entire pregnancy
A. 5 mSv (500mrem) B. 50mSv (5000mrem) C. 0.5mSv (50mrem) D. 0.005mSv (5mrem) |
12. A pregnant technologist should be monitored/restricted to assure that the fetal dose is for the entire pregnancy
A. 5 mSv (500mrem) B. 50mSv (5000mrem) C. 0.5mSv (50mrem) D. 0.005mSv (5mrem) Answer: A – remember that the limit is 50mrem/mo as well. I remember the two numbers by thinking the pregnancy is really about 10 months (40wks), so: 50mrem/mo x 10 months = 500mrem/pregnancy |
|
|
13. Most of the energy deposited in biological tissue from diagnostic radiation is from:
A. protons B. the photoelectric effect C. electrons |
13. Most of the energy deposited in biological tissue from diagnostic radiation is from:
A. protons B. the photoelectric effect C. electrons Answer: C – The bottom line is most of the energy deposited in tissues is from electrons, and the photoelectric effect deposits all its energy locally. Compton scatter electrons also deposit energy locally. |
|
|
14. If an ultrasound pulse returns to the transducer 20 microseconds after being emitted, how deep in the tissue is the object? (velocity not provided)
A. 3.0 cm B. 1.5 cm C. 0.77 cm D. 7.7 cm E. 15 cm |
14. If an ultrasound pulse returns to the transducer 20 microseconds after being emitted, how deep in the tissue is the object? (velocity not provided)
A. 3.0 cm B. 1.5 cm C. 0.77 cm D. 7.7 cm E. 15 cm Answer: B – remember the simplified equation: Depth (cm) = 0.077 x time (microseconds) Depth (cm) = 0.077 x 20 microseconds = 1.5 cm |
|
|
15. A radiation POINT SOURCE is used to evaluate a SPECT machine with the collimator ON at a variety of angles. What function is being measured?
A. system dead time B. something about linear response at a variety of angles C. Center of Rotation D. Flood view E. Intrinsic resolution |
15. A radiation POINT SOURCE is used to evaluate a SPECT machine with the collimator ON at a variety of angles. What function is being measured?
A. system dead time B. something about linear response at a variety of angles C. Center of Rotation D. Flood view E. Intrinsic resolution Answer: C – Center of Rotation is tested with a point source at varying angles with the collimator. |
|
|
16. Narrowing the optical aperture of a fluoroscopy system is likely to do which of the following?
A. Increase exposure B. Reduce the field of view C. Decreases the f-number D. Decrease exposure |
16. Narrowing the optical aperture of a fluoroscopy system is likely to do which of the following?
A. Increase exposure B. Reduce the field of view C. Decreases the f-number D. Decrease exposure Answer: A – decreasing aperture lets less light through and the AEC bumps up radiation to make up the difference. The f-number is inversely related to the size of the whole. Narrowing the aperture will increase the f-number. |
|
|
17. In mammography, a source to image distance (SID) of 600 to 750 mm is used rather than the standard 1000 mm of other modalities why?
A. To reduce the heel effect B. To allow for a stronger beam and a shorter exposure C. To accommodate the focal spot of the gird D. To improve geometric resolution throughout the breast E. To decrease magnification |
17. In mammography, a source to image distance (SID) of 600 to 750 mm is used rather than the standard 1000 mm of other modalities why?
A. To reduce the heel effect B. To allow for a stronger beam and a shorter exposure C. To accommodate the focal spot of the gird D. To improve geometric resolution throughout the breast E. To decrease magnification Answer: B – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
18. Which factors are most important for reducing image blur?
The possible answers were multiple combinations of these terms: Screen thickness Emulsion thickness film-screen contact |
18. Which factors are most important for reducing image blur?
The possible answers were multiple combinations of these terms: Screen thickness Emulsion thickness film-screen contact Answer: I think they want screen thickness here. |
|
|
19. Which change will decrease the ratio of radiation entering to radiation exiting the patient?
A. decreasing xray tube filtration B. decreasing the half value layer C. decreasing the kVp D. increasing the source to image distance while maintaining the subject to image distance |
19. Which change will decrease the ratio of radiation entering to radiation exiting the patient?
A. decreasing xray tube filtration B. decreasing the half value layer C. decreasing the kVp D. increasing the source to image distance while maintaining the subject to image distance Answer: D – you need to understand this type of question because it can be asked in a number of ways. The other options will make the beam “softer” and more radiation enters the patient that does not contribute to the image. |
|
|
20. A single exposure of 1 Gy (whole body) is likely to cause:
a) skin erythema b) partial cataracts c) diarrhea in 50% of the population d) decreased absolute lymphocyte count |
20. A single exposure of 1 Gy (whole body) is likely to cause:
a) skin erythema b) partial cataracts c) diarrhea in 50% of the population d) decreased absolute lymphocyte count Answer: D |
|
|
21. Pertaining to the image receptor in mammography, which of the following is true:
a) the screen moves to decrease grid lines showing b) the speed is 50 c) there are two screens in each cassette d) digital radiography is never used. |
. Pertaining to the image receptor in mammography, which of the following is true:
a) the screen moves to decrease grid lines showing b) the speed is 50 c) there are two screens in each cassette d) digital radiography is never used. Answer: B – Mammography cassettes use only a single thin screen, so the speed will be less than regular radiography. The grid lines have nothing to do with the receptor. The grid itself moves, not the screen. Read each option carefully! |
|
|
22. The Gibb’s phenomenon in 3rd generation CT scanners refers to the dark appearance around the brain directly adjacent to dense bone. This is caused by:
a) beam hardening b) algorithm differences c) patient movement d) angry leprechaun |
22. The Gibb’s phenomenon in 3rd generation CT scanners refers to the dark appearance around the brain directly adjacent to dense bone. This is caused by:
a) beam hardening b) algorithm differences c) patient movement d) angry leprechaun Answer B -- be sure to read about Gibbs because they love to ask about it for some reason. It can be seen in CT or MRI and is due to algorithm difference (not enough PEG in MR, unsure about CT). |
|
|
23. Why is the radionuclide F-18 more difficult to use than I-131 or Tcm99?
a) F-18 is more volatile and poses an inhalation risk b) F-18 causes positron emission c) F-18 is flammable |
23. Why is the radionuclide F-18 more difficult to use than I-131 or Tcm99?
a) F-18 is more volatile and poses an inhalation risk b) F-18 causes positron emission c) F-18 is flammable d) F-18 releases gamma rays that are 511keV and therefore shielding is difficult Answer: B – Well, because positrons annihilate with electrons and lead to 511 keV photons compared to about 360 something for I -131 and 140 for Tc99. Note option D is wrong b/c the photons are NOT gamma rays but annihilation photons. Read each option carefully. |
|
|
24. Horizontal resolution on video is improved by
A. Increasing the number of scan lines B. Increasing refresh rate C. Increasing bandwidth D. Increasing the illuminence of the monitor |
24. Horizontal resolution on video is improved by
A. Increasing the number of scan lines B. Increasing refresh rate C. Increasing bandwidth D. Increasing the illuminence of the monitor Answer: C – The key word is horizontal. Horizontal resolution is limited by bandwidth; vertical resolution is limited by number of horizontal lines. Got it? Vote for Pedro. |
|
|
25. The linear attenuation coefficient (LAC) (of something?) is
a) the product of the PE, mass attenuation coefficient (MAC), LAC and Compton scatter b) the product of PE, Compton Scatter, and LAC c) the sum of LAC, PE, and Compton scatter d) only PE e) only Compton scatter |
25. The linear attenuation coefficient (LAC) (of something?) is
a) the product of the PE, mass attenuation coefficient (MAC), LAC and Compton scatter b) the product of PE, Compton Scatter, and LAC c) the sum of LAC, PE, and Compton scatter d) only PE e) only Compton scatter 25. The linear attenuation coefficient (LAC) (of something?) is a) the product of the PE, mass attenuation coefficient (MAC), LAC and Compton scatter b) the product of PE, Compton Scatter, and LAC c) the sum of LAC, PE, and Compton scatter d) only PE e) only Compton scatter Answer: C – all the possible interactions are added together to make the LAC. See Bushberg syllabus. Eat it, Huda! The linear attenuation coefficient is the sum of the individual linear attenua tion coefficients for each type of interaction: LAC= Rayieigh+ Photoelectric Effect + Compton Scatter + pair production |
|
|
When using a scintillation camera, spatial resolution is affected most by
a. collimator b. the crystal c. the photomultiplier tubes d. the ADC |
26. When using a scintillation camera, spatial resolution is affected most by
a. collimator b. the crystal c. the photomultiplier tubes d. the ADC Answer: A – the collimator resolution limits the system and is best at the collimator's surface. The intrinsic resolution (crystal) is not changed with increased distance. |
|
|
27. Recent analysis of data compiled from the affects of the atomic bomb in Japan have revealed that the likelihood of solid tumors and radiation dose has what relationship:
a. a linear relationship with a threshold dose of…. b. A linear relationship with a threshold dose of…. c. A linear quadratic relationship with no threshold d. A linear quadratic relationship with a threshold dose of… e. linear relationship with no threshold |
27. Recent analysis of data compiled from the affects of the atomic bomb in Japan have revealed that the likelihood of solid tumors and radiation dose has what relationship:
a. a linear relationship with a threshold dose of…. b. A linear relationship with a threshold dose of…. c. A linear quadratic relationship with no threshold d. A linear quadratic relationship with a threshold dose of… e. linear relationship with no threshold Answer: E |
|
|
28. Calculate the change in minification gain with a 1.25 inch output phosphor and a change from 9-inch mode to 4.5-inch mode.
a. 4x original b. 2x original c. ¼ original d. ½ original |
28. Calculate the change in minification gain with a 1.25 inch output phosphor and a change from 9-inch mode to 4.5-inch mode.
a. 4x original b. 2x original c. ¼ original d. ½ original Answer: C – Take the ratio of the input phosphor and square it. If you go from a larger screen to a smaller screen, make sure the bigger number is on the bottom (minification gain decreases) and visa versa if you go from smaller input to larger one. |
|
|
29. Chemical shift artifact in MRI results from
a) T1 effects b) T2 effects c) Resonance frequency d) Patient motion |
29. Chemical shift artifact in MRI results from
a) T1 effects b) T2 effects c) Resonance frequency d) Patient motion Answer: C – KNOW THIS. It is on every recall ever made. |
|
|
30. What intervention will most reduce image unsharpness caused by patient motion?
a. Nuclear medicine: Increase dose of radiopharmaceutical by 10% b. Radiography: Double mA and halve exposure time c. MR: Double the RF power (while keeping TR constant) d. US: Increase transducer frequency |
30. What intervention will most reduce image unsharpness caused by patient motion?
a. Nuclear medicine: Increase dose of radiopharmaceutical by 10% b. Radiography: Double mA and halve exposure time c. MR: Double the RF power (while keeping TR constant) d. US: Increase transducer frequency Answer: B |
|
|
. A well counter has a background count rate of 200 CPM. If a sample is placed in the counter for 2 minutes, how many counts will be 3 standard deviations above the mean?
A. 212 B. 242 C. 400 D. 460 E. 475 |
31. A well counter has a background count rate of 200 CPM. If a sample is placed in the counter for 2 minutes, how many counts will be 3 standard deviations above the mean?
A. 212 B. 242 C. 400 D. 460 E. 475 Answer: D – these statistics questions can be tricky. Hopefully there won't be more than 1 or 2 on the test. This one isn't that bad, just get the total number of counts (400) and take the square root to get the standard deviation (20). Then multiply the SD by 3, which gives you 60. Then add it to the total number of counts to get 460. |
|
|
32. A 60 keV photon is most likely to interact in soft tissue by:
A. Compton scatter B. Photoelectric effect C. Pair production D. Coherent scatter |
32. A 60 keV photon is most likely to interact in soft tissue by:
A. Compton scatter B. Photoelectric effect C. Pair production D. Coherent scatter Answer: A – below 36keV is Photoelectric effect, above is Compton scatter. |
|
|
33. Compared to an ultrasound transducer with focal zone, a transducer with four zones will have increased:
A. Axial resolution B. Lateral resolution C. Temporal resolution D. Contrast resolution |
33. Compared to an ultrasound transducer with focal zone, a transducer with four zones will have increased:
A. Axial resolution B. Lateral resolution C. Temporal resolution D. Contrast resolution Answer: B – four zones increases the length of the focal spot, and the lateral resolution is best at the focal spot (½ the beam diameter). Remember that axial resolution is independent of depth, and relies on the spatial pulse length (SPL). |
|
|
34. In computed radiography, a severely underexposed film will appear:
A. Too dark B. Too light C. Contrast enhanced D. Contrast deficient |
34. In computed radiography, a severely underexposed film will appear:
A. Too dark B. Too light C. Contrast enhanced D. Contrast deficient Answer: D – an underexposed film will have increased noise b/c the number of xray photons used to make the image will be decreased. Increasing the noise will decrease the contrast. The wide dynamic range will allow the film to be “windowed” to the correct OD (won't be too dark or too light). |
|
|
35. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding PET:
A. It uses electronic collimation B. Random coincidences can produce noise in clinical images C. Typical dose with F-18 FDG is between 0.5 and 1.0 rem D. The ideal positron energy is slightly above 1.02MeV |
35. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding PET:
A. It uses electronic collimation B. Random coincidences can produce noise in clinical images C. Typical dose with F-18 FDG is between 0.5 and 1.0 rem D. The ideal positron energy is slightly above 1.02MeV Answer: D – The energy of the annihilation photons add up to 1.02MeV, but their energy is a function of their all their mass turning into energy via Einstein's equation (E = mc2). If the positron energy was 1.02MeV, it would travel a far distance from the site of degradation and spatial resolution would be terrible. |
|
|
36. Increased collimation during fluoroscopy does not:
A. Decrease patient integral dose B. Reduce dose to the fluoroscopist C. Improve contrast resolution D. Improve spatial resolution |
36. Increased collimation during fluoroscopy does not:
A. Decrease patient integral dose B. Reduce dose to the fluoroscopist C. Improve contrast resolution D. Improve spatial resolution Answer: D – the integral dose is the total dose to the body and is given in joules. The integral dose is NOT corrected for volume or mass. Absorbed dose is given in Gy or rad and is corrected for mass (joules/kg). So, the integral dose will decrease, but the absorbed dose will be unchanged with collimation. The contrast will be improved due to lower scatter, but the spatial resolution is unchanged. |
|
|
37. A 99Mo generator is eluted at 6AM and 12noon. Which is true?
a. Tc activity is lower at 6am than 12noon b. Tc concentration is lower at 6am than 12noon c. Tc concentration is higher at 6am than 12noon d. The generator is in secular equilibrium at 12noon e. The generator is in transient equilibrium at 6am |
37. A 99Mo generator is eluted at 6AM and 12noon. Which is true?
a. Tc activity is lower at 6am than 12noon b. Tc concentration is lower at 6am than 12noon c. Tc concentration is higher at 6am than 12noon d. The generator is in secular equilibrium at 12noon e. The generator is in transient equilibrium at 6am Answer: C – the elution at 6am will be after 4 half-lives, and the elution at noon will be after only one half life. |
|
|
38. What’s the appropriate configuration for mammography?
Four diagrams shown: a. Cathode against chest wall b. Anode against chest wall c. Cathode near, but not on, chest wall d. Anode near, but not on, chest wall |
38. What’s the appropriate configuration for mammography?
Four diagrams shown: a. Cathode against chest wall b. Anode against chest wall c. Cathode near, but not on, chest wall d. Anode near, but not on, chest wall Answer: A – the beam configuration of mammography has the cathode over the chest wall and anode over the nipple. It is a half beam geometry. In other words the center of the beam is at the chest wall. The “other half” of the beam is filtered out. |
|
|
39. A patient received 200 mCi I-131 for treatment of thyroid cancer. What is the best way to determine exposure around the patient?
a. NaI uptake probe. b. Mobile scintillation camera c. Ionization chamber d. GM counter e. Dose calibrator |
39. A patient received 200 mCi I-131 for treatment of thyroid cancer. What is the best way to determine exposure around the patient?
a. NaI uptake probe. b. Mobile scintillation camera c. Ionization chamber d. GM counter e. Dose calibrator Answer: C – ionization chambers are good for measuring the gamma emission associated with I-131 (~339 keV). Ionization chambers are also good at finding the roentgen exposure, since roentgen is defined as ionizations (charge) in kg of air and ionization chambers are filled with air. So, if you see the word EXPOSURE, think IONIZATION CHAMBER!! |
|
|
40. 10 rad of any type of radiation is equal to what:
A. 0.1 R B. 0.2 Sv C. 0.1 Gy D. 0.1 mGy |
40. 10 rad of any type of radiation is equal to what:
A. 0.1 R B. 0.2 Sv C. 0.1 Gy D. 0.1 mGy Answer: C – remember that 100 rad = 1 Gy (and 100 rem = 1 Sv) |
|
|
Human lethal LD 50/60 equals:
A. 0.5 Gy B. 1.0 Gy C. 2.5 Gy D. 3.5 Gy |
41. Human lethal LD 50/60 equals:
A. 0.5 Gy B. 1.0 Gy C. 2.5 Gy D. 3.5 Gy Answer: D – I have also seen 3.0 Gy commonly quoted. |
|
|
42. When using a parallel collimator for nucs, moving the object closer to the collimator causes:
A. Magnification B. Inversion of image C. Improved spatial resolution D. Increased quantum mottle |
42. When using a parallel collimator for nucs, moving the object closer to the collimator causes:
A. Magnification B. Inversion of image C. Improved spatial resolution D. Increased quantum mottle Answer: C – parallel collimator does not cause magnification or inversion of image. The sensitivity of the parallel collimator is independent of distance (sort of counter intuitive, so be aware). The collimator, and therefore the system, spatial resolution is best at the surface of the collimator. |
|
|
43. Use of a medium energy collimator instead of a low energy collimator when imaging Tc99 causes:
A. Reduced sensitivity B. Reduced uniformity C. Reduced focal length D. Reduced intrinsic efficiency |
43. Use of a medium energy collimator instead of a low energy collimator when imaging Tc99 causes:
A. Reduced sensitivity B. Reduced uniformity C. Reduced focal length D. Reduced intrinsic efficiency E. Increased image distortion Answer: A – Would also cause increase spatial resolution. |
|
|
44. What do SPECT and CT share in common:
A. Both use filtered backprojection for image formation B. Both rely on energy selection to filter out scattered photons C. Both rely on a revolving external source of photons D. Both rely on attenuation of beam for contrast differences |
44. What do SPECT and CT share in common:
A. Both use filtered backprojection for image formation B. Both rely on energy selection to filter out scattered photons C. Both rely on a revolving external source of photons D. Both rely on attenuation of beam for contrast differences E. Both have allowances for beam hardening Answer: A |
|
|
45. When using a well counter to determine activity of sample, make allowance for all of these EXCEPT:
A. Geometric efficiency B. Intrinsic efficiency C. Sample volume D. Temperature |
45. When using a well counter to determine activity of sample, make allowance for all of these EXCEPT:
A. Geometric efficiency B. Intrinsic efficiency C. Sample volume D. Temperature Answer: D |
|
|
46. The processing so that a vessel of uniform caliber has uniform contrast throughout the image despite differing soft tissue contrast is referred to as:
A. Frame integration B. K-shell subtraction C. Logarithmic integration D. Window setting E. Dual energy absorption |
46. The processing so that a vessel of uniform caliber has uniform contrast throughout the image despite differing soft tissue contrast is referred to as:
A. Frame integration B. K-shell subtraction C. Logarithmic integration D. Window setting E. Dual energy absorption Answer: C – not sure where they got this question. I hope that is the answer! |
|
|
47. Daily checks required in mamms include:
A. Compression device B. Screen-film contact C. Processor density difference D. Focal spot |
47. Daily checks required in mamms include:
A. Compression device B. Screen-film contact C. Processor density difference D. Focal spot Answer: C – See chart below for mammography quality control: Test Time Processor Density Daily Base + Fog Daily Phantom OD Weekly Image quality Weekly Repeat Analysis Quarterly Reproducibility Quarterly Darkroom Fog Semiannually Compression Semiannually Screen-film Contact Semiannually |
|
|
48. To test the film processor, run through a film which has been exposed to a known degree by a:
A. Densitometer B. Sensitometer C. Photometer |
48. To test the film processor, run through a film which has been exposed to a known degree by a:
A. Densitometer B. Sensitometer C. Photometer Answer: B – Sensitometer exposes it and a densitometer reads it. This comes up a lot on recalls. Just memorize it. Think Densitometer reads optical Density |
|
|
49. The time gain compensation (TGC) is used for which purpose?
A. Compensate for attenuation loss with depth B. Compensate for drift of overall gain C. Correct for the appearance of grating lobes D. Compensate for drift of line voltage E. Correct for pulse duration |
49. The time gain compensation (TGC) is used for which purpose?
A. Compensate for attenuation loss with depth B. Compensate for drift of overall gain C. Correct for the appearance of grating lobes D. Compensate for drift of line voltage E. Correct for pulse duration Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
50. What portion of the cell cycle is most variable in length?
A. S B. M C. G1 D. G2 |
50. What portion of the cell cycle is most variable in length?
A. S B. M C. G1 D. G2 Answer: C – The cell stays in G1 until it is about to divide. Some cells (neurons) stay in G1 your entire life. Also, remember what part of the cell cycle is most radiosensitive? M (the chromosomes are tightly packed so a hit is more likely to be lethal). What about the most radioresistant? S (there are tons of repair enzymes floating around to fix any damage). What about G1 vs G2? G1 is more radioresistant than G2 because there is only one copy of the genome in G1 (hasn't gone through S yet), so there is less chance of radiation hitting the chromosomes. |
|
|
51. Which of the following does not contribute to patient dose?
A. Photoelectric effect B. Compton Scatter C. Free radicals D. Coherent scatter |
51. Which of the following does not contribute to patient dose?
A. Photoelectric effect B. Compton Scatter C. Free radicals D. Coherent scatter Answer: D – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
52. The amount of noise in digital subtraction angiography is usually:
A. greater in the mask than in the subtracted image B. greater in the subtracted image than in the mask C. greater in the larger structures than in the smaller structures D. decreased by increasing the time interval between the mask E. unaffected by the changes in kVp and mAs |
52. The amount of noise in digital subtraction angiography is usually:
A. greater in the mask than in the subtracted image B. greater in the subtracted image than in the mask C. greater in the larger structures than in the smaller structures D. decreased by increasing the time interval between the mask E. unaffected by the changes in kVp and mAs Answer: B – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
53. Why does the number of counts have to be greater in SPECT than in planar scintigraphic imaging?
A. resolving time is greater B. beam hardening is greater C. increased error propagation through the reconstruction D. detection efficiency is less E. photopeak window is smaller |
53. Why does the number of counts have to be greater in SPECT than in planar scintigraphic imaging?
A. resolving time is greater B. beam hardening is greater C. increased error propagation through the reconstruction D. detection efficiency is less E. photopeak window is smaller Answer: C – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
54. The attenuation of photons through soft tissue is best described by what equation?
A. 1-e-t A. et B. e-t |
54. The attenuation of photons through soft tissue is best described by what equation?
A. 1-e-t A. et B. e-t Answer: A – Know this! Easy to mix this up, but it comes up on a lot of old recalls. e-t is the probability of photon transmission, so 1-e-t is the probability of photon attenuation. |
|
|
55. Which of the following do deterministic and stochastic radiation effects have in common?
A. A linear non-threshold curve B. Increased risk of cancer C. No sensation at the time of exposure D. Increased risk of cataracts |
55. Which of the following do deterministic and stochastic radiation effects have in common?
A. A linear non-threshold curve B. Increased risk of cancer C. No sensation at the time of exposure D. Increased risk of cataracts Answer: C – deterministic effects have a threshold after which the severity of the process is worse with increasing dose. Deterministic events involve death of multiple cells (examples include cataracts and skin erythema). Stochastic effects have no threshold but the probability of the effect is increased with increased dose. Stochastic effects involve a few cells (example include cancer and genetic defects). |
|
|
56. Which of the following about the Linear Attenuation Coefficient (LAC) is FALSE?
A. Directly proportional to the mass attenuation coefficient (MAC). B. Directly proportional to the half-value layer (HVL) C. Increases with atomic number D. Can be calculated if the HVL is known. |
56. Which of the following about the Linear Attenuation Coefficient (LAC) is FALSE?
A. Directly proportional to the mass attenuation coefficient (MAC). B. Directly proportional to the half-value layer (HVL) C. Increases with atomic number D. Can be calculated if the HVL is known. Answer: B – the higher the HVL, the lower the LAC. |
|
|
57. What is the purpose of the ramp filter in CT image reconstruction
|
57. What is the purpose of the ramp filter in CT image reconstruction
Removes star artifact and edge enhancement. I would look this up. |
|
|
58. Positron decay of F (with mass number 18, atomic number 9) is?
A. O (mass number 18, atomic number 8) B. O (mass number 18, atomic number 9) C. F (mass number 19, atomic number 8) D. Ne (mass number 18, atomic number 8) |
58. Positron decay of F (with mass number 18, atomic number 9) is?
A. O (mass number 18, atomic number 8) B. O (mass number 18, atomic number 9) C. F (mass number 19, atomic number 8) D. Ne (mass number 18, atomic number 8) Answer: A – Mass number stays the same but atomic number goes down. A proton turns into a neutron b/c you lose a positive charge. Positron decay is common in accelerator produced radioisotopes. |
|
|
59. The greatest amount of signal loss in fast spin echo imaging is the result of
A. Magnetic field inhomogeneities B. T1 relaxation C. T2 relaxation D. Repeated use of phase encoding gradient |
59. The greatest amount of signal loss in fast spin echo imaging is the result of
A. Magnetic field inhomogeneities B. T1 relaxation C. T2 relaxation D. Repeated use of phase encoding gradient Answer: C – the magnetic field inhomogeneities are canceled out b/c the multiple 180 pulses, and FSE is the sequence least affected by susceptibility artifacts. T1 relaxation causes the loss of signal between the 90 degree pulses. I'm not sure about option D. |
|
|
60. An adult is given a dose of 20 mCi of I 131 with a thyroid weight of 40g. His uptake was 20% and the dose to the thyroid was 30 centiGy. If a child is given 10 mCi with a thyroid weight of 10g and his uptake was 40%, what was his thyroid dose?
A. 20 B. 30 C. 40 D. 60 E. 120 |
60. An adult is given a dose of 20 mCi of I 131 with a thyroid weight of 40g. His uptake was 20% and the dose to the thyroid was 30 centiGy. If a child is given 10 mCi with a thyroid weight of 10g and his uptake was 40%, what was his thyroid dose?
A. 20 B. 30 C. 40 D. 60 E. 120 Answer: E – take the adult dose (30 cGy) and divide by 2 (dose), multiply by 4 (thyroid weight), and muliply by 2 (uptake). 30 cGy x 0.5 x 2 x 4 = 120 cGy. |
|
|
61. The mAs for CT of a child can be decreased from the mAs usually used for an adult because:
a. The patient attenuation is less b. there is only a 180 degree rotation comparted to 360 degree in adults c. filtered backprojection is not used in pediatic Cts d. the chance of tissue heating is greater in children than adults |
61. The mAs for CT of a child can be decreased from the mAs usually used for an adult because:
a. The patient attenuation is less b. there is only a 180 degree rotation comparted to 360 degree in adults c. filtered backprojection is not used in pediatic Cts d. the chance of tissue heating is greater in children than adults Answer: A – I made up Options B-D b/c the original recall only had one option (A). They are obviously wrong, crazy things to say about CT. |
|
|
62. The dose to a radiologist from scatter radiation during fluoroscopy will be decreased by the greatest amount by performing which of the following:
a. wearing a wrap-around lead apron of 0.3mm b. standing behind a clear lead-equivalent shield of 0.5mm c. decreasing fluoro time by 3 d. increasing distance by 2 |
62. The dose to a radiologist from scatter radiation during fluoroscopy will be decreased by the greatest amount by performing which of the following:
a. wearing a wrap-around lead apron of 0.3mm b. standing behind a clear lead-equivalent shield of 0.5mm c. decreasing fluoro time by 3 d. increasing distance by 2 Answer: B |
|
|
63. For bone densitometry the value that describes the standard deviation of relative bone densitometry above and below that of a young adult (thirty years-old) is:
a. T value b. Z value c. BMD value d. QCT value |
63. For bone densitometry the value that describes the standard deviation of relative bone densitometry above and below that of a young adult (thirty years-old) is:
a. T value b. Z value c. BMD value d. QCT value Answer: A – Z score is the age matched control. For T-score think Thirty year old. |
|
|
64. What is the sensitivity of a test (chest radiography) for lung cancer in which 2% of patients have lung cancer. 90% of those patients with lung cancer will have a positive test and 5% of patients with lung cancer will have a negative test.
a. 95% b. 98% c. 5% d. 2% e. 93% |
64. What is the sensitivity of a test (chest radiography) for lung cancer in which 2% of patients have lung cancer. 90% of those patients with lung cancer will have a positive test and 5% of patients with lung cancer will have a negative test.
a. 95% b. 98% c. 5% d. 2% e. 93% Answer: A – Sensitivity = TP/(TP+FN) 90/95 = 94.7 I think the question is wrong. |
|
|
65. What study does not expose the patient to electromagnetic radiation?
a. MRI b. Fluroscopy c. CT d. Plain radiography e. Ultrasound |
65. What study does not expose the patient to electromagnetic radiation?
a. MRI b. Fluroscopy c. CT d. Plain radiography e. Ultrasound Answer: E |
|
|
66. A patient is most likely to have intellectual abnormalities if they are exposed to 15 rems in utero at how many weeks of gestation?
a. 1 week b. 3 weeks c. 6 weeks d. 9 weeks e. 18 weeks |
66. A patient is most likely to have intellectual abnormalities if they are exposed to 15 rems in utero at how many weeks of gestation?
a. 1 week b. 3 weeks c. 6 weeks d. 9 weeks e. 18 weeks Answer: D At 10 – 15 weeks 40% per Sv and at 15 – 25 weeks 10% per Sv. |
|
|
67. If a large obese patient develops a pruritic rash that is 7 x 10 cm in size on the right mid back 2 weeks after undergoing 5 hours of cardiac fluoroscopy that had a window size of 16 x 16 cm what is the cause of his rash?
a. electric burn from wrong placement of a defibrillator pad b. allergic reaction to adhesive on defibrillator pad c. radiation injury d. electrical burn from broken defibrillator wire e. Fat Fever |
67. If a large obese patient develops a pruritic rash that is 7 x 10 cm in size on the right mid back 2 weeks after undergoing 5 hours of cardiac fluoroscopy that had a window size of 16 x 16 cm what is the cause of his rash?
a. electric burn from wrong placement of a defibrillator pad b. allergic reaction to adhesive on defibrillator pad c. radiation injury d. electrical burn from broken defibrillator wire e. Fat Fever Answer: C |
|
|
68. Which of the following models are used in the development of radiation protection protocols:
a. Linear threshold b. Linear nonthreshold c. Quadratic threshold d. Quadratic nonthreshold e. Exponential threshold |
68. Which of the following models are used in the development of radiation protection protocols:
a. Linear threshold b. Linear nonthreshold c. Quadratic threshold d. Quadratic nonthreshold e. Exponential threshold Answer: B – overestimates risk, so it is used. |
|
|
69. A person sustains an exposure of 600 to 1000millirems to his hands. Which of the following is the most likely result:
a. skin breakdown within 2 weeks b. immediate blistering of the skin c. nothing d. erythma |
69. A person sustains an exposure of 600 to 1000millirems to his hands. Which of the following is the most likely result:
a. skin breakdown within 2 weeks b. immediate blistering of the skin c. nothing d. erythma Answer: C – the threshold for erythema is 2Gy. This patient only received 1 rem. |
|
|
70. Interventional radiologist receives total of 60 rem over 20 year period
a. exceeds 1993 NCRP guidelines b. within 1993 ICRP guidelines c. likely to cause cataracts d. could cause radiation-induced hair loss e. he will most certainly die soon |
70. Interventional radiologist receives total of 60 rem over 20 year period
a. exceeds 1993 NCRP guidelines b. within 1993 ICRP guidelines c. likely to cause cataracts d. could cause radiation-induced hair loss e. he will most certainly die soon Answer: B – this is probably the right answer, but it is hard to say for sure without know the radiologist's age. There is a limit of 1 rem/yr total with no more than 5 rem per any one year. |
|
|
71. For a square 10 inch by 10 inch image is digitized with a goal of 5 lp/mm, how many pixels will the image require?
a) 300,000 b) 6,450,000 c) 3.225.000 d) 1,000,000 e) 9,000,000 |
71. For a square 10 inch by 10 inch image is digitized with a goal of 5 lp/mm, how many pixels will the image require?
a) 300,000 b) 6,450,000 c) 3.225.000 d) 1,000,000 e) 9,000,000 Answer: B – This question is on multiple old tests, so know how to do it. Here is how: FOV = 10 inches * 2.5cm/inch * 10mm/cm = 250mm # = 250mm * 5lp/mm = 1250lp # pixels in FOV = 1250lp * 2lp/pixel = 2500 pixels Total # pixels = 2500 * 2500 = 6,250,000 pixels NOTE: the actual conversion factor for inches to cm is 2.54, which gives the answer of 6,450,000 pixels. The estimation above will get you close enough for this test though. |
|
|
72. Non contrast tissue harmonic imaging
a. used to reduce receiving clutter at the transducer b. increasing penetration c. increase frequency gain d. uses the periphery of the u/s beam |
72. Non contrast tissue harmonic imaging
a. used to reduce receiving clutter at the transducer b. increasing penetration c. increase frequency gain d. uses the periphery of the u/s beam Answer: A |
|
|
73. What device can be used to directly measure radiation exposure?
A. Ionization chamber B. TLD C. Geiger counter D. Well counter |
73. What device can be used to directly measure radiation exposure?
A. Ionization chamber B. TLD C. Geiger counter D. Well counter Answer: A – the unit of exposure is the Roentgen (charge in air). Ionization chambers are filled with air and are ideal for measuring R/hr. If you see the word EXPOSURE, think IONIZATION CHAMBER! If you see the word CONTAMINATION think GM COUNTER! GM counters are gas filled, but they are not ionization chambers b/c they operate at a higher potential voltage (the GM region). If you see the words WIPE TEST think NaI WELL COUNTER! |
|
|
74. Of studies of persons in Nagasaki, which organ system was most frequently affected by in utero radiation exposure?
A. Skeletal B. CNS C. GU D. GI |
74. Of studies of persons in Nagasaki, which organ system was most frequently affected by in utero radiation exposure?
A. Skeletal B. CNS C. GU D. GI Answer: B – danged old baby brains. |
|
|
75. In the following diagram, dose area product (DAP) at the detector measures 8000 cG*cm2 at 25 cm away from the x-ray source. The table is 50 cm away from the source, ignore absorption of x-rays by the table. At the II, 100 cm away from the x-ray source, the cross sectional area is 400cm2. What is the DAP in cG*cm2 at the level of the table?
A - 2000 B - 4000 C - 6000 D - 8000 E – 16000 |
I'll get back to this one.
|
|
|
76. In 2D Fourier of MRI, phase encoding gradient is
A. Applied while RF signal is turned on B. Applied multiple times during a single TR C. Is used to create each row in k-space D. Is used to create each column in the k-space |
76. In 2D Fourier of MRI, phase encoding gradient is
A. Applied while RF signal is turned on B. Applied multiple times during a single TR C. Is used to create each row in k-space D. Is used to create each column in the k-space Answer: C – In k-space, the PEG is the y-axis, and FEG is the x-axis. So, the PEG places the signal in a row (y value), and FEG places the signal in a column (x value). |
|
|
77. Which of the following during fluoroscopy will increase patient dose?
A. Opening the aperture wider B. Adding copper filtration C. Using occasional fluoro rather than continuous fluoro D. Magnification views |
77. Which of the following during fluoroscopy will increase patient dose?
A. Opening the aperture wider B. Adding copper filtration C. Using occasional fluoro rather than continuous fluoro D. Magnification views Answer: D – magnification views decrease the minification gain (less surface of the input phosphor projects onto the output phosphor). So the AEC sees less light and calls for more radiation. |
|
|
78. What is this device used for?
Pretty picture is supposed to show a monitor with multiple peaks and a detector that looks like a cylinder on a counter top – this is the best I could find. |
78. What is this device used for?
Pretty picture is supposed to show a monitor with multiple peaks and a detector that looks like a cylinder on a counter top – this is the best I could find. A. measuring activities of radiopharmaceuticals B. for wipe test measurements C. measuring decay of radioactive waste about to be thrown away D. measuring in vivo I - 131 Answer: B – Go see this stuff in nucs because these questions show up! NOTE: a dose calibrator, which is an ionization chamber (answer A) does not have a screen. NaI well counter, used for wipe tests, is a scintillation detector and has a screen. NaI well counter is a spectrometer, but a dose calibrator is not. A spectrometer can tell the difference in the type or energy of the radiation. |
|
|
79. If one wants to be 95% confident that the measured counts will lie within 2% of the average counts from a sample, how many counts does one need to acquire?
a. 4,000 b. 10,000 c. 16,000 d. 25,000 e. 100,000 |
79. If one wants to be 95% confident that the measured counts will lie within 2% of the average counts from a sample, how many counts does one need to acquire?
a. 4,000 b. 10,000 c. 16,000 d. 25,000 e. 100,000 Answer : B – Seems like a hard question, but here is how you do it: First, to find the percent standard deviation, take the square root of the number and divide it by the number. Since the standard deviation is the square root of the number (the numerator), and this question is asking for 2SD (95% CI), multiply this equation times 2. 2√N/N = 0.02 2/√N = 0.02 √N = 2/0.02 = 100 N = 10,000 NOTE: There has been some question as to how the equation 2√N/N = %SD can be simplified to 1/√N = %SD. Well, it is a little math trick. Remember that: (√N x √N) = N So, you can substitute (√N x √N) for the denominator in the original equation: 2(√N)/(√N x √N) = %SD Then you can do simple algebra “canceling out” of √N in the denominator and numerator to get the final equation: 2/√N = %SD |
|
|
80. A diagram in this question illustrates an ultrasound probe pointing 90 degrees towards a vessel on Doppler. Frequency of the probe is 5 MHz. The flow of blood in the vessel is 21 cm/sec. What is the measured blood velocity on Doppler?
a. 0 cm/sec b. 21 cm/sec c. 42 cm/sec d. 63 cm/sec |
80. A diagram in this question illustrates an ultrasound probe pointing 90 degrees towards a vessel on Doppler. Frequency of the probe is 5 MHz. The flow of blood in the vessel is 21 cm/sec. What is the measured blood velocity on Doppler?
a. 0 cm/sec b. 21 cm/sec c. 42 cm/sec d. 63 cm/sec Answer : A – the cos 90 = 0, so you can't get Doppler flow at 90 degrees. |
|
|
81. In MR image reconstruction, what is true among the following statements?
a. Filtered back projection is used for image reconstruction. b. 2-D Fourier transformation to transform K-space spatial information onto image c. Half Fourier transformation decreases sampling time by one half d. Collimators are used to decrease noise. |
81. In MR image reconstruction, what is true among the following statements?
a. Filtered back projection is used for image reconstruction. b. 2-D Fourier transformation to transform K-space spatial information onto image c. Half Fourier transformation decreases sampling time by one half d. Collimators are used to decrease noise. Answer : B |
|
|
82. A 4-inch long object is placed on the fluoroscopy table. The image intensifier (II) is 12 inches above the table and the image on the II is measured to be 6 inches long. How far away is the X-ray source underneath the table?
a. 6 inches b. 12 inches c. 24 inches d. 36 inches e. 48 inches |
82. A 4-inch long object is placed on the fluoroscopy table. The image intensifier (II) is 12 inches above the table and the image on the II is measured to be 6 inches long. How far away is the X-ray source underneath the table?
a. 6 inches b. 12 inches c. 24 inches d. 36 inches e. 48 inches Answer : C – learn to draw triangles because evidently the ACR thinks it is very, very important for radiologist to be able to draw similar triangles! I knew 9th grade trigonometry would come back to haunt me... Then solve for x: x/4 = (12 + x)/ 6 6x = 48 + 4x 2x = 48 x = 24 cm |
|
|
83. A quality control film developed from a film processor after exposure demonstrates higher than normal optical density throughout the film. Which of the following could be the cause?
a. Lower than usual developing temperature. b. Higher than usual rate of developer replenishment. c. Higher than usual fixing temperature. d. Higher than usual fixing agent replenishment. |
83. A quality control film developed from a film processor after exposure demonstrates higher than normal optical density throughout the film. Which of the following could be the cause?
a. Lower than usual developing temperature. b. Higher than usual rate of developer replenishment. c. Higher than usual fixing temperature. d. Higher than usual fixing agent replenishment. Answer: I don't have any idea. Note: Higher developing temperature or longer developing time were not choices. |
|
|
83. A quality control film developed from a film processor after exposure demonstrates higher than normal optical density throughout the film. Which of the following could be the cause?
a. Lower than usual developing temperature. b. Higher than usual rate of developer replenishment. c. Higher than usual fixing temperature. d. Higher than usual fixing agent replenishment. |
83. A quality control film developed from a film processor after exposure demonstrates higher than normal optical density throughout the film. Which of the following could be the cause?
a. Lower than usual developing temperature. b. Higher than usual rate of developer replenishment. c. Higher than usual fixing temperature. d. Higher than usual fixing agent replenishment. Answer: I don't have any idea. Note: Higher developing temperature or longer developing time were not choices. -Film speed, contrast, and base and fog levels are all affected by developer chem- istry and temperature. -Increasing the developer temperature or time increases the film contrast and den- sity and also fog. - The best possible answer would be developer replenishment - Activity of the developer: under replenishment will lower the Speed Index - Over replenishment will result in increased Speed Index. - Contaminated Developer: If fixer gets into the developer, the developer will be contaminated. |
|
|
84. Quantum mottle in fluoroscopy is primarily determined by which of the following?
a. X-rays exiting the patient b. X-rays absorbed by the input phosphor c. Photons emitting from the input phosphor d. Photons absorbed by the output phosphor e. Photons exiting the output phosphor |
84. Quantum mottle in fluoroscopy is primarily determined by which of the following?
a. X-rays exiting the patient b. X-rays absorbed by the input phosphor c. Photons emitting from the input phosphor d. Photons absorbed by the output phosphor e. Photons exiting the output phosphor Answer : B – Quantum mottle is determined by the number of photons absorbed by the input phosphor. This is confusing because Nichholoff states that the absorption efficiency does not affect QM. However, both are true statements b/c what matters is the NUMBER of photons absorbed, not the percent. The more efficient (faster) system will call for less radiation via the AEC, but since a higher fraction of the photons are absorbed, the number of photons absorbed (and the quantum mottle) will be unchanged. Got it? This exact question is on multiple tests, so see those explanations as well if you are still confused. |
|
|
85. Which of the following interactions of photons does not deposit energy in a patient:
A. Compton scatter B. Photoelectric effect C. Coherent scatter D. Pair production E. Positron emmision |
85. Which of the following interactions of photons does not deposit energy in a patient:
A. Compton scatter B. Photoelectric effect C. Coherent scatter D. Pair production E. Positron emmision Answer: C – on multiple old tests. |
|
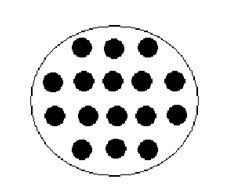
86. A Tc-99m flood source is placed in front of a gamma camera. What is the most likely cause of the poor image?
A. Complete decoupling of the scintillator and the PMT’s B. Off peak imaging C. Broken scintillator D. All of the PMT’s are broken |
86. A Tc-99m flood source is placed in front of a gamma camera. What is the most likely cause of the poor image?
A. Complete decoupling of the scintillator and the PMT’s B. Off peak imaging C. Broken scintillator D. All of the PMT’s are broken Answer: B – it is highly unlikely that all the PMTs are broken. |
|
|
87. Which one of the following does NOT decrease radiation dose on CT in children:
A. Increase table increment on axial sections B. Decrease pitch on a helical CT C. Skip non-contrast portion of the examination D. Decrease mAs E. Optimize tube output based on patient’s size |
87. Which one of the following does NOT decrease radiation dose on CT in children:
A. Increase table increment on axial sections B. Decrease pitch on a helical CT C. Skip non-contrast portion of the examination D. Decrease mAs E. Optimize tube output based on patient’s size Answer: B – all the other options decrease radiation dose. Decreasing pitch will cause a greater overlap of tissue and more radiation dose. |
|
|
88. As a radiologist in nuclear medicine, which of the following radiopharmaceuticals would you use to minimize absorption dose in the patient:
A. Agent with short decay constant B. Agent with long half-life C. Emitting corpuscular radiation less than 100 keV D. Emitting gamma ray between 100 and 300 keV |
88. As a radiologist in nuclear medicine, which of the following radiopharmaceuticals would you use to minimize absorption dose in the patient:
A. Agent with short decay constant B. Agent with long half-life C. Emitting corpuscular radiation less than 100 keV D. Emitting gamma ray between 100 and 300 keV Answer: D – Answers A and B say the same thing. C would cause too much local radiation deposition. |
|
|
89. Which of the following is correct regarding the disease and test
Tested positive Tested negative Disease positive 90 10 Disease negative 90 710 A. The positive predictive value is 50% B. The sensitivity of the examination is 90/180 C. The specificity of the examination is 50% D. The false negative fraction is 10/720 |

89. Which of the following is correct regarding the disease and test
Tested positive Tested negative Disease positive 90 10 Disease negative 90 710 A. The positive predictive value is 50% B. The sensitivity of the examination is 90/180 C. The specificity of the examination is 50% D. The false negative fraction is 10/720 Answer: A – get these ideas straight in you head b/c there is always 1 question on each test, and it should be easy points. |
|
|
. Background count rate of 200cpm for 2 minutes, what is the total count 3 standard deviation above the background count:
A. 200 B. 220 C. 400 D. 440 E. 460 |
90. Background count rate of 200cpm for 2 minutes, what is the total count 3 standard deviation above the background count:
A. 200 B. 220 C. 400 D. 440 E. 460 Answer: E – This is the exact same question as #31. |
|
|
91. Which of the following is not a benefit of breast compression:
A. increase sharpness B. decrease average glandular dose C. decrease quantum mottle D. increase contrast |
91. Which of the following is not a benefit of breast compression:
A. increase sharpness B. decrease average glandular dose C. decrease quantum mottle D. increase contrast Answer: C – anything that lowers the dose (as in this case compression) will increase quantum mottle. |
|
|
92. Microcephaly induced by 150 rem radiation:
A. none seen at this dose B. most likely to occur 18th -21st week C. may not be related with mental retardation D. secondary to defective cranial bone development |

Answer: C – huh, didn't know that. Fun cocktail party factoid... Here is a slide summerizing mental retardation and interuterine exposure:
|
|
|
93. Radiation dose of 60-100 rad will have what effect on the skin:
A. no effect B. erythma C. immediate blister D. skin necrosis within 2 week |
93. Radiation dose of 60-100 rad will have what effect on the skin:
A. no effect B. erythma C. immediate blister D. skin necrosis within 2 week Answer A – you need at least 2 Gy to cause erythema. The other options require more than 2 Gy |
|
|
94. A question about Gibb artifact
|
Ringing artifact also Imown as the Gibbs phenomenon occurs near sharp bound
aries and high-contrast transitions in the image, and appears as multiple, regularly spaced parallel bands of alternating bright and dark signal that slowly fades with dis tance. ‘l’he cause is the insufficient sampling of high frequencies inherent at sharp discontinuities in the signal. Images of objects can be reconstructed from a sum mation of sinusoidal waveforms of specific amplitudes and frequencies, as shown in Fig. 1 5-37A for a simple rectangular object. In the figure, the summation of fre quency harmonics, each with a particular amplitude and phase, approximates the distribution of the object, but initially does very poorly, particularly at the sharp edges. As the number of higher frequency harmonics increase, a better estimate is achieved, although an infinite number of frequencies are theoretically necessary to reconstruct the sharp edge perfectly. In the MR acquisition, the number of fre quency samples is determined by the number of pixels frequency, k, or phase, k, increments across the k-space matrix. For 256 pixels, 1 28 discrete frequencies are depicted, and for 128 pixels, 64 discrete frequencies are specified the k-space matrix is symmetric in quadrants and duplicated about irs center. A lack of high- frequency signals causes the "ringing" at sharp transitions described as a diminish ing hyper- and hypointense signal oscillation from the transition. Ringing artifacts are rhus more likely for smaller digital matrix sixes Fig. 15-37C, 256 versus 128 matrix. Ringing artifact commonly occurs at skull/brain interfaces, where there is a large transition in signal amplitude. |
|
|
95. What artifact occurs in the frequency encoding direction?
A. chemical shift B. motion C. magnetic susceptibility D. Gibbs artifact E. Reach around |
95. What artifact occurs in the frequency encoding direction?
A. chemical shift B. motion C. magnetic susceptibility D. Gibbs artifact E. Reach around Answer: A – fat and water precess at different frequencies, so this artifact shows up in the frequency encoding direction. On every single set of recalls. |
|
|
96. In MRI, if TR 2000, what is the effect of increasing TE from 20 to 80:
A. increase T1 weighting B. increase T2 weighting C. increase proton density weighting D. increase SNR |
96. In MRI, if TR 2000, what is the effect of increasing TE from 20 to 80:
A. increase T1 weighting B. increase T2 weighting C. increase proton density weighting D. increase SNR Answer: B – increasing TE will increase T2 but less signal is obtained, so the SNR decreases. |

