![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
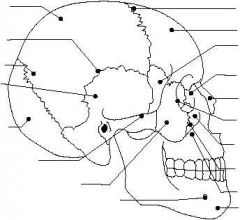
Name the major skull bones
|
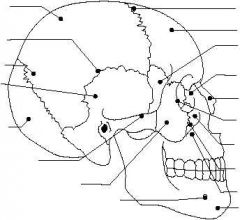
|
|
|
Where are the two pairs of salivary glands that are accessible on examination of the face? (3rd is sublingual)
|
1. The parotic gland: in the cheeks over the mandible anteriro to and below the ear...normally not palpable
2. Submandibular glands: beneatht eh mandible at teh angle of the jaw. |
|
|
Name the major neck vessels
|
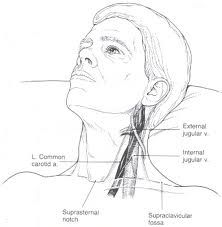
|
|
|
Name the major neck muscles
|
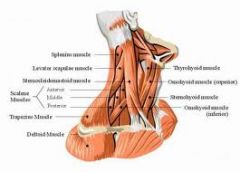
|
|
|
Which cranial nerve innervates the neck muscles?
|
Cranial nerve XI
|
|
|
describe the boundaries of the anterior triangle of the neck (helpful in describing findings in neck)
|
lies in front between the sternomastoid and the midline of the body with its base up along the lower border of the mandible and apex at the suprasternal notch
|
|
|
describe the boundaries of the posterior triangle of the neck (helpful in describing findings in neck)
|
behind the sternomastoid muscle, with the trapezius muscle on the other side and with its base along the clavicle below
|
|
|
where is the thyroid gland/
|
straddles trachea in middle of neck
|
|
|
What is the thyroid gland?
|
an endocrine gland that secretes hormones (T3 and T4) that control rates of metabolism.
|
|
|
Where is the "Adam's Apple" exactly?
|
It is the palpable notch on the upper edge of the thyroid cartilage
|
|
|
Name and locate structures/cartilage landmarks of the larynx
|
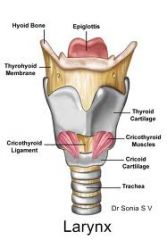
cricoid cartilage, adams apple (top of thyroid cartilage), hyoid bone, trachea, thyroid gland, sternomastoid muscle, manubrium, clavicle
|
|
|
Which direction do the head/neck lymph nodes drain
|
mostly in a generally inferior direction
|
|
|
If a lymph node is swollen what area should you explore?
|
area proximal (upstream) to that lymph node(s)
|
|
|
purpose of the lymph nodes
|
filter lymph and engulf pathogens, preventing harmful substances from entering circulation
|
|
|
Nodes are located throughout the body but only accessible for examination in what four areas?
|
head and neck
arms axillae groin |
|
|
where is the greatest supply of lymph nodes?
|
head and neck
|
|
|
Describe location of majority of the head/neck lymph nodes
|
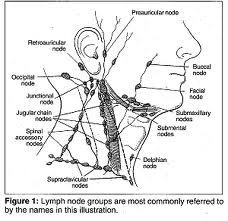
(see picture)
|
|
|
when vertigo is objective the person feels like _____ and when vertigo is subjective the person feels like _______
|
the room spins,
they themselves spin |
|
|
major symptoms of meningeal inflammation
|
acute onset of neck stiffness with headache and fever
|
|
|
normocephalic
|
denotes a round symmetric skull that is appropriately r/t body size
|
|
|
microcephaly
|
abnormally small head
|
|
|
macrocephaly
|
abnormally large head
|
|
|
edema in the face occurs where first?
|
around the eyes and cheeks where subq tissue is relatively loose
|
|
|
mumps swells which gland?
|
the parotid gland (salivary gland in front of ear)
|
|
|
edema in the face occurs where first?
|
around the eyes and cheeks where subq tissue is relatively loose
|
|
|
mumps swells which gland?
|
the parotid gland (salivary gland in front of ear)
|
|
|
fontanels
|
the spaces where sutures have not fully intersected in neonatal skull.
|
|
|
Purpose of fontanels?
|
Allow for growth of the brain during the first year of life.
|
|
|
When do fontanels close?
|
triangle shaped posterior fontanel closes by 1 to 2 months and the diamondshape anterior fontanel closes between 9 months to 2 years
|
|
|
lymphadenopathy
|
enlargement of the lymph nodes (>1cm) d/t infection, allergy or neoplasm
|
|
|
signs that a lymph node is cancerous
|
unilateral, hard, , >3cm, nontender, matted and fixed
|
|
|
in chronic inflammation, lymph nodes are usually _______
|
clumped
|
|
|
Which lymph nodes are commonly enlarged in HIV?
|
occipital
|
|
|
Is the normal thyroid gland usually palpable?
|
no
|
|
|
The trachea is pulled towards the unaffected side in what conditions?
|
aortic aneurysm
a tumor unilateral thyroid lobe enlargement pneumothorax |
|
|
The trachea is pulled towards the affected side in what conditions?
|
large atelectasis
pleural adhesions fibrosis |
|
|
What is "tracheal tug"?
|
A rhythmic synchronous downward pull that occurs with systole often in presence of an aortic arch aneurysm
|
|
|
Auscultating a bruit in thyroid means.....
|
A bruit occurs with accelerated/turbulent blood flow, so it indicates hyperplasia (proliferation of cells) of the thyroid
e.g. hyperthyroidism |
|
|
caput succedaneum
(kay-put sux sidane ium) |
edamatous swelling ad ecchymosis of the presenting part of teh head caused by birth trauma
|
|
|
cephalhematoma
|
subperiosteal hemorrhage, result of birth trauma (head cones back towards back-top of scalp) No treatment. Is reabsorbed during first few weeks of life.
|
|
|
periosteum
|
mebrane that lines the outer surface of all bones
|
|
|
skull sutures are palpable in infants until they reach ______ of age
|
6 months
|
|
|
tonic neck reflex
|
lay an infant supine, turn head to side, same side arm extends and leg flexes
|
|
|
when should the tonic neck reflex disappear
|
by 5 months (if not, may indicate brain damage)
|
|
|
Nuchal Rigidity
|
inability to flex head forward d/t stiff neck. Sign of meningitis.
|
|
|
3 major types of headaches
|
tension
migraine cluster |
|
|
tension headache
|
usually both sides
tight non throbbing mild-moderate pain gradual onset lasts 30" to days associated with stress occurs situationally (stress) |
|
|
migraine headache
|
commonly one sided,sometimes both
throbbing/pulsating rapid onset, lasts 4 hours mod to severe pain about 2x a month often preceded by aura (tingling, visual changes, vertigo abd pain) |
|
|
cluster headache
|
always one sided
continuous burning piercing pain abrupt onset lasts 45-90 minutes can occur multiple x in day (clusters) exacerbated by ETOH, stress, wind or heat exposure relieved by moving/pacing |
|
|
hydrocephalus
|
obstruction of drainage of CSF results in excessive accumulation, increasing ICP and enlargement of head
|
|
|
Macewen's sign
|
"crack pot" sound on percussing head, common in hydrocephalus, normal in infants pre fontanel closure
|
|
|
hydrocephalus
|
obstruction of drainage of CSF results in excessive accumulation, increasing ICP and enlargement of head
|
|
|
Macewen's sign
|
"crack pot" sound on percussing head, common in hydrocephalus, normal in infants pre fontanel closure
|
|
|
Paget's disease ("padge-it")
|
skeletal disease of increased bone resorption and formation which softens, thickens and deforms bone. Affects 10% of those older than 80, more in males.
Characterisitcs: bowed legs, fractures, enlarged skull presses on cranial nerves-headaches, deafness etc. |
|
|
Acromegaly
|
excessive sxrn of growth hormone from pituitary gland after puberty creates enlarged skull and thickened cranial bones (often pituitary tumor)
|
|
|
Torticollis (Wryneck)
|
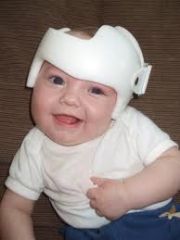
hematoma in one sternomastoid muscle (often d/t intrauterine malposition) results in head tilt. Permanent ROM problems if not treated
|
|
|
goiter
|
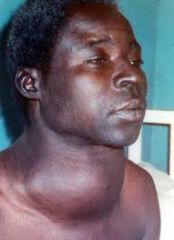
chronic enlargement of the thyroid gland that occurs in some regions of the world where the soil is low in iodine. NOT d/t neoplasm
|
|
|
Pilar Cyst (Wen)
|
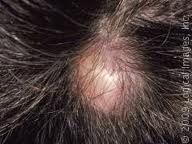
smooth firm swelling on scalp that contains sebum and keratin. Benign growth.
|
|
|
Parotid gland enlargement
|
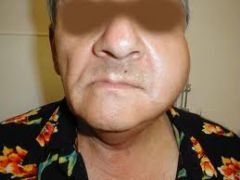
rapid painful enlargement of the parotid, occurs with mumps or blockage of duct, abscess or tumor. Can occur with dehydration.
|
|
|
Fetal alcohol syndrome
|
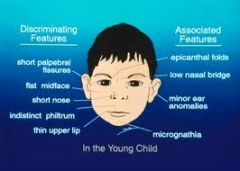
growth and developmental abnormalities from drinking during pregnancy.
Characteristic facies: mid facial hypoplasia, short pallpebral fissures (eyes), thin upper lip |
|
|
Down syndrome
|
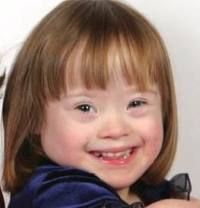
chromosomal aberration (trisomy 21).
|
|
|
Cushing syndrome
|

excessive sxrn of corticotropin hormone (ACTH) and chronic steroid use, person develops "moon face", prominent jowls, red cheeks, hirsuitism upper lip
|
|
|
myxedema
|
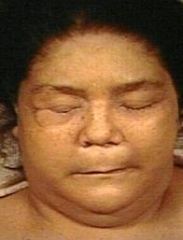
deficiency of thyroid hormone, when severe, causes a non pitting edema or myxedema
|
|
|
Bell's palsy
|

lower motor neuron lesion (peripheral) producing cranial nerve VII paralysis which is almost always unilateral. rapid onset.
Cant' whistle, raise eyebrows etc. |
|
|
scleroderma
|
literally "hard skin", rare connective tissue disease characterized by chronic hardening and shrinking, degenerative changes in skin, vessels, skeletal muscles, synovium.
Characteristic facies: hard shiny skin, thin pursed lips |
|
|
atopid (allergic) facies
|
children with chronic allergies have these facial characteristics: exhausted face, blue shadows below eyes d/t sluggish venous return, open mouth breathing, central facial pallor
|
|
|
Parkinson syndrome
|
deficiency of neurotransmitter dopamine and degeneration fo basal ganglia in the brain. Immobility of features produces flat expression.
|
|
|
most common cause of hyperthyroidism
|
Grave's disease (goiter, bulging eyes)
|
|
|
cachetic appearance
|
accompanies chronic wasting disease such as cancer, dehydration, starvation. sunken eyes, hollow cheeks, exhausted, defeated expression
|
|
|
stroke facies
|
an upper motor neuron (central ) lesion. Upper half of face not affected because of the intact nerve from the unaffected hemisphere. can still close eyes/wrinkle forehead.
|

