![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
173 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
1. acoustic shadowing distal to bone is due to:
a. increased absorption of sound waves by the bone b. increased transmission c. refraction d. decreased velocity through bone |
1. acoustic shadowing distal to bone is due to:
a. increased absorption of sound waves by the bone b. increased transmission c. refraction d. decreased velocity through bone Answer: A – bone is the classic example of a substance the absorbs sound waves. Air (the lung) is the classic example of a substance that reflects sound waves. |
|
|
2. spin echo sequence in MR
a. 90 followed by 180 degree pulse b. 180 followed by 90 c. 90 followed by 90 d. 90 followed by 180, followed by 180, followed by 180, followed by 180 |
2. spin echo sequence in MR
a. 90 followed by 180 degree pulse b. 180 followed by 90 c. 90 followed by 90 d. 90 followed by 180, followed by 180, followed by 180, followed by 180 Answer: A – Option B describes inversion recovery and option D describes FSE. Option C describes a drunk tech or leprechaun or both. |
|
|
3. Echoplanar sequence is used for
a. increased spatial resolution b. Increase contrast c. Increased SNR d. Very fast less than 100ms |
3. Echoplanar sequence is used for
a. increased spatial resolution b. Increase contrast c. Increased SNR d. Very fast less than 100ms Answer D – just remember that when a patient is moving, the tech does those fuzzy T2 looking images that say EPI on them (for Echo Planar Imaging). |
|
|
4. If the fractional standard deviation is 1% at count rate 50cps what is fractional standard deviation if count rate is increased to 100cps.
a. 2% b. 1% c. 0.1% d. 0.5% |
4. If the fractional standard deviation is 1% at count rate 50cps what is fractional standard deviation if count rate is increased to 100cps.
a. 2% b. 1% c. 0.1% d. 0.5% Answer: C – another statistics question. The fractional SD is 1/√N. N is the count rate times the time. 1/√N = 0.01 √N = 1/0.01 = 100 N = 10,000 If you double the count rate, then you should double N. So plug 2N into the equation (Fractional SD = 1/√N) Fractional SD = 1/√20,000 = 0.001 |
|
|
5. What is the minimal resolution in line pair/mm allowed if the line pair device is placed 4.5 cm on the table.
a. 11 to 20 b. 21 to23 c. 30-34 d. 40-45 |
5. What is the minimal resolution in line pair/mm allowed if the line pair device is placed 4.5 cm on the table.
a. 11 to 20 b. 21 to23 c. 30-34 d. 40-45 Answer: I'm not sure about this one either. Seems like some info is missing. The original recalls say the answer is A, but who knows... |
|
|
6. In DSA what is the post-processing method by which one can reduce the movement artifact (patient swallowed during carotid angio)
a. increasing line pair b. change the mask image c. alter video display |
6. In DSA what is the post-processing method by which one can reduce the movement artifact (patient swallowed during carotid angio)
a. increasing line pair b. change the mask image c. alter video display Answer: B – on multiple old tests. |
|
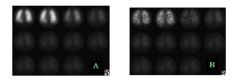
7. What is the cause for the image quality of B compared to A?
a. B has less counts than A b. A has a lower sensitivity collimator than B c. B has less quantum mottle than A d. Artifacts in B is from movement. |
7. What is the cause for the image quality of B compared to A?
a. B has less counts than A b. A has a lower sensitivity collimator than B c. B has less quantum mottle than A d. Artifacts in B is from movement. Answer: A – Image B has more quantum mottle, due to fewer counts. Possible causes include shorter imaging time and lower sensitivity collimator for Image B compared to Image A. |
|
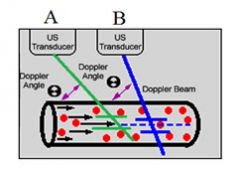
8. Two Doppler study images were shown with the probe at different angulations A less than B.
a. A has more velocity than B. b. B has more velocity than A. c. different perception of the vessel diameter |
8. Two Doppler study images were shown with the probe at different angulations A less than B.
a. A has more velocity than B. b. B has more velocity than A. c. different perception of the vessel diameter Answer: B As you increase the angle, the V max increases up to an angle of 90 degrees, when the cos 90 = 0. Also, the larger the angle, the larger the percent error. That is why you should measure Doppler shift at less than 60 degrees Vmax = (PRF * c)/(2fi * cosθ) |
|
|
9. . Which of the following CT window is best for cranial anatomy
A. L: –1000 W: 1000 B. L: –20 W: 200 C. L: 0 W: 1000 D. L: –1000 W: 0 E. L: 30 W: 100 |
9. . Which of the following CT window is best for cranial anatomy
A. L: –1000 W: 1000 B. L: –20 W: 200 C. L: 0 W: 1000 D. L: –1000 W: 0 E. L: 30 W: 100 Answer: E |
|
|
10. The binding energy of L and K shells are 30 keV and 40 keV, respectively, what would be the dynamic energy of the photoelectrons from L and K shells if the incident photon has an energy of 50 keV?
A. 30 and 40 keV B. 20 and 10 keV C. 40 and 30 keV D. 50 and 50 keV |
10. The binding energy of L and K shells are 30 keV and 40 keV, respectively, what would be the dynamic energy of the photoelectrons from L and K shells if the incident photon has an energy of 50 keV?
A. 30 and 40 keV B. 20 and 10 keV C. 40 and 30 keV D. 50 and 50 keV Answer: B – Take the incident xray photon and subtract the binding energies. Also be familiar with what the energies of the characteristic xrays would be (not asked on this question). |
|
|
11. What is FDA’s guideline for MR during pregnancy?
A. Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) less than 8 W/Kg peak in any 1 gram of tissue B. No MRI during pregnancy C. Only with scanner less than 2 tesla D. Should not stay in scanner longer than 3 hours |
11. What is FDA’s guideline for MR during pregnancy?
A. Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) less than 8 W/Kg peak in any 1 gram of tissue B. No MRI during pregnancy C. Only with scanner less than 2 tesla D. Should not stay in scanner longer than 3 hours Answer: A – MR is often done in pregnancy (for appendicitis for example). |
|
|
12. Reduced scatter of PET is due to
A. Coincident detection B. Optimal energy level C. Better pulse height analyzer (PHA) D. Superior photomultiplier (PMT) |
12. Reduced scatter of PET is due to
A. Coincident detection B. Optimal energy level C. Better pulse height analyzer (PHA) D. Superior photomultiplier (PMT) Answer: bad question. The UC Davis syllabus states that coincident detection does not reduce scatter because scatter coincidence is true coincidences. PHA is used to reject some scatter, but is is not as useful as in SPECT and other nuc med images. Shortening the time window of detection will decrease RANDOM coincidence but not scatter coincidences. 2D acquisition is the only thing that reduces scatter fraction, but it also reduces efficiency. If I got this question on the test as remembered here, I don't know what I would pick... |
|
|
13. Given fixed focal spot size, how can we minimize focal spot blur? By
A. increase the distance between subject to image (with fixed source to subject distance) B. decrease the distance between subject to image (with fixed source to subject distance) C. use faster film D. use slower screen E. use Beryllium filter instead of aluminum filter |
13. Given fixed focal spot size, how can we minimize focal spot blur? By
A. increase the distance between subject to image (with fixed source to subject distance) B. decrease the distance between subject to image (with fixed source to subject distance) C. use faster film D. use slower screen E. use Beryllium filter instead of aluminum filter Answer B – Option A describes moving the image (cassette) farther away from the subject, which will increase the penumbra. |
|
|
14. If there is a 20% window in a system using Tc99m, what is the window width?
A. 126-154 B. 112-168 C. 140-160 D. 112-168 |
14. If there is a 20% window in a system using Tc99m, what is the window width?
A. 126-154 B. 112-168 C. 140-160 D. 112-168 Answer: A – 140 x 0.2 = 28. So, the window is 140 +/- 14. |
|
|
. What is the role of the Automatic Brightness Control in a fluoro unit?
A. Appropriate exposures B. Limiting scatter radiation C. Decreasing heat capacity of the anode D. Appropriate developer concentration in the processing unit. E. Proper aliment of th FOV and the cassette. |
15. What is the role of the Automatic Brightness Control in a fluoro unit?
A. Appropriate exposures B. Limiting scatter radiation C. Decreasing heat capacity of the anode D. Appropriate developer concentration in the processing unit. E. Proper aliment of th FOV and the cassette. Answer: A – also known as the Automatic Exposure control. Located just before the video camera (on the camera side of the aperture). Can adjust mA, kVp, or aperture size (last resort b/c image quality suffers from increased quantum mottle). |
|
|
16. In a mammographic unit with a Moly anode and a max 28 kVp, what is the max keV?
A. 28 B. 17.5 C. 19.6 D. 20.2 E. 22.7 |
16. In a mammographic unit with a Moly anode and a max 28 kVp, what is the max keV?
A. 28 B. 17.5 C. 19.6 D. 20.2 E. 22.7 Answer: A – the max keV is always the max kVp. The characteristic xrays for Moly are 17.5 and 19.6 keV, and the characteristic xrays for Rhodium are 20.2 and 22.7 keV. So those numbers should look familiar. |
|
|
17. A 1994 FDA rule concerning interventional fluoro units was concerned about what?
A. Patient cancer rates B. Personnel cancer rates C. Faulty machinery D. Skin entrance doses to patients. |
17. A 1994 FDA rule concerning interventional fluoro units was concerned about what?
A. Patient cancer rates B. Personnel cancer rates C. Faulty machinery D. Skin entrance doses to patients. Answer: D – I added answer D to the recalls, but I think it is correct. See the following link if you want: http://www.fda.gov/cdrh/fluor.html |
|
|
18. Dark streaks in between 2 bones on a CT is due to what artifact?
A. Beam hardening B. Aliasing C. Gibbs Artifact D. Volume averaging |
18. Dark streaks in between 2 bones on a CT is due to what artifact?
A. Beam hardening B. Aliasing C. Gibbs Artifact D. Volume averaging Answer: A |
|
|
19. Which of the following is FALSE concerning radiation dose to a fetus?
A. The CNS risk is greater at 25–26 weeks vs. 8–15 weeks B. The risk of mental retardation is 40% per Sv C. Mental retardation is unlikely if exposure occurs during first week gestation D. Microcephaly can be seen with radiation induced mental retardation |
19. Which of the following is FALSE concerning radiation dose to a fetus?
A. The CNS risk is greater at 25–26 weeks vs. 8–15 weeks B. The risk of mental retardation is 40% per Sv C. Mental retardation is unlikely if exposure occurs during first week gestation D. Microcephaly can be seen with radiation induced mental retardation Answer: A |
|
|
20. The probability of decay in a radionuclide is given by what expression?
A. 1-e-t B. et C. e-t |
20. The probability of decay in a radionuclide is given by what expression?
A. 1-e-t B. et C. e-t Answer: A – e-t is the probability of radionuclide remaining, and 1-e-t is the probability of decay. |
|
|
20. The probability of decay in a radionuclide is given by what expression?
A. 1-e-t B. et C. e-t |
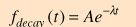
20. The probability of decay in a radionuclide is given by what expression?
A. 1-e-t B. et C. e-t Answer: A – e-t is the probability of radionuclide remaining, and 1-e-t is the probability of decay. |
|
|
21. In 2D Fourier transform in MR, extending k-space to higher values does what?
|
21. In 2D Fourier transform in MR, extending k-space to higher values does what?
A. Improves spatial resolution. |
|
|
22. If a 3MHz transducer is used to image an object 5 cm deep which reflects 50%, what is the attenuation of the beam, in decibels (given 2 dB/cm/MHz)?
A. 33 B. 63 C. 30 D. 50 |
22. If a 3MHz transducer is used to image an object 5 cm deep which reflects 50%, what is the attenuation of the beam, in decibels (given 2 dB/cm/MHz)?
A. 33 B. 63 C. 30 D. 50 Answer: B. On the way to the object, there is 5cm x 3MHz x 2dB/cm/MHx = 30 dB. Then 50% is reflected (3dB loss) and then 30dB lost on the way back to the transducer. 30 + 3 + 30 = 63 dB. |
|
|
23. In a radiologist who develops erythema in his hands:
A. Use of lead surgical gloves would decrease the dose by 90% B. Chronic cumulative doses of 3–4 Gy are often associated with erythema of the hands. C. The radiologist dose must have been greater than 2 Gy D. The radiologist will probabily experience moist desquamation in the coming weeks |
23. In a radiologist who develops erythema in his hands:
A. Use of lead surgical gloves would decrease the dose by 90% B. Chronic cumulative doses of 3–4 Gy are often associated with erythema of the hands. C. The radiologist dose must have been greater than 2 Gy D. The radiologist will probabily experience moist desquamation in the coming weeks Answer: C – See the small chart below. Note that option A is incorrect. Surgical lead gloves are considered to offer “minimal protection.” The lead is thin and the AEC increases the dose to penetrate the gloves, resulting in about the same dose to the hands. |
|
|
24. What is the typical range of effective dose for a CT of the chest?
A. 20–30 mSv B. 5–7 mSv C. 0.6–2 mSv D. 30–80 Sv. |
24. What is the typical range of effective dose for a CT of the chest?
A. 20–30 mSv B. 5–7 mSv C. 0.6–2 mSv D. 30–80 Sv. Answer: B CT chest = 7 mSv CT A/P = 10 mSv |
|
|
25. There are 70 people in a study, and 50 people have the disease in question. If 40 people are correctly diagnosed as having the disease and the remaining 30 people are called normal, what is the sensitivity of the study?
a. 4/5 b. 4/7 c. 5/7 d. 3/4 |
25. There are 70 people in a study, and 50 people have the disease in question. If 40 people are correctly diagnosed as having the disease and the remaining 30 people are called normal, what is the sensitivity of the study?
a. 4/5 b. 4/7 c. 5/7 d. 3/4 Anwser: A – Know sensitivity and specificity. It is on every old test in some form or fashion. Sensitivity = TP/(TP+FN) Sensitivity = 40/(40+10) = 4/5 Specificity [TN/(TN+FP)] would be 100% since nobody without the disease had a positive test. |
|
|
26. For a 256x256 matrix with 256 shades of gray per pixel, how many megabytes per second are required for real-time transmission at 32 frames per second?
a. 21 b. 16 c. 8 d. 2 e. 1 |
6. For a 256x256 matrix with 256 shades of gray per pixel, how many megabytes per second are required for real-time transmission at 32 frames per second?
a. 21 b. 16 c. 8 d. 2 e. 1 Anwser: D – First figure out how many MB are needed for each frame. 256 x256 x 1 byte = 0.06MB/frame NOTE: 256 shades of gray equals 8 bits, which is 1 byte. Remember the number of shades of gray equals 2n, where n = #bits. Okay, so each frame needs 0.06MB, and they want 32 frames per second. 0.06MB/frame x 32 frames/sec = ~2MB/sec. |
|
|
27. If the computed tomography dose index (CTDI) is 20 mGy at the surface of the abdomen, what is the effective skin dose of 20 consecutive slices with 1 cm slice thickness?
a. 20 mGy b. 40 mGy c. 100 mGy d. 200 mGy e. 400 mGy |
27. If the computed tomography dose index (CTDI) is 20 mGy at the surface of the abdomen, what is the effective skin dose of 20 consecutive slices with 1 cm slice thickness?
a. 20 mGy b. 40 mGy c. 100 mGy d. 200 mGy e. 400 mGy Answer: A – I don't know how to do this one, and I have no interest in figuring it out. I wonder if some info is missing (pitch, weighted CDTI) Maybe next year somebody can explain it. |
|
|
28. Which of the following is true for a radioactive sample in transient equilibrium?
a. sample activity is constant b. parent activity is constant c. progeny activity is constant d. number of disintegrations per second is constant e. fraction of radionuclide undergoing decay per second is constant |
28. Which of the following is true for a radioactive sample in transient equilibrium?
a. sample activity is constant b. parent activity is constant c. progeny activity is constant d. number of disintegrations per second is constant e. fraction of radionuclide undergoing decay per second is constant Answer: E – the daughter concentration is higher than the parent, and the apparent daughter half-life equals the parent half-life. |
|
|
29. The best advise from the safety standpoint to a breast-feeding mother who is to undergo a radioiodine treatment for hyperthyroidism is:
A) Stop breast-feeding indefinitely 2 weeks prior to treatment B) Stop breast-feeding indefinitely at the time of treatment C) Stop breast-feeding for 3 weeks starting 2 weeks prior to treatment D) Stop breast-feeding for 3 weeks starting at the time of treatment E) Stop breast-feeding for 5 days at the time of treatment |
29. The best advise from the safety standpoint to a breast-feeding mother who is to undergo a radioiodine treatment for hyperthyroidism is:
A) Stop breast-feeding indefinitely 2 weeks prior to treatment B) Stop breast-feeding indefinitely at the time of treatment C) Stop breast-feeding for 3 weeks starting 2 weeks prior to treatment D) Stop breast-feeding for 3 weeks starting at the time of treatment E) Stop breast-feeding for 5 days at the time of treatment Answer: A – I-131 is concentrated in breast milk. You want the woman to stop lactating before getting 1-131 not only to decrease dose to baby but also the mother's breast. In other words, you don't want I-131 hanging around in the woman's breast (bad, bad thing). |
|
|
30. Compared with the 3 MHz transducer crystal, a 5 MHz transducer is:
A) greater in diameter B) smaller in diameter C) thinner D) thicker |
30. Compared with the 3 MHz transducer crystal, a 5 MHz transducer is:
A) greater in diameter B) smaller in diameter C) thinner D) thicker Answer: C – the wavelength is ½ the crystal diameter. Higher frequency transducer has a shorter wavelength and a thinner crystal. |
|
|
31. The automatic brightness control function in fluoroscopy is to ensure that:
A) Same amount of light strikes the TV camera B) Same radiation exposure is used for every patient regardless of body habitus C) Same number of electrons strike the output phosphor D) Same number of electrons strike the input phosphor |
31. The automatic brightness control function in fluoroscopy is to ensure that:
A) Same amount of light strikes the TV camera B) Same radiation exposure is used for every patient regardless of body habitus C) Same number of electrons strike the output phosphor D) Same number of electrons strike the input phosphor Answer: A – the AEC is located on the backside of the aperture just before the TV camera. Can call for more kVp or mAs. If the radiation is maxed out, then the AEC will open the aperture (smaller f-number). |
|
|
32. The FDA regulation of 1995 dealing with fluoroscopy was concerned with:
A. Injury risk to patients B. Injury risk to personnel C. Cancer risk in patients D. Cancer risk in personnel |
32. The FDA regulation of 1995 dealing with fluoroscopy was concerned with:
A. Injury risk to patients B. Injury risk to personnel C. Cancer risk in patients D. Cancer risk in personnel Answer: A – specificity skin injury |
|
|
33. The physical half-life of a radioisotope is 4 hours. If its effective half-life is 2 hours, what is its biological half-life?
a. 0.5 hours b. 2 hours c. 4 hours d. 6 hours e. 8 hours |
33. The physical half-life of a radioisotope is 4 hours. If its effective half-life is 2 hours, what is its biological half-life?
a. 0.5 hours b. 2 hours c. 4 hours d. 6 hours e. 8 hours Answer: C – Here's how you do it: Teff = (Tb x Tp)/(Tb + Tp) 2 hr = 4Tb /(4+ Tb) 4 Tb = 8 hrs + 2 Tb 2 Tb= 8 hrs Tb = 4 hrs |
|
|
34. The percent standard deviation of pixel values in an abdominal CT will decrease by reducing:
a. mAs b. kVp c. Scan time d. Slice thickness e. Patient size |
34. The percent standard deviation of pixel values in an abdominal CT will decrease by reducing:
a. mAs b. kVp c. Scan time d. Slice thickness e. Patient size Answer: E. The question is asking what will decrease relative noise (increase N). Reducing the other options decreases the number of photons reaching the detector. Just a point about test taking – if all of the options except one change the noise in one direction, then the answer has to be the option that changes noise in the opposite direction. |
|
|
35. In linear tomography, a streak artifact in the plane of the image is caused by:
a. structure parallel to motion of x-ray tube b. structure perpendicular to motion c. moves in and out of plane d. at an obtuse angle e. at a right angle |
35. In linear tomography, a streak artifact in the plane of the image is caused by:
a. structure parallel to motion of x-ray tube b. structure perpendicular to motion c. moves in and out of plane d. at an obtuse angle e. at a right angle Answer: A – who cares? They might as well ask us about leech therapy for removing demons. |
|
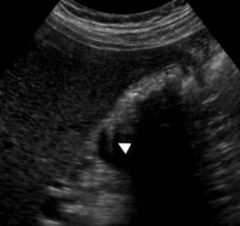
36. The following artifact is caused by what occurring proximal to the artifact?
a. high attenuating material b. low attenuating material c. two close interfaces d. side beam interference |
36. The following artifact is caused by what occurring proximal to the artifact?
a. high attenuating material b. low attenuating material c. two close interfaces d. side beam interference Answer: C – Ring down artifact is a form of reverberation. |
|
|
37. All other things equal, the SNR of a 1.5 T scanner (A) to a 0.5 T scanner (B) is:
a. SNR A = 9 times SNR B b. SNR A = 3 times SNR B c. SNR A = SNR B d. SNR A times 3 = SNR B e. SNR A times 9 = SNR B |
Answer: B – SNR is proportional to:
B1.0 to B1.5 NEX0.5 Bandwidth-0.5 (decreasing BW causes more time and allows more signal) Volume |
|
|
38. An ROC curve without labels was given. The y and x axes represent:
a. true positive fraction and false positive fraction b. true positive fraction and true negative fraction c. false positive and true positive d. sensitivity and specificity e. specificity and sensitivity |
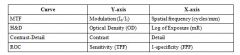
38. An ROC curve without labels was given. The y and x axes represent:
a. true positive fraction and false positive fraction b. true positive fraction and true negative fraction c. false positive and true positive d. sensitivity and specificity e. specificity and sensitivity Answer: A – also sensitivity and 1-specificity. Here a chart of x and y axises to review: |
|
|
39. According to the quality control procedures of a nuclear medicine laboratory, a Co-57 source can be measured in a dose calibrator under the Tc-99m setting to ensure the instrument’s
a. constancy b. spatial linearity c. count-rate linearity d. energy calibration e. dead time |
39. According to the quality control procedures of a nuclear medicine laboratory, a Co-57 source can be measured in a dose calibrator under the Tc-99m setting to ensure the instrument’s
a. constancy b. spatial linearity c. count-rate linearity d. energy calibration e. dead time Answer: A – constancy must be checked daily with a long lived radionuclide, such as Co-57. Basically the same test as accuracy except only one radionuclide is used and activity is compared to the value from the day instead of a national standard as in accuracy. Many places just do a daily accuracy test though. Usually Cesium is used for constancy and Cobalt for flood uniformity. |
|
|
40. Which of the following statements regarding the radiation pathology of skin is true?
a. Changes several hours after exposure occur only with doses greater than 5 Gy (500 rad) b. The main erythematous reaction occurring about 10 days following exposure is due to inflammation secondary to basal epithelial cell death c. The latent period for cell necrosis following exposure is 2 to 4 weeks d. The changes seen after a latent period of approximately 26 weeks are characterized by thickening of the dermal layer. |
40. Which of the following statements regarding the radiation pathology of skin is true?
a. Changes several hours after exposure occur only with doses greater than 5 Gy (500 rad) b. The main erythematous reaction occurring about 10 days following exposure is due to inflammation secondary to basal epithelial cell death c. The latent period for cell necrosis following exposure is 2 to 4 weeks d. The changes seen after a latent period of approximately 26 weeks are characterized by thickening of the dermal layer. Answer: B – Option A is wrong (you need 6 Gy for main erythema). The latent period for desquamation or necrosis is 4-6 weeks (C is wrong). Delayed response (>26 weeks) is atrophy, not thickening (D is wrong). See chart of skin reactions at #23. |
|
|
49. Lateral resolution in U/S is affected by
A. Width of transducer B. Spatial pulse length C. Thickness of the crystal D. Frequency of operation |
49. Lateral resolution in U/S is affected by
A. Width of transducer B. Spatial pulse length C. Thickness of the crystal D. Frequency of operation Answer: A – the lateral resolution is determined by the width of the beam and is strongly depth dependent. The lateral resolution is best at the focal spot where the beam width is ½ the width of the transducer. So, the best resolution is ¼ the transducer width. Remember, axial resolution is determined by the SPL and is depth independent. |
|
|
50. Filters in film badges are for:
A. allowing response to different energies B. for protection C. Allows for instantaneous reading. D. Are made of beryllium |
50. Filters in film badges are for:
A. allowing response to different energies B. for protection C. Allows for instantaneous reading. D. Are made of beryllium Answer: A – there are several thickness of filters that help discriminate against penetrating radiation (gamma and xrays) and particulate radiation (beta). |
|
|
51. Something about the LD50 given a lot of radiation.
|
51. Something about the LD50 given a lot of radiation.
An example of a crappy recall. Just know the LD50/30 for people is 3.0 Gy. |
|
|
52. For counts from a sample Ns in a time Ts with background counts of Nb in a time Tb, what is the variance in the counts?
A. Ns/Ts + Nb/Tb B. Ns/Ts – Nb/Tb C. Ns/Ts^2 – Nb/Tb^2 D. Ns/Ts^2 + Nb/Tb^2 |
52. For counts from a sample Ns in a time Ts with background counts of Nb in a time Tb, what is the variance in the counts?
A. Ns/Ts + Nb/Tb B. Ns/Ts – Nb/Tb C. Ns/Ts^2 – Nb/Tb^2 D. Ns/Ts^2 + Nb/Tb^2 Answer: A |
|
|
53. In scintillation cameras, backscatter is eliminated by:
A. detector assembly B. collimator C. pulse height analyzer D. Crystal |
53. In scintillation cameras, backscatter is eliminated by:
A. detector assembly B. collimator C. pulse height analyzer D. Crystal Answer: C – remember the collimator does not reduce scatter fraction, only makes a projection of the image. The PHA is responsible for removing scatter, and backscatter is a type of scatter. |
|
|
54. Which of the following will decrease large area contrast given a fixed kVp?
a. increase anode angle from 12 to 18 degrees b. increase focal spot size c. change from a single phase generator to a medium frequency generator d. decrease tube rating from 80 to 60 kW e. decrease stator frequency from 180 to 60 Hz |
54. Which of the following will decrease large area contrast given a fixed kVp?
a. increase anode angle from 12 to 18 degrees b. increase focal spot size c. change from a single phase generator to a medium frequency generator d. decrease tube rating from 80 to 60 kW e. decrease stator frequency from 180 to 60 Hz Answer: C – I don't really understand this one. I've heard that electronic questions are not going to be on the test anymore. One can only hope that is true. Just a note about test taking, options A and B same the same thing, so they cannot be the answer. That narrows it down to a 1/3 chance. Good luck! |
|
|
55. For scintillation cameras, the spatial resolution is:
a. better for I-131 than for In-111 b. best on the surface of the collimator c. independent of the collimator sensitivity d. same for all gamma ray energies e. improved with increased width of the energy window |
55. For scintillation cameras, the spatial resolution is:
a. better for I-131 than for In-111 b. best on the surface of the collimator c. independent of the collimator sensitivity d. same for all gamma ray energies e. improved with increased width of the energy window Answer: B – the collimator resolution degrades with distance from the surface of the collimator. Crystal (intrinsic) resolution is independent of distance from the crystal. |
|
|
56. The expected exposure from scattered radiation perpendicular to the beam at a point 2 meters away would be:
a. 0.01% b. 0.025% c. 0.1% d. 0.25% e. 1.0% ♦ |
56. The expected exposure from scattered radiation perpendicular to the beam at a point 2 meters away would be:
a. 0.01% b. 0.025% c. 0.1% d. 0.25% e. 1.0% Answer: B – kind of a tricky, 2 part question. Here is how you do it. First, you just have to know that radiation at 1 meter is 0.1% of skin entrance dose. Memorize this b/c it is on almost every old test. Then you have to apply the inverse square law to find the dose at 2 meters: 0.1% x (½)2 = 0.025% |
|
|
65. A malfunctioning ultrasound transducer results in increased pulse length. Which of the following measurements would provide best quality-control?
A. Axial resolution B. Lateral resolution C. Accuracy D. Frequency |
65. A malfunctioning ultrasound transducer results in increased pulse length. Which of the following measurements would provide best quality-control?
A. Axial resolution B. Lateral resolution C. Accuracy D. Frequency Answer: A – axial resolution is determined by the SPL, so testing the axial resolution would reveal a faulty transducer that is making an increased SPL. Got it? |
|
|
66. The greatest contribution to collective dose of the population is from which?
A. GI fluoroscopy B. CT C. Angiography/interventional radiology D. Chest and musculoskeletal radiography |
66. The greatest contribution to collective dose of the population is from which?
A. GI fluoroscopy B. CT C. Angiography/interventional radiology D. Chest and musculoskeletal radiography Answer: B – thank you ER doctors. |
|
|
67. The relative difference in intensity of x-rays transmitted by two adjacent structures is which?
A. Absorption coefficient B. Film contrast C. Subject contrast D. Linear energy transfer E. Conversion ratio |
67. The relative difference in intensity of x-rays transmitted by two adjacent structures is which?
A. Absorption coefficient B. Film contrast C. Subject contrast D. Linear energy transfer E. Conversion ratio Answer: C – this is the definition of contrast. subject contrast, the difference in x-ray beam intensities across the beam area after emerging from the part being radiographed. |
|
|
68. Which of the following describes motion of the patient couch during a helical (spiral) CT exam?
A. It is slip-ring controlled. B. It is one of the factors that determines pitch. C. It accelerates until the middle slice of the exam, then decelerates. D. It is performed in discrete steps under computer control. |
68. Which of the following describes motion of the patient couch during a helical (spiral) CT exam?
A. It is slip-ring controlled. B. It is one of the factors that determines pitch. C. It accelerates until the middle slice of the exam, then decelerates. D. It is performed in discrete steps under computer control. Answer: B – remember the equation: Pitch = (table mvt per 360 rotation)/(slice thickness) |
|
|
69. Which of the following statements regarding 99mTc is false:
A. 99mTc is present in a free state B. 99mTc has a half life that is favorable for use in tagging pharmaceuticals C. 99mTc photon energy is optimal for detection by a scintigraphic camera D. 99mTc may be used to label a wide range of biological entities in order to make radiopharmaceuticals |
69. Which of the following statements regarding 99mTc is false:
A. 99mTc is present in a free state B. 99mTc has a half life that is favorable for use in tagging pharmaceuticals C. 99mTc photon energy is optimal for detection by a scintigraphic camera D. 99mTc may be used to label a wide range of biological entities in order to make radiopharmaceuticals Answer: D is not correct. I think the key term is “biological entities,” whatever that means. |
|
|
70. What is the absorbed dose in mGy of 7 seconds of cardiac cinefluorography performed at 30 frames per second?
A. 1 B. 24 C. 70 D. 300 E. 800 |
70. What is the absorbed dose in mGy of 7 seconds of cardiac cinefluorography performed at 30 frames per second?
A. 1 B. 24 C. 70 D. 300 E. 800 Answer: B Cardiac cine = 300 mSv / minute |
|
|
71. The following regarding radiation induced dicentric chromosomes is true:
A. chromosomal break resulting in chromosome with two centromeres B. genetic mutation that is present in daughter cells C. results in daughter cells that have two nucleoli D. arises in an inversion homozygote as a result of crossing over between two normal chromosomal segments. |
Answer: A
|
|
|
72. A 4 cm diameter flat object is imaged. The projected image measures 7 cm on a screen that is 12 cm from the object. How far away (in cm) is the source from the object?
A. 8 B. 12 C. 16 D. 20 E. 24 |
72. A 4 cm diameter flat object is imaged. The projected image measures 7 cm on a screen that is 12 cm from the object. How far away (in cm) is the source from the object?
A. 8 B. 12 C. 16 D. 20 E. 24 Answer: C |
|
|
81. Utilizing an air gap, resulting in reduced scatter, will result in the following
a. it will allow the peak kilovoltage to be reduced b. results in increased absorption of scattered xrays compared to the primary xray beam c. results in increased dose to the patient d. will not change the contrast resolution of the final image |
81. Utilizing an air gap, resulting in reduced scatter, will result in the following
a. it will allow the peak kilovoltage to be reduced b. results in increased absorption of scattered xrays compared to the primary xray beam c. results in increased dose to the patient d. will not change the contrast resolution of the final image Answer: C – less x-rays are absorbed (although there is a higher primary to scatter ratio), so the AEC increases dose to compensate. |
|
|
83. 10to the13 atoms of Tc 99m result in what activity in megabequerels?
Lambda= 3 x 10-5 sec-1 Half life= 6 hours a. 3 Mbq b. 30 Mbq c. 300Mbq d. 3000Mbq |
Answer: C – In order to do this one, you have to know that activity = lambda x number of atoms.
Activity = 3 x 10-5 sec-1 x 10to the13 Activity = 3 x 108 atom/sec Activity = 300 MBq |
|
|
84. A woman involved in a traffic accident complained of lower back pain and underwent AP and lateral lumbosacral spine radiography. Two months later she was found to be 18 weeks pregnant. Which of the following is true?
A. The radiographs should not have been obtained. B. A therapeutic abortion should be recommended. C. The cancer incidence to the fetus is < 0.5%. D. The fetus probably received an absorbed dose of 0.1 – 0.15 Gy. E. There is an increased risk of neonatal death. |
84. A woman involved in a traffic accident complained of lower back pain and underwent AP and lateral lumbosacral spine radiography. Two months later she was found to be 18 weeks pregnant. Which of the following is true?
A. The radiographs should not have been obtained. B. A therapeutic abortion should be recommended. C. The cancer incidence to the fetus is < 0.5%. D. The fetus probably received an absorbed dose of 0.1 – 0.15 Gy. E. There is an increased risk of neonatal death. Answer: C – there are questions like this on every old test, and the answer is always “it's going to be okay” or something like that. The xrays were warrented in the situation (A is wrong). The total dose the the mother is <1 rad, so D is obviously way off. Neonatal death is only a concern in the preimplantation time period (E is wrong). B is a crazy thing to say. |
|
|
85. Concerning high level fluoroscopy after 1995, which of the following is false?
A. need an alarm to sound while in this mode B. exposure is less than 20 R/min C. need AEC activated D. need a machine to record cumulative dose E. need to activate it separately from regular fluoroscopy |
85. Concerning high level fluoroscopy after 1995, which of the following is false?
A. need an alarm to sound while in this mode B. exposure is less than 20 R/min C. need AEC activated D. need a machine to record cumulative dose E. need to activate it separately from regular fluoroscopy Answer: D – some machines do this, but it is not a requirement. |
|
|
86. The linear attenuation coefficient can best be described as
A. 1 / HVL B. The probability of X-ray beam absorption. C. The fractional attenuation of the X-ray beam per unit thickness. D. The average distance the X-ray beam traverses in unit thickness. |
86. The linear attenuation coefficient can best be described as
A. 1 / HVL B. The probability of X-ray beam absorption. C. The fractional attenuation of the X-ray beam per unit thickness. D. The average distance the X-ray beam traverses in unit thickness. Answer: C |
|
|
87. Scintillation well counters are used for:
A. wipe tests to check for removable sources of radiation B. calculating dose of radiopharmaceuticals prior to administration C. measuring exposure of CT scanner D. Surveying for contamination in the town square following dirty bomb explosion |
87. Scintillation well counters are used for:
A. wipe tests to check for removable sources of radiation B. calculating dose of radiopharmaceuticals prior to administration C. measuring exposure of CT scanner D. Surveying for contamination in the town square following dirty bomb explosion Answer: A – also remember what a well counter looks like, b/c there are questions on old tests. The well counter has a T.V. screen. A dose calibrater dose not. A well counter is a spectrometer and a dose calibrator is not. |
|
|
88. The ratio of beam exposure at the entrance to exit = 100 (thickness is t). What is the beam exposure at the center realative to the entrance dose (thickness = t/2)?
A. 100 % B. 50 % C. 20 % D. 10 % E. 5 % |
88. The ratio of beam exposure at the entrance to exit = 100 (thickness is t). What is the beam exposure at the center realative to the entrance dose (thickness = t/2)?
A. 100 % B. 50 % C. 20 % D. 10 % E. 5 % Answer: D – this is kind of tricky, and there maybe an easier way to do this. Here is how I did it though: Eentrance/Eexit = 100 Eexit = 0.01 x Eentrance To find the HVL, solve for n in the following equation: 1/(2n) = 0.01 2n = 1/0.01 = 100 n = ~6.6 HVL So, in the center, there will be ½ as many HVL, or about 3.3 HVL. Plug into the above equation and solve: 1/(23.3) = ~10 % |
|
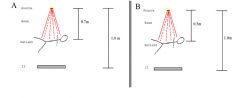
89. In a TIPS procedure, the given parameters being equal, e.g., patient characteristic, fluoroscopy time, fluorography, fluorographic equipment.
If procedure A has an entrance exposure of 3 mGy, the entrance exposure for procedure B: a. 1.5 b. 2.2 c. 3.0 d. 4.2 e. 5.9 |
Answer: E – Just use the inverse square law. Make sure the dose goes up (moving closer to source).
(0.7/0.5)2 = 2.0 3 mGy x 2 = 6 mGy |
|
|
90. Using a high kVp instead of low kVp for screen film chest radiography reduces:
a. quantum mottle b. rib detail c. penetrability of xray beam d. scatter from the image e. scatter penetrating through the grid |
90. Using a high kVp instead of low kVp for screen film chest radiography reduces:
a. quantum mottle b. rib detail c. penetrability of xray beam d. scatter from the image e. scatter penetrating through the grid Answer: B – higher kVp decreases the photoelectric effect (Z/E)3, so the bony contrast is decreased. Just FYI, Rib series are taken at 60 kVp instead of 120 kVp. |
|
|
91. In magnification mammography, geometric unsharpness is most limited by:
a. focus spot b. kVp c. intensifying screen d. breast thickness e. film |
91. In magnification mammography, geometric unsharpness is most limited by:
a. focus spot b. kVp c. intensifying screen d. breast thickness e. film Answer: A |
|
|
92. 99mT MDP bone scan using 20 mCi (740 MBq), the dose to the red marrow:
a. 0.05 – 0.25 mGy b. 0.3 – 2.5 mGy c. 3.0 – 100 mGy d. >100mGy |
92. 99mT MDP bone scan using 20 mCi (740 MBq), the dose to the red marrow:
a. 0.05 – 0.25 mGy b. 0.3 – 2.5 mGy c. 3.0 – 100 mGy d. >100mGy Answer: C |
|
|
93. Data gained from the Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic bomb survivors indicate that a person receiving a 0.01 Gy dose of low rate, low LET radiation, has an excess cancer risk of 4 in
a. 100 b. 1000 c. 10,000 d. 100,000 e. 1,000,000 |
Answer: C – In order to do this problem, you have to realize that 1 Sv is equal to 1 Gy for our purposes and the risk of cancer is 4% per Sv (memorize this number b/c it comes up a lot on old tests). Here's how you do the math:
Gy x (1Sv/ 1 Gy) = 0.01 Sv 0.01 Sv x 0.04 episodes of ca/Sv = 4 x 10-4 episodes of ca That equals 4 episodes of cancer per 10,000 people. |
|
|
94. In MR, chemical shift is due to differences in
a. Proton resonance frequency b. Proton magnetic susceptibility c. Patient motion d. Aliasing e. Truncation |
94. In MR, chemical shift is due to differences in
a. Proton resonance frequency b. Proton magnetic susceptibility c. Patient motion d. Aliasing e. Truncation Answer: A – on almost every old test. |
|
|
. The frequency shift detected in Doppler Ultrasound studies is not dependent on
a. Speed of the moving object b. Incident beam frequency c. Beam velocity d. Size of the moving object e. Angle between beam and the moving object |
95. The frequency shift detected in Doppler Ultrasound studies is not dependent on
a. Speed of the moving object b. Incident beam frequency c. Beam velocity d. Size of the moving object e. Angle between beam and the moving object Answer: D – here is the equation for the max velocity (v). Understand relationships in order to fix alaising: Vmax = (PRF * c)/(2fi * cosθ) Increase Vmax (fix aliasing): Increase PRF Increase angle Decrease transducer frequency |
|
|
96. Theoretically, an interventional radiologist using flouro and iodinated IV contrast should utilize an X-ray beam of what energy for the best contrast.
a. 1 Kev b. 2 Kev c. Kev just below Iodine K-edge d. Kev just above Iodine K-edge e. Kev of twice the Iodine K-edge |
96. Theoretically, an interventional radiologist using flouro and iodinated IV contrast should utilize an X-ray beam of what energy for the best contrast.
a. 1 Kev b. 2 Kev c. Kev just below Iodine K-edge d. Kev just above Iodine K-edge e. Kev of twice the Iodine K-edge Answer: D |
|
|
97. 10% uncertainty is associated with a 1 second count interval. If a 100 second count interval is used, the percent uncertainty is
a. .1% b. 0% c. 1% d. 3.2% e. 5% f. 10% |
97. 10% uncertainty is associated with a 1 second count interval. If a 100 second count interval is used, the percent uncertainty is
a. .1% b. 0% c. 1% d. 3.2% e. 5% f. 10% Answer: C – another silly math question that has nothing whatsoever to do with radiology. Here is how you do it: Assume the # of counts in 1 sec is represented by the integer x 1/√(x) = 0.10 √(x) = 10 x = 100 So if we count for 100 seconds, we will have 100x counts or 100 x 100 = 10,000 The percent uncertainty can then be calculated as follows: 1/√(10000) = % uncertainty 1/100 = % uncertainty % uncertainty = 0.01 = 1% |
|
|
98. As part of a liver/spleen scan, an adult patient receives 5 mCi IV, resulting in a liver dose of 15 mGy. A pediatric patient with half the liver mass and receiving 1 mCi IV receives what liver dose?
a. 1.5 mGy b. 3.0 mGy c. 6.0 mGy d. 9.0 mGy e. 15 mGy |
98. As part of a liver/spleen scan, an adult patient receives 5 mCi IV, resulting in a liver dose of 15 mGy. A pediatric patient with half the liver mass and receiving 1 mCi IV receives what liver dose?
a. 1.5 mGy b. 3.0 mGy c. 6.0 mGy d. 9.0 mGy e. 15 mGy Answer: C – Take the dose to the adult and multiply times 2 (half the liver mass) and divide by 5 (one fifth the dose). This gives you a dose of 6.0 mGy. |
|
|
99. Theoretically, in plane scatter encountered during a multidetector CT examination can be reduced by using
a. Higher pitch b. Increased slice thickness c. Increased filtration d. Longer tube side collimators e. Collimators between detectors |
99. Theoretically, in plane scatter encountered during a multidetector CT examination can be reduced by using
a. Higher pitch b. Increased slice thickness c. Increased filtration d. Longer tube side collimators e. Collimators between detectors Answer: E – unsure about this one. Increasing filtration seems to be another correct answer b/c it would increase the kVp of the beam. Collimation b/t detectors would definitely decrease scatter, however. Tube side collimators will decrease scatter from plane to plane (they are being particular on this one). |
|
|
100. In a Computed Radiography system, spatial resolution is most limited by
a. Analog to digital conversion b. Phosphor plate size c. Laser readout device d. Patient size e. Patient dose |
100. In a Computed Radiography system, spatial resolution is most limited by
a. Analog to digital conversion b. Phosphor plate size c. Laser readout device d. Patient size e. Patient dose Answer: C – don't know about this one b/c the MTF curves I've seen seem to place the screen phosphor as the lowest component, but that is not an option... The CR is a noise limited device, so the answer may be E as well... Who knows... Um hasn't converting a analog to digital signal always been the big deal. |
|
|
101. Increasing the distance between the film and screen within a cassette will cause
a. increased quantum mottle b. increased processor artifacts c. decreased contrast d. decreased spatial resolution |
101. Increasing the distance between the film and screen within a cassette will cause
a. increased quantum mottle b. increased processor artifacts c. decreased contrast d. decreased spatial resolution Answer: D – the images will be blurry if the screens don't contact the films |
|
|
102. The SI unit of activity is
a. curie b. becquerel c. sievert d. gray |
102. The SI unit of activity is
a. curie b. becquerel c. sievert d. gray Answer: B |
|
|
103. For mammography, which one of the following combinations of film base, film emulsion, and film screen will result in the highest resolution for a cassette
X-RAY Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 A. base emulsion screen B. emulsion base screen C. screen base emulsion D. screen emulsion base |
103. For mammography, which one of the following combinations of film base, film emulsion, and film screen will result in the highest resolution for a cassette
X-RAY Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 Layer 1 Layer 2 Layer 3 A. base emulsion screen B. emulsion base screen C. screen base emulsion D. screen emulsion base Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
104. A patient receives 2nd and 3rd degree burns over 50% of their body after an explosion at a radiopharmaceutical plant. Effects and treatment should include
a. isolation and treatment in the ER b. determine radioactivity before approaching c. the radiation exposure will cause immediate damage d. shower to wash off possible exposure |
104. A patient receives 2nd and 3rd degree burns over 50% of their body after an explosion at a radiopharmaceutical plant. Effects and treatment should include
a. isolation and treatment in the ER b. determine radioactivity before approaching c. the radiation exposure will cause immediate damage d. shower to wash off possible exposure Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
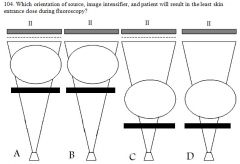
|
104. Which orientation of source, image intensifier, and patient will result in the least skin entrance dose during fluoroscopy?
Answer: B – The larger SOD and the lack of a grid lowers dose. C would give the most dose for the opposite reasons. |
|
|
105. Given an acute dose of radiation, a person is most likely to die within 3-5 days from the effects to which system
A. CNS B. GI C. Cardiovascular D. Hematopoetic |
105. Given an acute dose of radiation, a person is most likely to die within 3-5 days from the effects to which system
A. CNS B. GI C. Cardiovascular D. Hematopoetic Answer: B – weird question, GI causes death in 4-10 days. CNS causes death in hours – days. |
|
|
106. Radioactive decay product which is not emitted from the nucleus
A. Auger electron B. Positron C. Beta particle D. Gamma ray E. Alpha particle |
106. Radioactive decay product which is not emitted from the nucleus
A. Auger electron B. Positron C. Beta particle D. Gamma ray E. Alpha particle Answer: A |
|
|
107. Spiral CT image production relies on
|
Spiral CT image production relies on
E. Obtaining information in a spiral fashion and reconstructing parallel pixel information to produce axial images. |
|
|
108. The signal to noise ratio in two MRI systems, one (A) 1.5T and one (B) 0.5 T has a signal to noise ratio of
System A System B A. 1 3 B. 1 2 C. 3 1 D. 6 1 |
108. The signal to noise ratio in two MRI systems, one (A) 1.5T and one (B) 0.5 T has a signal to noise ratio of
System A System B A. 1 3 B. 1 2 C. 3 1 D. 6 1 Answer: C – same question as # 37. SNR is proportional to: B1.0 to B1.5 NEX0.5 Bandwidth-0.5 (decreasing BW causes more time and allows more signal) Volume |
|
|
109. Which of the following diagrams best represents a system with high contrast but low resolution
|
109. Which of the following diagrams best represents a system with high contrast but low resolution
? SPECT (also CT) |
|
|
110. MRI with spin echo technique uses
A. 90 degree pulse followed by a 180 degree pulse B. 180 degree pulse followed by a 180 degree pulse C. 90 degree pulse followed by a 90 degree pulse D. 180 degree pulse followed by a 90 degree pulse |
110. MRI with spin echo technique uses
A. 90 degree pulse followed by a 180 degree pulse B. 180 degree pulse followed by a 180 degree pulse C. 90 degree pulse followed by a 90 degree pulse D. 180 degree pulse followed by a 90 degree pulse Answer: A |
|
|
1. What is the minification factor of a fluoroscopic system with an input diameter of 9 inches and an output diameter of 1.5 inches?
A. 6.25 B. 8 C. 9 D. 36 E. 71 |
1. What is the minification factor of a fluoroscopic system with an input diameter of 9 inches and an output diameter of 1.5 inches?
A. 6.25 B. 8 C. 9 D. 36 E. 71 Answer: D – the minification factor is the square of the input phosphor diameter divided by the square of the output phosphor diameter. |
|
|
2. Heat units are calculated in which of the following manners?
A. kVp x mA/sec B. kVp x sec/mA C. kVp/(mA x sec) D. kVp x mA x sec E. mA x sec/kVp |
2. Heat units are calculated in which of the following manners?
A. kVp x mA/sec B. kVp x sec/mA C. kVp/(mA x sec) D. kVp x mA x sec E. mA x sec/kVp Answer: D |
|
|
3. The time gain compensation (TGC) is used for which purpose?
A. Compensate for attenuation loss B. Compensate for drift of overall gain C. Correct for the appearance of grating lobes D. Compensate for drift of line voltage E. Correct for pulse duration |
3. The time gain compensation (TGC) is used for which purpose?
A. Compensate for attenuation loss B. Compensate for drift of overall gain C. Correct for the appearance of grating lobes D. Compensate for drift of line voltage E. Correct for pulse duration Answer: A |
|
|
4. MOST of the energy deposited in organic molecules is accomplished by:
A. electrons B. degraded photons C. protons D. the photoelectric effect E. pair production |
4. MOST of the energy deposited in organic molecules is accomplished by:
A. electrons B. degraded photons C. protons D. the photoelectric effect E. pair production Answer: A – on multiple old tests |
|
|
5. Which of the following is TRUE concerning sublethal damage from radiation?
A. Experiments demonstrate repair between fractionated sublethal doses B. Damage is irreversible C. Repair is facilitated by high dose radiation D. Other wrong answer |
5. Which of the following is TRUE concerning sublethal damage from radiation?
A. Experiments demonstrate repair between fractionated sublethal doses B. Damage is irreversible C. Repair is facilitated by high dose radiation D. Other wrong answer Answer: A |
|
|
6. Quantum mottle in fluoroscopy is primarily determined by the numbers of which of the following?
A. X-rays exiting the patient B. X-rays absorbed by input screen C. Photons released by the input screen D. Photons absorbed by the photocathode E. Electrons released by the photocathode |
6. Quantum mottle in fluoroscopy is primarily determined by the numbers of which of the following?
A. X-rays exiting the patient B. X-rays absorbed by input screen C. Photons released by the input screen D. Photons absorbed by the photocathode E. Electrons released by the photocathode Answer: B – quantum mottle is determined by the number of xray photons absorbed by the input phosphor. The question is basically asking where is the quantum sink? A confusing point is that QM is independent of absorption efficiency, which seems to be contrary to the answer for this question. However, the QM is determined by the NUMBER of photons absorbed, not the PERCENT! If you increase the QDE (quantum detection efficiency – aka absorption efficiency), then the the AEC (automatic exposure control) will decrease the mA, and fewer photons will be incident of the input phosphor. However, a higher percent of the photons are absorbed, and the NUMBER absorbed stays constant. Therefore QM doesn't change. Any questions??? Remember, increasing conversion efficiency INCREASES QM because the AEC will turn down the mA and fewer photons will be absorbed at the input phosphor. Sorry about the wordy explanation, but this concept gave me some trouble at first. So, the recap: QM is determined by the NUMBER of absorbed xrays increase/decrease absorption efficiency = no change in QM INCREASE the conversion efficiency = INCREASE QM DECREASE the conversion efficiency = DECREASE QM |
|
|
7. The decay coefficient represents which of the following:
A. Number of atoms decaying per unit time B. Fraction of atoms decaying per unit time C. Ratio of number of decays to atom samples D. Probability of an atomic decay E. Likelihood that there is NO decay within a unit time |
7. The decay coefficient represents which of the following:
A. Number of atoms decaying per unit time B. Fraction of atoms decaying per unit time C. Ratio of number of decays to atom samples D. Probability of an atomic decay E. Likelihood that there is NO decay within a unit time Answer: B |
|
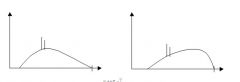
8. An aluminum filter has been added to an X-ray beam, producing the following pre-filter and post-filter spectra. Which of the following is TRUE? (Maximum energy is indicated by the tick mark on the x-axis at 120 keV for BOTH diagrams)
Prefilter Postfilter A. Approximately 4 HVL of aluminum was added B. The maximum energy of the beam was increased C. The energy of characteristic X-rays was reduced D. The mean beam energy was increased E. Increased X-ray production rate |
8. An aluminum filter has been added to an X-ray beam, producing the following pre-filter and post-filter spectra. Which of the following is TRUE? (Maximum energy is indicated by the tick mark on the x-axis at 120 keV for BOTH diagrams)
Prefilter Postfilter A. Approximately 4 HVL of aluminum was added B. The maximum energy of the beam was increased C. The energy of characteristic X-rays was reduced D. The mean beam energy was increased E. Increased X-ray production rate Answer: D |
|
|
9. Film badges used to monitor personnel radiation doses can make reasonable measurements of which of the following types of radiation?
A. X-rays, gamma rays, and beta emission B. X-rays, gamma rays, beta emission, and alpha emission C. X-rays and gamma rays, but not beta emission D. X-rays and gamma rays, but not alpha emission E. X-rays and beta emission but not gamma rays |
. Film badges used to monitor personnel radiation doses can make reasonable measurements of which of the following types of radiation?
A. X-rays, gamma rays, and beta emission B. X-rays, gamma rays, beta emission, and alpha emission C. X-rays and gamma rays, but not beta emission D. X-rays and gamma rays, but not alpha emission E. X-rays and beta emission but not gamma rays Answer: A – film badges can determine between penetrating radiation (xrays) and non-penetrating radiation (beta). Alpha particles only travel several cm in air and are unlikely to be detected on a film badge. |
|
|
. The annual occupational exposure limit of the lens of the eye is which of the following?
A. 5 rem B. 10 rem C. 15 rem D. 20 rem |
10. The annual occupational exposure limit of the lens of the eye is which of the following?
A. 5 rem B. 10 rem C. 15 rem D. 20 rem Answer: C – just memorize this stuff. Here is a short chart of exposure limits: Limit Occupational worker Total effective Dose Equivalent 5 rem/yr Total dose equivalent (DE) to lens 15 rem/yr Total DE to any organ (including extremities) 50 rem/yr Pregnant worker 50 mrem/mo. 500 mrem/preg – think 50mrem/mo. x 10 mo. General Public Total effective DE 0.1 rem/yr Work Areas Controlled Area 10 mR/wk |
|
|
11. Which of the following is a unit of dose equivalent?
A. Pascal B. Gray C. Sievert D. Becquerel E. Newton |
11. Which of the following is a unit of dose equivalent?
A. Pascal B. Gray C. Sievert D. Becquerel E. Newton Answer: C |
|
|
12. In a single slice CT exam, which of the following will DECREASE volume-averaging artifacts?
A. Increasing pitch B. Reducing the amount of time for a gantry rotation C. Increasing the smoothing of the reconstruction algorithm D. Decreasing the width of the X-ray beam in the Z axis E. Increasing mAs |
12. In a single slice CT exam, which of the following will DECREASE volume-averaging artifacts?
A. Increasing pitch B. Reducing the amount of time for a gantry rotation C. Increasing the smoothing of the reconstruction algorithm D. Decreasing the width of the X-ray beam in the Z axis E. Increasing mAs Answer: D – slice thickness in a single slice CT is determined by the x-ray beam width. |
|
|
13. What is the typical absorbed dose in the center of a patient during a CT exam of the abdomen of an average patient?
A. 2 mrad B. 20 mrad C. 200 mrad D. 2 rad E. 20 rad |
13. What is the typical absorbed dose in the center of a patient during a CT exam of the abdomen of an average patient?
A. 2 mrad B. 20 mrad C. 200 mrad D. 2 rad E. 20 rad Answer: D – UC Davis syllabus states the following: Scan Type kV & mAs Slice Thickness Dose Head (16 cm dia) 120 kV/ 420 mAs 10 mm 6.5 Rads Spine (16 cm dia) 140 kV/ 420 mAs 5 mm 2.3 Rads Body (32 cm dia) 120 kV/ 420 mAs 10 mm 1.5-2.5 Rads |
|
|
15. Two brass wires are placed 5 cm apart on the fluoro table. The screen is 36 cm above the table. The brass wires are 9 cm apart on the screen. How far under the table is the x-ray source?
A. 9cm B. 28cm C. 36cm D. 45cm E. 81cm |
Answer: D
|
|
|
16. The optical density on a sensitometry strip is too high. Why?
A. The developer replenishment rate is too high. B. The developer temperature is too low. C. Inadequate fixing. D. Inadequate washing |
16. The optical density on a sensitometry strip is too high. Why?
A. The developer replenishment rate is too high. B. The developer temperature is too low. C. Inadequate fixing. D. Inadequate washing Answer: C – heard this type of question wasn't on the test anymore. Hope that is right. |
|
|
17. The CT numbers are higher at the periphery of a water phantom because:
A. noise fluctuations B. differences in beam hardening C. beam divergence D. detector malfunction E. presence of a diverging filter |
17. The CT numbers are higher at the periphery of a water phantom because:
A. noise fluctuations B. differences in beam hardening C. beam divergence D. detector malfunction E. presence of a diverging filter Answer: B – hardening the beam causes the HVL to increase (linear attenuation coefficient decreases). Deceasing the LAC makes the CT numbers go down b/c of the equation below. Since there is less attenuation in the periphery, there is less beam hardening and the HU will be elevated. The LAC of water is a constant. HU = [(μmaterial - μwater)/(μwater)]x 1000 |
|
|
18. The pulse height analyzer is supposed to:
A. increase the sensitivity of the camera B. compensate for photon absorption C. reduce the effect of scatter D. increase photon detection |
18. The pulse height analyzer is supposed to:
A. increase the sensitivity of the camera B. compensate for photon absorption C. reduce the effect of scatter D. increase photon detection Answer: C |
|
|
19. To perform magnification radiography, it is desirable to have:
A. hooded anode B. heavy beam filtration C. small focal spot size D. induction filaments |
19. To perform magnification radiography, it is desirable to have:
A. hooded anode B. heavy beam filtration C. small focal spot size D. induction filaments Answer: C – the penumbra is exaggerated in the magnification views, so you want a small focal spot. |
|
|
20. A technologist is three months pregnant and has recorded 400mrem on her dosimetry badge over the past three months. Her badge is worn on her collar and she always her lead apron on.
A. The FDA should be notified. B. She should have a therapeutic abortion C. There is a 2 percent chance of fetal malformations. D. She has not exceeded her maximal dose. E. She should not enter a fluoroscopy room for the remainder of her pregnancy. |
20. A technologist is three months pregnant and has recorded 400mrem on her dosimetry badge over the past three months. Her badge is worn on her collar and she always her lead apron on.
A. The FDA should be notified. B. She should have a therapeutic abortion C. There is a 2 percent chance of fetal malformations. D. She has not exceeded her maximal dose. E. She should not enter a fluoroscopy room for the remainder of her pregnancy. Answer: D – this type of question comes up a lot on old tests, and the answer is usually “its gonna be okay” or some derivation. Another answer I've seen is to tell the technologist to wear a second badge beneath her lead apron. |
|
|
21. When performing ultrasound, there is always a trade-off between spatial resolution and:
A. velocity B. contrast C. penetration D. temporal resolution |
. When performing ultrasound, there is always a trade-off between spatial resolution and:
A. velocity B. contrast C. penetration D. temporal resolution Answer: C |
|
|
. The banging noise heard during a magnetic resonance imaging procedure is due to vibration of:
A. Shim coil B. Gradient coil C. Receiver coil D. Static magnetic field E. Frequency encoding |
. The banging noise heard during a magnetic resonance imaging procedure is due to vibration of:
A. Shim coil B. Gradient coil C. Receiver coil D. Static magnetic field E. Frequency encoding Answer: B – on mulitple old tests. |
|
|
23. When there are equal numbers of spin dipoles in the direction of the magnetic field as against the magnetic field, this is called:
A. Quantum B. Saturation C. Equilibrium D. Spin Echo |
23. When there are equal numbers of spin dipoles in the direction of the magnetic field as against the magnetic field, this is called:
A. Quantum B. Saturation C. Equilibrium D. Spin Echo Answer: C – its equal, I guess that makes sense. |
|
|
24. The most radioresistant portion of the cell cycle is:
A. G1 B. G2 C. M D. S |
24. The most radioresistant portion of the cell cycle is:
A. G1 B. G2 C. M D. S Answer: D – there are a bunch of repair enzymes floating around ready to fix any damage. The most radiosensitive portion is M. G1 is more radioresistant than G2 because there is only 1 copy of the genome (less chance of getting hit). Another question that comes up is why a colony of cells that survived radiation are synchronized. It is b/c most of the survivors will be in S phase. |
|
|
25. The amount of noise in digital subtraction angiography is usually:
A. greater in the mask than in the subtracted image B. greater in the subtracted image than in the mask C. greater in the larger structures than in the smaller structures D. decreased by increasing the time interval between the mask E. unaffected by the changes in kVp and mAs |
25. The amount of noise in digital subtraction angiography is usually:
A. greater in the mask than in the subtracted image B. greater in the subtracted image than in the mask C. greater in the larger structures than in the smaller structures D. decreased by increasing the time interval between the mask E. unaffected by the changes in kVp and mAs Answer: B – this question is on multiple old tests... |
|
|
26. In radiography, increased geometric unsharpness is seen with increased:
A. target focus distance B. exposure time C. focal spot size D. kVp E. film speed |
26. In radiography, increased geometric unsharpness is seen with increased:
A. target focus distance B. exposure time C. focal spot size D. kVp E. film speed Answer: C – exaggerates image penumbra. |
|
|
27. Absorbed fraction is the fraction of:
A. effective dose that has disintegrated B. administered dose absorbed by the organ C. effective dose absorbed D. absorbed source related activity E. disintegration via gamma decay |
27. Absorbed fraction is the fraction of:
A. effective dose that has disintegrated B. administered dose absorbed by the organ C. effective dose absorbed D. absorbed source related activity E. disintegration via gamma decay Answer: B. - it is the f in the equation: Ã = 1.44 * f * Ao * Te |
|
|
28. In SPECT calibration, when a point source of Tc 99 is used with the collimators on, the calibration is for:
A. photomultiplier sensitivity B. center-of-rotation centering C. spatial linearity D. field uniformity E. PHA frequency analysis |
28. In SPECT calibration, when a point source of Tc 99 is used with the collimators on, the calibration is for:
A. photomultiplier sensitivity B. center-of-rotation centering C. spatial linearity D. field uniformity E. PHA frequency analysis Answer: B – COR uses a point source. |
|
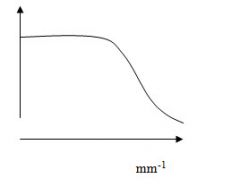
29. What does the following curve represent?
mm-1 A. absorption of an xray B. H & D curve C. MTF curve D. Receiver Operator curve E. Contrast-detail curve |
29. What does the following curve represent?
mm-1 A. absorption of an xray B. H & D curve C. MTF curve D. Receiver Operator curve E. Contrast-detail curve Answer: C – know the x and y of each of these curves |
|
|
30. For a nonspiral, single slice CT image, if the slice thickness is cut in half while maintaining the same signal to noise ratio, what happens to patient dose:
A. quartered B. halved C. no change D. doubled E. quadrupled |
30. For a nonspiral, single slice CT image, if the slice thickness is cut in half while maintaining the same signal to noise ratio, what happens to patient dose:
A. quartered B. halved C. no change D. doubled E. quadrupled Answer: D – the key phrase is maintaining the same signal to noise ratio. If you cut the volume in half (and the signal), then you must “make up” for the lost signal by increase mA to keep SNR constant. |
|
|
31. Which radionuclide of 30MBq-100MBq?s activity should not be disposed of as regular hospital waste after one year:
A. 18F as fluorodeoxyglucose B. Co as calibrator source C. Tl-201 D. Ga-67 citrate E. Tc99m |
31. Which radionuclide of 30MBq-100MBq?s activity should not be disposed of as regular hospital waste after one year:
A. 18F as fluorodeoxyglucose B. Co as calibrator source C. Tl-201 D. Ga-67 citrate E. Tc99m Answer: B – T(1/2) is too long. Below is a chart of the half lives of some common radiopharmaceuticals. I haven't seen this asked specifically on any recalls, so don't feel like you have to memorize these numbers. |
|
|
32. To increase the resonant frequency of an ultrasound transducer:
A. increase the thickness of the piezoelectric crystal B. decrease the thickness of the piezoelectric crystal C. increase the radius of the piezoelectric crystal D. decrease the radius of the piezoelectric crystal |
32. To increase the resonant frequency of an ultrasound transducer:
A. increase the thickness of the piezoelectric crystal B. decrease the thickness of the piezoelectric crystal C. increase the radius of the piezoelectric crystal D. decrease the radius of the piezoelectric crystal Answer: B – the wavelength is 2x the thickness of the crystal. A thinner crystal will cause a smaller wavelength and an increased frequency. |
|
|
33. In relation to radiation-induced cataracts:
A. likely with a single acute exposure of 1 Gy B. likely with fractionated exposure totaling 4 Gy C. occur in 6-12 months following exposure D. vision-impairing cataracts are preceded by asymptomatic opacities in the lens E. originate at the anterior surface of the lens |
33. In relation to radiation-induced cataracts:
A. likely with a single acute exposure of 1 Gy B. likely with fractionated exposure totaling 4 Gy C. occur in 6-12 months following exposure D. vision-impairing cataracts are preceded by asymptomatic opacities in the lens E. originate at the anterior surface of the lens Answer: D - You need an acute dose of 2 Gy or a chronic dose of 6 Gy to cause cataracts. Cataracts start in the posterior aspect of the lens, and asymptomatic opacities precede clinically apparent cataracts. Latency is about 8 years. |
|
|
34. What term relates to constructive and destructive interference created by objects which are smaller than the pulse wavelength of the ultrasound beam?
A. specular reflectors B. nonspecular reflectors C. reverberation D. attenuation |
34. What term relates to constructive and destructive interference created by objects which are smaller than the pulse wavelength of the ultrasound beam?
A. specular reflectors B. nonspecular reflectors C. reverberation D. attenuation Answer: B |
|
|
35. Which of these statements regarding the indirect effects of ionizing radiation are TRUE?
A. It does not occur with low- LET radiation B. It requires neutrons C. It involves the production of free radicals D. Oxygen tension does not contribute to its effects E. It does not contribute significantly to radiation-induced biologic damage |
35. Which of these statements regarding the indirect effects of ionizing radiation are TRUE?
A. It does not occur with low- LET radiation B. It requires neutrons C. It involves the production of free radicals D. Oxygen tension does not contribute to its effects E. It does not contribute significantly to radiation-induced biologic damage Answer: C |
|
|
36. Which of these statements regarding photon interactions are TRUE?
A. In mammography, the photoelectric effects is responsible for most of the scatter B. In mammography, Compton scatter provides most of the contrast C. In CT, Compton scatter provides most of the scatter. D. In chest radiography at 120 kVp, pair production sometimes occurs E. X-rays interact with the magnetic moments of calcium in bone |
36. Which of these statements regarding photon interactions are TRUE?
A. In mammography, the photoelectric effects is responsible for most of the scatter B. In mammography, Compton scatter provides most of the contrast C. In CT, Compton scatter provides most of the scatter. D. In chest radiography at 120 kVp, pair production sometimes occurs E. X-rays interact with the magnetic moments of calcium in bone Answer: C |
|
|
37. The “use factor” in radiation protection is defined as:
A. The number of hours per week an x-ray tube is in use B. The number of milliampere-minutes an xray tube is used per week C. The fraction of time that the primary xray beam is directed at a barrier D. The exposure from an xray tube measured per week E. The number of hours an xray tube is in use during a working week |
37. The “use factor” in radiation protection is defined as:
A. The number of hours per week an x-ray tube is in use B. The number of milliampere-minutes an xray tube is used per week C. The fraction of time that the primary xray beam is directed at a barrier D. The exposure from an xray tube measured per week E. The number of hours an xray tube is in use during a working week Answer: C – just a definition you have to memorize. |
|
|
38. Collimation in flouro does NOT result in which of the following:
A. Decreased skin dose exposure rate to the patient B. Decreased volume of tissue irradiated C. Decreased scatter from the patient D. Decreased risk of stochastic effects E. Increased image contrast |
38. Collimation in flouro does NOT result in which of the following:
A. Decreased skin dose exposure rate to the patient B. Decreased volume of tissue irradiated C. Decreased scatter from the patient D. Decreased risk of stochastic effects E. Increased image contrast Answer: A – the skin that is exposed will be exposed at the same rate (mR/cm2) |
|
|
39. During thyroid scintigraphy, an image of the thigh is often obtained to
A. Obtain the background counts of radioactive iodine in the circulating blood B. Create an energy spectrum to determine the optimal photopeak C. Determine the scatter from a plastic neck phantom D. Determine the rate of clearance of radioactive iodine from the body |
39. During thyroid scintigraphy, an image of the thigh is often obtained to
A. Obtain the background counts of radioactive iodine in the circulating blood B. Create an energy spectrum to determine the optimal photopeak C. Determine the scatter from a plastic neck phantom D. Determine the rate of clearance of radioactive iodine from the body Answer: A – may not be remembered correctly. Not a true “background”. Instead it is a nonthyroidal activity correction. Just fyi. |
|
|
40. The probability of a photoelectric interaction increases as
A. 1/square root of Z of target electron B. Z Cubed of incident electron C. Square root of E (of photon) D. 1/E cubed (of photon) |
40. The probability of a photoelectric interaction increases as
A. 1/square root of Z of target electron B. Z Cubed of incident electron C. Square root of E (of photon) D. 1/E cubed (of photon) Answer: D – remember Z3/E3. Don't want to miss easy points. |
|
|
41. In MRI, if a rapidly switching gradient is applied as part of an echo planar imaging experimental protocol instead of the sequences used for standard imaging, there is concern for
A. Production of free radicals B. Stimulation of peripheral nerves C. Increased RF deposition to the patient D. Increased heat deposition in the patient E. Creation of ambient magnetic fields near the computer console |
41. In MRI, if a rapidly switching gradient is applied as part of an echo planar imaging experimental protocol instead of the sequences used for standard imaging, there is concern for
A. Production of free radicals B. Stimulation of peripheral nerves C. Increased RF deposition to the patient D. Increased heat deposition in the patient E. Creation of ambient magnetic fields near the computer console Answer: B – see #75 on the 2007 RSNA Radiation Biology Syllabus (link below). Changing gradients stimulate peripheral nerves. Kind of a bad question b/c changing magnetic gradients can also raise temperature. At very high magnetic fields (~20T) proton degradation and free radicals are possible. |
|
|
42. The amount of ionizing radiation in air is most reflective of:
A. Radiation absorbed dose B. Equivalent dose. C. Photon energy D. Exposure |
42. The amount of ionizing radiation in air is most reflective of:
A. Radiation absorbed dose B. Equivalent dose. C. Photon energy D. Exposure Answer: D – other tests ask what is exposure (charge per unit air). |
|
|
43. I-131 is used as an agent in a study. The biological and physical half-lives of the critical organ are both 8 days. The total absorbed dose of the critical organ is 4.0 rads. What is the critical organ absorbed dose during the first 8 days?
A. 1.0 rad B. 2.0 rad C. 2.5 rad D. 3.0 rad E. 4.0 rad |
43. I-131 is used as an agent in a study. The biological and physical half-lives of the critical organ are both 8 days. The total absorbed dose of the critical organ is 4.0 rads. What is the critical organ absorbed dose during the first 8 days?
A. 1.0 rad B. 2.0 rad C. 2.5 rad D. 3.0 rad E. 4.0 rad Answer: D – the effective half-life is 4 days (8*8/8+8 = 4). So there are 2 half-lives in 8 days and 75% of total activity (50% for the 1st T1/2 and 25% for the second T1/2). 4.0 rads * 0.75 = 3.0 rads |
|
|
44. In linear tomography the position of the focal zone is most related to:
A. Position of the fulcrum. B. Distance between source and patient. C. Distance between patient and cassette. D. Angle through which the tube moves. |
44. In linear tomography the position of the focal zone is most related to:
A. Position of the fulcrum. B. Distance between source and patient. C. Distance between patient and cassette. D. Angle through which the tube moves. Answer: A |
|
|
45. A radiologist is performing an interventional procedure using fluoroscopy. In order to reduce his or her exposure by a factor of 2, keeping all other factors equal, he would have to:
A. Decrease fluoroscopy time from 25 to 15 minutes B. Decrease mAs by a factor of 2 C. Decrease kVp by a factor of 2 D. Increase distance from tube from 2 to 3 feet. |
45. A radiologist is performing an interventional procedure using fluoroscopy. In order to reduce his or her exposure by a factor of 2, keeping all other factors equal, he would have to:
A. Decrease fluoroscopy time from 25 to 15 minutes B. Decrease mAs by a factor of 2 C. Decrease kVp by a factor of 2 D. Increase distance from tube from 2 to 3 feet. Answer: B – This is kind of a random question b/c they are so specific about decreasing exposure “by a factor of 2.” I guess they are testing if we know the relationship b/t the factors above and xray production. Time and mA are linear relationships, so decreasing mA by a factor of 2 is the answer. Distance and kVp are squared relationships, so Option C will cause a decrease of ¼ original dose. Option D will decrease dose by 4/9 of original dose. So, if they ask what will decrease the dose the most, then C would be the correct answer. Got it? |
|
|
46. For Gd-DTPA, the enhancement is related to what property?
A. Paramagnetic effect of Gd. B. Interaction between Gd and DTPA. C. Magnetic effect of DTPA D. Mass number of Gd. |
46. For Gd-DTPA, the enhancement is related to what property?
A. Paramagnetic effect of Gd. B. Interaction between Gd and DTPA. C. Magnetic effect of DTPA D. Mass number of Gd. Answer: A – gadolinium shortens T1 (increasing T1 contrast and signal). |
|
|
47. What population of women is LEAST sensitive to radiation-induced breast cancers?
A. <20 years. B. 21-30 years C. 31-40 years D. 41-50 years E. >50 years |
47. What population of women is LEAST sensitive to radiation-induced breast cancers?
A. <20 years. B. 21-30 years C. 31-40 years D. 41-50 years E. >50 years Answer: E – highest risk for cancer but lowest risk of RADIATION induced cancer. |
|
|
48. A 10 inch by 10 inch image is digitized with a goal of 5 lp/mm resolution. How many total pixels will this image require?
A. 300,000 B. 6,450,000 C. 3.225.000 D. 1,000,000 E. 9,000,000 |
48. A 10 inch by 10 inch image is digitized with a goal of 5 lp/mm resolution. How many total pixels will this image require?
A. 300,000 B. 6,450,000 C. 3.225.000 D. 1,000,000 E. 9,000,000 Answer: B – This question is on multiple old tests, so know how to do it. Here is how: FOV = 10 inches * 2.5cm/inch * 10mm/cm = 250mm #lp = 250mm * 5lp/mm = 1250lp # pixels in FOV = 1250lp * 2lp/pixel = 2500 pixels Total # pixels = 2500 * 2500 = 6,250,000 pixels NOTE: the actual conversion factor for inches to cm is 2.54, which gives the answer of 6,450,000 pixels. The estimation above will get you close enough for this test though. |
|
|
49. In secular equilibrium A1/A2 where A1 is parent and A2 is daughter the ratio is closest to?
A. T1/T2 B. Infinity C. 1 D. 0 |
49. In secular equilibrium A1/A2 where A1 is parent and A2 is daughter the ratio is closest to?
A. T1/T2 B. Infinity C. 1 D. 0 Answer: C |
|
|
50. Two films with optical densities of 1 are placed back to back. What is the percent transmittance?
A. 0.1 B. 1 C. 0.001 D. 0 |
50. Two films with optical densities of 1 are placed back to back. What is the percent transmittance?
A. 0.1 B. 1 C. 0.001 D. 0 Answer: B – a little tricky, but here is how you do it: 1 OD + 1 OD = 2 OD (ODs add) OD = log (1/T) 2 = log (1/T) 102 = 1/T T = 0.01 or 1% |
|
|
51. Film with optical density of 1 at 10 and 3 at 100 what is the average gradient
A. 0.02 B. 0.5 C. 2 D. 4 |
51. Film with optical density of 1 at 10 and 3 at 100 what is the average gradient
A. 0.02 B. 0.5 C. 2 D. 4 Answer: C – The average gradient is the slope between two points on the H&D curve, which has a y-axis of OD and a x-axis of log of exposure. Ave Gradient = (OD2 – OD1)/(log E2 – log E1) Ave Gradient = (3-1)/(log 100 – log 10) Ave Gradient = 2/(2-1) = 2 |
|
|
52. LD 50/60 for humans
A. 300rad B. 200rad C. 150rad D. 50 rad |
52. LD 50/60 for humans
A. 300rad B. 200rad C. 150rad D. 50 rad Answer: A – on multiple tests. |
|
|
53. Doses for radioprotection guidelines are based on
A. linear nonthreshold B. linear threshold C. quadratic nonthreshold D. quadratic theshold |
53. Doses for radioprotection guidelines are based on
A. linear nonthreshold B. linear threshold C. quadratic nonthreshold D. quadratic theshold Answer: A – overestimates risks, which is why we use it. We want to be conservative. |
|
|
54. Doppler imaging based on
A. frequency delivered compared to frequency received B. frequency delivered to depth C. phase shift D. velocity delivered compared to velocity received |
54. Doppler imaging based on
A. frequency delivered compared to frequency received B. frequency delivered to depth C. phase shift D. velocity delivered compared to velocity received Answer: A – Doppler is based on frequency shift. Color flow imaging is based on phase shift. (Just FYI). |
|
|
55. The optimal kVp for carotid angiography is:
A. 40-60 B. 60-80 C. 100-120 D. 140 –180 |
55. The optimal kVp for carotid angiography is:
A. 40-60 B. 60-80 C. 100-120 D. 140 –180 Answer: B – according to the techs in the cath lab, the general kVp is about 70. The mA are high, around 470. |
|
|
56. How many counts do you need for a 95% confidence interval if the % SD equals 0.2%:
A 104 B.105 C.106 D.107 in power ot so 107 is 10 power 7 |
56. How many counts do you need for a 95% confidence interval if the % SD equals 0.2%:
A 104 B.105 C.106 D.107 ¬ Answer: C – this is on multiple old tests, so know how to do this. It seems hard, but it isn't too bad. Here's how to do it. % SD = 0.002 (given in the form of 0.2%) %SD = sqrt(N)/N = 0.002 They want 2SD (95% is 2 SD). The SD is the sqrt(N), so the equation becomes: 0.002 = 2 sqrt(N)/N This can be simplified to: 0.002 = 2/sqrt(N) N = 106 An easy thing to do is just see how many SD they want (1SD = 68%, 2 SD = 95%, 3SD = 99%) and just go straight to the simplified equation and put the number of SD on top of the sqrt(N) and solve. Hope this helps. |
|
|
57. What does NOT accentuate cell death from radiation?
A. Magnetization B. Hyperthermia C. Doxorubicin D. Hyperbaric oxygen |
57. What does NOT accentuate cell death from radiation?
A. Magnetization B. Hyperthermia C. Doxorubicin D. Hyperbaric oxygen Answer: A |
|
|
58. Greatest marrow dose is with
A. AP and LAT lumbar spine B. AP and LAT thoracic spine C. upper GI D. barium enema |
58. Greatest marrow dose is with
A. AP and LAT lumbar spine B. AP and LAT thoracic spine C. upper GI D. barium enema Answer: D |
|
|
59. Ionization chamber operates at the
A. plateau at peak kvp B. avalanche phenomena (i.e geiger mueller) C. recombination zone D. continuous discharge |
59. Ionization chamber operates at the
A. plateau at peak kvp B. avalanche phenomena (i.e geiger mueller) C. recombination zone D. continuous discharge Answer: A – review the chart in UC Davis syllabus |
|
|
60. A x-ray beam is attenuates by 8 HVL’s after traversing a patient. What is the relative beam strength (compared to the skin entrance) at the center of the patient.
A. 50% B. 25% C. 9% D. 6% E. 0.4% |
60. A x-ray beam is attenuates by 8 HVL’s after traversing a patient. What is the relative beam strength (compared to the skin entrance) at the center of the patient.
A. 50% B. 25% C. 9% D. 6% E. 0.4% Answer: D – Remember relative strength is 1/2n and n is the number of half lives. If there are 8 HVL through the patient, then there should be 4 HVL at the center of the patient. 1/(24) = 1/16 = 0.0625 |
|
|
61. Milliampere- second (mAs) relates to what aspect of the electrons:
A. velocity B. number C. flow rate D. kinetic energy E. potential energy |
61. Milliampere- second (mAs) relates to what aspect of the electrons:
A. velocity B. number C. flow rate D. kinetic energy E. potential energy Answer: B – on multiple old tests |
|
|
62. Cumulative activity is expressed by:
A. µCi (Bq) B. µCi-hr (Bq-s) C. mCi/cm3 (Bq/m3) D. mCi/g (Bq/kg) |
62. Cumulative activity is expressed by:
A. µCi (Bq) B. µCi-hr (Bq-s) C. mCi/cm3 (Bq/m3) D. mCi/g (Bq/kg) Answer: B – particular question, but it is on multiple old tests. |
|
|
63. Daily quality assurance testing for the X-ray tube and processor includes measuring:
A. kVp B. mAs C. Focal spot size D. Processor sensitometry E. Light field convergence |
63. Daily quality assurance testing for the X-ray tube and processor includes measuring:
A. kVp B. mAs C. Focal spot size D. Processor sensitometry E. Light field convergence Answer: D |
|
|
64. All of the following can be used for PET EXCEPT:
A. 11C B. 13N C. 15O D. 18F E. 32P |
64. All of the following can be used for PET EXCEPT:
A. 11C B. 13N C. 15O D. 18F E. 32P Answer: E – in general, isotopes used in PET have odd mass numbers; 18F is the exception. |
|
|
65. In computed radiography, decreasing dose while maintaining image quality is limited by:
A. look up table B. quantum mottle C. modulation transfer function D. laser reader scan time E. efficiency of X-ray to light photon conversion |
65. In computed radiography, decreasing dose while maintaining image quality is limited by:
A. look up table B. quantum mottle C. modulation transfer function D. laser reader scan time E. efficiency of X-ray to light photon conversion Answer: B – CR is a noise limited modality. |
|
|
66. The cell type with highest radiation sensitivity is:
A. Spermatazoa B. Lymphocytes C. Fibrocytes D. Granulocytes E. Chondrocytes |
66. The cell type with highest radiation sensitivity is:
A. Spermatazoa B. Lymphocytes C. Fibrocytes D. Granulocytes E. Chondrocytes Answer: B – see table below: |
|
|
67. In a scintillation camera, conversion of photons to electrical signals is done by the:
A. NaI crystal B. Photomultiplier tube C. Multichannel analyzer D. Pinhole collimator E. Photopeak detector |
67. In a scintillation camera, conversion of photons to electrical signals is done by the:
A. NaI crystal B. Photomultiplier tube C. Multichannel analyzer D. Pinhole collimator E. Photopeak detector Answer: B |
|
|
68. Reducing workstation flicker can be accomplished by:
A. Data compression B. Lower bandwidth C. Higher refresh rate D. Contrast suppression E. Synchronization |
68. Reducing workstation flicker can be accomplished by:
A. Data compression B. Lower bandwidth C. Higher refresh rate D. Contrast suppression E. Synchronization Answer: C – on multiple old tests |
|
|
69. The standard peak kilovoltage range for an upright chest radiograph with a grid is:
A. 40-60 B. 70-90 C. 110-130 D. 140-160 E. 210-230 |
69. The standard peak kilovoltage range for an upright chest radiograph with a grid is:
A. 40-60 B. 70-90 C. 110-130 D. 140-160 E. 210-230 Answer: C – usually right at 120 kVp |
|
|
70. PACS is an acronym for:
A. Picture Archive and Communication System B. Other made up choices |
70. PACS is an acronym for:
A. Picture Archive and Communication System B. Other made up choices Answer: B – just kidding, the answer is A. Wish they were this easy on the real test. |
|
|
71. Studies of heritable effects of radiation have shown that mutations in germ cells
secondary to diagnostic x-rays are: A. negligible B. most likely to be seen in first generation offspring C. most likely to be seen in second generation offspring D. other choices |
71. Studies of heritable effects of radiation have shown that mutations in germ cells
secondary to diagnostic x-rays are: A. negligible B. most likely to be seen in first generation offspring C. most likely to be seen in second generation offspring D. other choices Answer: A – heritable effects have been seen in mice and flies but not in humans. |
|
|
72. The most constant high kVp is most likely to be generated from which type of
generator? A. single phase B. three phase 6-pulse C. three phase 12-pulse D. capacitor discharge |
72. The most constant high kVp is most likely to be generated from which type of
generator? A. single phase B. three phase 6-pulse C. three phase 12-pulse D. capacitor discharge Answer: C |
|
|
73. In a PET scanner, the scintillation crystal measures:
A. positrons B. annihilation photons C. gamma radiation D. neutrons E. alpha particles |
73. In a PET scanner, the scintillation crystal measures:
A. positrons B. annihilation photons C. gamma radiation D. neutrons E. alpha particles Answer: B – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
74. Resolution in the axial dimension of ultrasound relies primarily upon
A. spatial pulse length B. spatial pulse rate frequency C. focusing length D. beam width E. line density |
74. Resolution in the axial dimension of ultrasound relies primarily upon
A. spatial pulse length B. spatial pulse rate frequency C. focusing length D. beam width E. line density Answer: A – on multiple old tests. |
|
|
76. What is the distance (in cm) of an object from the face of a transducer if the time from pulse origin to return to the transducer is 0.1ms?
A. 3.3 cm B. 6.7 cm C. 7.7 cm D. 14.4 cm E. 33 cm |
76. What is the distance (in cm) of an object from the face of a transducer if the time from pulse origin to return to the transducer is 0.1ms?
A. 3.3 cm B. 6.7 cm C. 7.7 cm D. 14.4 cm E. 33 cm Answer: C – this type of question is on almost every old test, so remember the shortcut equation: depth of object (cm) = 0.077 x time (µsec) 0.1ms = 100 µsec depth (cm) = 0.077 x 100 = 7.7 cm |
|
|
77. What MR sequence uses a sequence of 90, 180, 180,180, 180, 180, 180 flip angles?
A. IR B. SE C. EPI D. FSE E. GE |
77. What MR sequence uses a sequence of 90, 180, 180,180, 180, 180, 180 flip angles?
A. IR B. SE C. EPI D. FSE E. GE Answer: D |
|
|
78. What is the main function of a pulse height analyzer?
A. increase detector efficiency and, consequently, increase sensitivity B. minimize the effect of scatter radiation C. improve directional response D. compensate for absorption of photons |
78. What is the main function of a pulse height analyzer?
A. increase detector efficiency and, consequently, increase sensitivity B. minimize the effect of scatter radiation C. improve directional response D. compensate for absorption of photons Answer: B |
|
|
79. What are the correct settings for a compression mammography view with a breast thickness of 4.5 cm under compression and an average breast composition (50% adipose, 50% fibrous)?
A. 22 kvp, 4 mA B. 23 kvp, 20 mA C. 26 kvp, 100 mA D. 26 kvp, 160 mA E. 30 kvp, 4 mA |
79. What are the correct settings for a compression mammography view with a breast thickness of 4.5 cm under compression and an average breast composition (50% adipose, 50% fibrous)?
A. 22 kvp, 4 mA B. 23 kvp, 20 mA C. 26 kvp, 100 mA D. 26 kvp, 160 mA E. 30 kvp, 4 mA Answer: C – use 100mA with 0.3mm focal spot (screening mammogram), and 30 mA with 0.1mm focal spot (magnification view). Here is a table to keep all the modalities straight (numbers are from books and from our techs): kVp mA Chest xray (dedicated unit) ~120 500-800 Cardiac Cath and Angio 70 ~500 Mammography 26 30 (0.1mm focal spot) & 100 (0.3mm focal spot) CT 120-140 250-500 Flouro 70-100 0.8 - 4.0 KUB 80 500 Bone film 60 250 |
|
|
80. What is the maximum allowable exposure to a fetus?
A. 0.1 mSv (10 mrem) B. 5 mSv (0.5 rem) C. 1.0 mSv (0.1 rem) D. 10.0 mSv (1 rem) E. 100 mSv (10 rem) |
80. What is the maximum allowable exposure to a fetus?
A. 0.1 mSv (10 mrem) B. 5 mSv (0.5 rem) C. 1.0 mSv (0.1 rem) D. 10.0 mSv (1 rem) E. 100 mSv (10 rem) Answer: B – The answer depends over the time period questioned. Limits are 0.5rem/9mo or 50 mrem/mo. See chart on #10 for more details. |
|
|
81. Which contributes the greatest to quantum mottle (photon noise) in a fluroscopic system?
A. number of photons exiting the patient B. number of photons absorbed at the input phosphor C. input phosphor generation of light photons D. input phosphor to output phosphor E. light exiting the vacuum tube |
81. Which contributes the greatest to quantum mottle (photon noise) in a fluroscopic system?
A. number of photons exiting the patient B. number of photons absorbed at the input phosphor C. input phosphor generation of light photons D. input phosphor to output phosphor E. light exiting the vacuum tube Answer: B – see #6 for explanation. This question is on this exam twice for some reason. |
|
|
82. Gadolinium is a good MRI ferromagnetic agent because of
A. the composition of its nucleus B. unpaired valence electrons C. increased T1 D. its ferromagnetic properties |
82. Gadolinium is a good MRI ferromagnetic agent because of
A. the composition of its nucleus B. unpaired valence electrons C. increased T1 D. its ferromagnetic properties Answer: B – Gd decrease T1 and has paramagnetic properties. |
|
|
83. A pregnant technologist, wearing lead during the first eight weeks of pregnancy has a dose of 4mrem on a badge which was always worn inside of her lead apron. Which statement is correct?
A. ACR recommends abortion B. Child has high risk of microcephaly C. Child will have IUGR D. Child has a high risk of limb anomalies E. The technologist is within exposure limits |
83. A pregnant technologist, wearing lead during the first eight weeks of pregnancy has a dose of 4mrem on a badge which was always worn inside of her lead apron. Which statement is correct?
A. ACR recommends abortion B. Child has high risk of microcephaly C. Child will have IUGR D. Child has a high risk of limb anomalies E. The technologist is within exposure limits Answer: E – This was the exact question as #20, so I changed it to read “inside her lead.” Just know the dose limits. 4mrem in 2 months is well within the 50mrem/mo limit. |
|
|
84. Lateral resolution in ultrasound
A. is determined by pulse length B. depends on frequency C. depends on the velocity of the sound waves D. is best with a focused transducer E. is best in the Fraunhofer zone |
84. Lateral resolution in ultrasound
A. is determined by pulse length B. depends on frequency C. depends on the velocity of the sound waves D. is best with a focused transducer E. is best in the Fraunhofer zone Answer: D – lateral resolution depends on the width of the beam (minimal resolution is ½ of the beam width). Lateral resolution changes with depth, and is best in the focal zone. The near field length (Fresnel Zone) is better than the far field (Fraunhofer Zone). Axial resolution is determined by spatial pulse length and is independent of depth. Axial resolution is better than lateral resolution, which is why you should measure the gallbladder wall (and other stuff) in the axial plane rather than the lateral plane. |
|
|
93. Mammogram of a breast with 50/50 glandular to fatty tissue ratio has mean glandular dose of 150mrad. What is the skin exposure?
A. 75mrad B. 300mrad C. 500mrad D. 1000mrad E. 150mrad |
93. Mammogram of a breast with 50/50 glandular to fatty tissue ratio has mean glandular dose of 150mrad. What is the skin exposure?
A. 75mrad B. 300mrad C. 500mrad D. 1000mrad E. 150mrad Answer: C (probability). The AGD is about 0.25 of the ESE, so 150mrad/0.25 = 600mrad. |
|
94. Which of the following result in the least patient skin exposure? (The dashed line represents a grid, the ellipse—the patient, the shaded box—screen/film)
A. A B. B C. C D. D |
94. Which of the following result in the least patient skin exposure? (The dashed line represents a grid, the ellipse—the patient, the shaded box—screen/film)
A. A B. B C. C D. D Answer: B – the large SOD and the lack of a grid lowers dose (C would be the most for opposite reasons). |
|
|
95. Given an increase from 50 cm to 75 cm SID to maintain film density mAs must be:
A. unchanged B. Decreased b ¾ C. Increased 9/4 D. Decreased by 9/4 E. Increased by 2/3 |
95. Given an increase from 50 cm to 75 cm SID to maintain film density mAs must be:
A. unchanged B. Decreased b ¾ C. Increased 9/4 D. Decreased by 9/4 E. Increased by 2/3 Answer: C – increasing the SID lowers radiation incident on the patient, so lowers OD. To keep OD constant, the radiation must be increased by the inverse square law. (75/50)2 = 9/4 |
|
|
96. K-shell binding energies increase with:
A. Atomic number B. Mass number C. Number of electrons in shell |
96. K-shell binding energies increase with:
A. Atomic number B. Mass number C. Number of electrons in shell Answer: A – more positive charges increase the binding energies of the negative electrons. |

