![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
solar system
|
the sun and all the objects that orbit around it
|
includes the sun
|
|
|
planet
|
any type of the nine primary bodies orbiting the sun a similar body orbiting another star
|
solar system
|
|
|
neutron star
|
a dead star woth the density of atomic nuclei
|
nuclei
|
|
|
red giant
|
a large reddish star late in its life cycle that fuses helium into carbon or oxygen
|
oxygen
|
|
|
white dwarf
|
a small very dense star that remains after fusion in a red giant stops
|
dense
|
|
|
supergiant
|
an extremely large star that creates elements as heavy as iron
|
large
|
|
|
supernova
|
a powerful explosion that occurs when a massive star dies
|
dies
|
|
|
constellation
|
a group of stars appearing in a pattern as seen from earth
|
group
|
|
|
big bang theory
|
a scientific theoty that the universe bagan 10 billion to 20 billion years ago in an enormous explosion
|
theory
|
|
|
red shift
|
a shift toward the red end of the spectrum in the observed spectral lines of stars or galaxies
|
shift
|
|
|
cluster
|
a group of galaxies bound by gravity
|
group
|
|
|
interstellar matter
|
the gas and dust located between the stars in a galaxy
|
galaxy
|
|
|
star
|
a huge ball of hot gas that emits light
|
emit
|
|
|
galaxy
|
a collection of millions or billions of stars bound together by gravity
|
together
|
|
|
light year
|
a unit of distance equal to the distance light travels in one year 1ly=9.5*10(15)
|
fast
|
|
|
universe
|
the sum of all matter and energy that exists that ever has existed and that ever will exist
|
exist
|
|
|
accuracy
|
the extent to which a measurment approaches the true value
|
measure
|
|
|
astronomical unit (au)
|
a unit of length, equal to the mean distance of the earth from the sun
|
earth to sun
|
|
|
kilometer
|
a unit of length, the common measure of distance equal to 1000 meters
|
length
|
|
|
exo planet
|
a planet that does not orbit the sun and orbits a different star
|
no sun
|
|
|
dwarf planet
|
a round body revolving about the sun
|
like pluto
|
|
|
rocky planet
|
a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals
|
metals
|
|
|
gas giant
|
a large planet of relatively low density consisting Helium and hydrogen
|
H and He
|
|
|
fusion
|
the process or result of joining 2 or more things to form one
|
1+1=2
|
|
|
accretion
|
the process of growth or increase typically by the gradual accumulation of multiple layers
|
grow
|
|
|
gravity
|
the force of attraction between all masses in the universe
|
force
|
|
|
Nebula
|
a immense cloud of gas and dust in interstellar or space
|
cloud
|
|
|
comet
|
a object consisting of a nucleus of ice and dust and mear where the sun
|
near the sun
|
|
|
astroid
|
large irregular shaped object in space that orbits the sun
|
sun
|
|
|
combustion
|
the process of burning something
|
fire
|
|
|
frequency
|
# of events in a given unit of time.
|
unit
|
|
|
amplitude
|
displacement of a wave from zero
|
zero
|
|
|
wavelength
|
the distance between successive crests of a wave, especially points in a sound wave or electromagnetic wave
|
distance
|
|
|
black hole
|
a region of space having a gravitational field so intense that no matter or radiation can escape
|
no escape
|
|
|
electromagnetic radiation
|
a kins of radiation including visible light, radio waves, gamma rays, and x rays in which electric magnetic fields vary simultaneously
|
rays
|
|
|
radio wave
|
an electromagnetic wave of a frequency between about 10(4) and 10(11) or 10(12) Hz, as used for long distance communication
|
10
|
|
|
infrared
|
electromagnetic radiation between microwaves and red visible light in the electromagnetic spectrum
|
electromagnetic
|
|
|
visual light
|
having a wavelength in the range between the infrared with longer wavelengths
|
wavelength
|
|
|
ultra violet
|
having a wave length shorter then of the violet end of the visible spectrum but longer that that of x rays
|
x rays
|
|
|
x ray
|
an electromagnetic wave of high energy and very short wavelength, which is ableto pass through many materials to light
|
light
|
|
|
gamma rays
|
|
rays
|
|
|
main sequence star
|
|
sun
|
|
|
proto star
|
|
medium
|
|
|
spectral line
|
|
nearby
|
|
|
|
fat
|
|
|
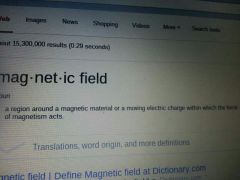
|
force
|
|
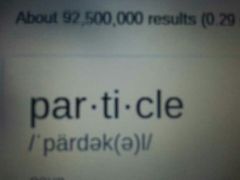
|
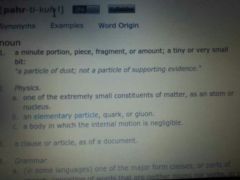
|
dust
|
|
|
hydrogen
|
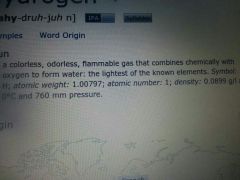
|
air
|
|
|
helium
|
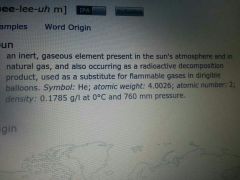
element
|
|
|
|
electrons
|
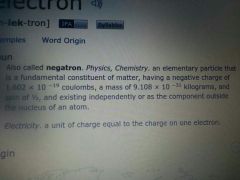
|
-
|
|
|
nucleus
|
|
|
|
|
neutron
|
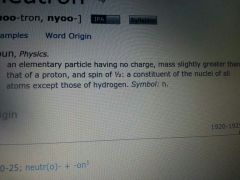
|
N
|
|
|
proton
|
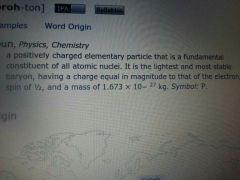
|
=
|
|
|
telescope
|
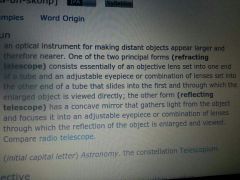
|
distant
|
|
|
elements
|
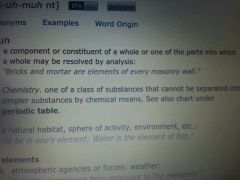
|
|
|
|
parallax
|
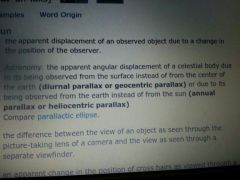
|
get it rigt
|
|
|
doppler effect
|
an increase or decrease in the frequency of sound, light, or other waves as the source and odserver move toward or away from each other.
|
sound
|
|
|
visible light spectrum
|
portion of the electromagnetic spectrun that is visible to the human eye
|
my eyes
|
|
|
earths crust
|
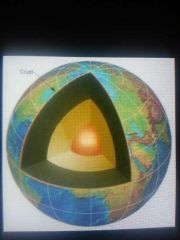
outermost solid shell of a rocky planet
|
outside
|
|
|
earths mantle
|
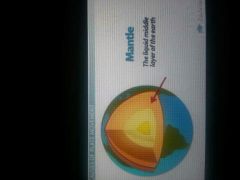
part of earth that lies beneath the crust and abovthe central core
|
under
|
|
|
earths outer core
|
outer boundary les beneath earths surface
|
surface
|
|
|
earths inner core
|
innermost part and is primarily solid ball
|
in
|
|
|
einstein
|

theoretical physicist and philosopher of science. He developed the general theory of relativity, one of the two pillars of modern day physics.
|
physics
|
|

stephen hawking
|
an english theoretical physicist and cosmologist
|
physics
|
|

issac Newton
|
english physicist and mathematics
|
math
|
|

Galileo Galilei
|
italian phyisicst, mathematician engineer astronomer and philosopher
|
space
|
|

Kepler
|
German mathematician astronomer and astrologer. planetary motion
|
math
|
|
|
experiment
|
test a hypothesis or demonstrate a known fact
|
test
|
|
|
independent variable
|
the variable that is varied or manipulated by the researcher
|
manipulate
|
|
|
dependent variable
|
the response that is measured.
|
call back
|
|
|
x axis
|
the x coordinates
|
horizontal
|
|
|
y axis
|
y coordinates
|
verticle
|
|
|
plot
|
what you need to know about statistics
|
plan
|
|
|
qualitative observation
|
subject, relies on the information
|
info
|
|
|
quantitative observations
|
using tools and methods that allow resultes to be objective in eays usually measurments or numbers
|
#
|
|
|
scientific law
|
a statement based on repeated experimental observations that observes the universe
|
observe
|
|
|
scientific theory
|
aspect of the natural world based on body facts. not guesses but reliable accounts of the real world
|
real
|
|
|
precision
|
the quality, condition, or fact of being exact and accurate
|
exact
|
|
|
accuracy
|
the quality or state of being correct or precise
|
perfect
|
|
|
aristotle
|
greek philosopher and scientist
|
philos
|
|
|
leonardo da vinci
|
italian polymath painter sculture architect musician mathematician engineer inventor anatomist geologist cartographer and writer
|
lots
|
|
|
charles darwin
|
geologist known for evolutionary theory
|
theory
|
|
|
hypothesis
|
educated guess
|
|
|
|
control
|
conducting a parallel experiment or by comparing with another standard
|
compare
|

