![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Equation for charge |
Q= I×t Q is charge (c) I is Amperes (A) t is time (s) |
|
|
|
Equation for current |
I=◇Q÷t |
Current is the change in charge over time |
|
|
Charge on 1 e- |
1.6×10^-19C |
|
|
|
Potential difference(Equation) |
Pd=E÷Q Pd is measured in volts(v) E is energy transferred (J) Q is charge (C) |
|
|
|
Electrical power |

|
|
|
|
Resistance |
R=pd÷current R is measured in ohms Pd=v Current =I |
|
|
|
Magnetic materials |
Iron, nickel, cobalt, steel |
|
|
|
Permanent magnets |
Magnetically hard materials that retain their magnetism |
|
|
|
Soft magnets |
Magnetically soft magnets that can lose their magnetism easily |
|
|
|
Law of magnets |
Like like repel Unlike poles attract Magnetic force goes from N to S |
|
|
|
Magnetic field |
A volume of space where magnetic force is exerted |
|
|
|
Uniform magnetic field |
This is where a force is constant over a region. These field lines are all parallel. |
|
|
|
Induced magnetism |
This can happen when a soft magnetic is placed in a magnetic field and loses its magnetism when removed |
|
|
|
Right hand grip rule |
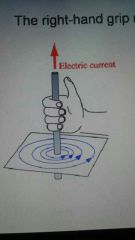
The thing is placed in the directions of the current and the direction the other fingers curl around the wire show the direction of the circular magnetic field |
|

