![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Where does the word ‘Geography’ come from? What does it mean? |
Greek meaning Earth description; to write about earth |
|
|
Know how the discipline of geography is divided (2 major types types)… which subjects are covered in geography?
|
Physical, Cultural |
|
|
What are the ‘Five Themes of Geography'? |
Location, Place, Movement/Migration, Region, Environment/Human Interaction |
|
|
What is a Great Circle? |
The shortest distance between two points on a globe. |
|
|
Know the basis of the geographic grid. How do these lines appear on the globe? Parallel? Do they ever connect? What are the important parallels?
|
Latitude = N & S Longitude = E & W, The latitudes are always straight, the meridians measure E and W, Meridians connect at poles |
|
|
Degrees, minutes and seconds… |
60 minutes in a degree, 60 seconds in a minute |
|
|
Why do seasons exist? |
Because of the tilt of the Earth's Axis and the rotation of the earth around the sun |
|
|
Where on the Earth are seasons more extreme, or less extreme? |
More extreme at the north and south pole, northern hemisphere has distinct seasons |
|
|
How is the tilt of the Earth related to seasonality and the length of day/night? |
The portion of the earth that is pointed towards the sun determines day/night |
|
|
What is the sub-solar point?
|
An area where the sun's rays shine perpendicular to the Earth's surface |
|
|
What is a solstice? |
Either of the two times in the year, the summer solstice and the winter solstice, when the sun reaches its highest or lowest point in the sky at noon, marked by the longest and shortest days |
|
|
What is an equinox? |
The time or date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the celestial equator, when day and night are of equal length |
|
|
Insolation… what is it? Where does it come from? |
Incoming radiation from the sun |
|
|
Diffusion… why is the Sun’s energy more direct at the equator than at the poles? |
The sun is pointed at the equator, making the energy more intense, whereas the energy is diffused by the time it reaches the poles |
|
|
‘Maps’ versus ‘Globes…’ which are more accurate? What happens when we project the Earth’s surface on a map?
|
Globes are more accurate since they are in 3d , maps distort distances between point or shape of the land |
|
|
What are ‘Isolines?’ Know the different types of isolines and what they measure… contour lines, isobars and isotherms
|
a line that connects points of the same value, countour lines join points of equal height above or below sea level, isobars are connecting points having the same atmospheric pressure, isotherms are connecting points having the same temperature |
|
|
What are GIS? |
A geographic information system (GIS) is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of spatial or geographical data |
|
|
What is GPS? |
A geographic positioning system is a satellite-based navigation system made up of a network of 24 satellites. |
|
|
What is remote sensing? |
Remote sensing is the science of obtaining information about objects or areas from a distance, typically from aircraft or satellites (photographs like in google earth) |
|
|
What is ‘Scale? |
A scale is a relationship on the map to earths surface. |
|
|
Representative fraction |
is ratio without units 1:10,000 hard to conceptualize |
|
|
Verbal Scale |
"1 inch= 1 mile" easy to understand but sometimes hard to conform to a paper map |
|
|
The Bar Scale |
reflects the size of the paper map |
|
|
Be able to tell a ‘Large Scale’ map from a ‘Small Scale’ map. |
A large scale map only shows a small area, but it shows it in great detail. A small scale map shows more territory, but is less detailed. Large scale "zoomed in" small scale "zoomed out" |
|
|
Global circulation and pressure systems… be able to identify major pressure cells and wind patterns. |
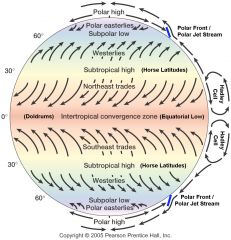
|
|
|
What is the ‘Electromagnetic Spectrum?’ |
The range of wavelengths or frequencies over which electromagnetic radiation extends |
|
|
‘Radiation?’ When/what kinds of radiation are harmful to people?
|
radiation is the emission or transmission of energy, UV rays harmful, infrared rays least harmful |
|
|
What is ‘Albedo?’ What does it mean to have a high albedo percentage? A low albedo? |
Albedo is ability to reflect energy or light, high albedo means light colors like snow or water that reflect the sun, low albedo is the asphalt or the color black |
|
|
What are the basic components of the ‘Atmosphere?’ What are the ‘Permanent Gasses,’ and which gasses do we consider ‘Variable/Greenhouse’?
|
Permanent= air we breathe gases Nitrogen, oxygen, argon; greenhouse gases Carbon dioxide, ozone, nitrous oxide |
|
|
What is ‘Atmospheric Pressure?’ |
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air in the atmosphere of Earth, Altitude affects air pressure due to gravity |
|
|
How does elevation/altitude affect atmospheric pressure/air consistency?
|
Gravity causes the pressure to increase or decrease based on the air's distance from sea level. Pressure decreases at higher altitudes. |
|
|
Know the layers of the atmosphere… how does air temperature change as it rises through each level? |
Exosphere, Thermosphere, Mesosphere, Stratosphere, Troposphere.
Gets hotter as it rises. |
|
|
What is the ‘Ozone Layer?’ Where is it? What’s happening to it? Why do we need it? |
Ozone is primarily in the stratosphere, absorbs harmful uv rays, has a hole |
|
|
What is the ‘Greenhouse Effect?’ Which factors cause it to be enhanced, or lessened? |
Short wave energy intercepts the Earth and reradiated back as long wave energy (heat). This heat becomes trapped underneath Earth’s atmosphere |
|
|
What is a ‘Pressure Gradient?’ How does it affect wind? |
The pressure gradient results in a net force that is directed from high to low pressure and this force is called the "pressure gradient force". This causes the air to move from place to place |
|
|
How does air move in areas of high pressure? How does it move in areas of low pressure? |
Wind ALWAYS flows from High to Low pressure.’ |
|
|
What causes sea breeze vs land breeze |
Wind will blow from the higher pressure over the water to lower pressure over the land causing the sea breeze. The sea breeze strength vary on the temperature difference between the land and the ocean. |
|
|
What causes Valley breeze vs mountain breeze |
During the day, the sun heats up valley air rapidly. Convection causes it to rise, causing a valley breeze. At night, the process is reversed. |
|
|
What is "El Nino" ? |
El Niño has come to refer to a whole complex of Pacific Ocean sea-surface temperature (specifically warm water) that changes and global weather events.
|
|
|
Know the steps of the water cycle .. what is a flow? what is a store? |
Precipitation, Evaporation, Condensation, and Transpiration. Flow: Water flows through the hydrological cycle |
|
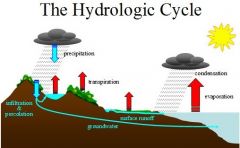
|
Water Cycle |
|
|
Know the dynamics of ‘Cyclones’ (depressions) versus ‘Anti Cyclones.’ |
Cyclones = low pressure anticyclones = high pressure |
|
|
Water Adhesion & Cohesion |
Cohesion: Water is attracted to water Adhesion: Water is attracted to other substances |
|
|
What are the phases of water? What do we know about their densities relative to each other? |
Solid, liquid, gas. Most dense = liquid, less dense = gas |
|
|
What is the ‘Saturation Curve?’ What does it measure? |
Shows how much water can be held |
|
|
What do we know about the temperature of air, and its ability to hold water vapor at various temps? |
The higher the temperature, the more water it can hold |
|
|
Three Ways to measure Humidity |
Absolute humidity is the water content of air. Relative humidity, expressed as a percent, measures the current absolute humidity relative to the maximum for that temperature. Specific humidity is a ratio of the water vapor content of the mixture to the total air content |
|
|
What is an ‘Air Mass?’ How is an air mass named? What determines its characteristics? |
Big piece of earth's atmosphere, most common = maritime tropical and continental polar |
|
|
Koeppen System |
A=Tropical/Wet, B=Dry, C=Humid/temperate, D=Wet/Extreme seasonal change |

