![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are the physical examinations techniques |
Inspection, palpating, percussion, auscultation, olfaction |
Inspection: observation of patient, use of otoscope, penlight etc Palpation: use of touch to gather data eg temperature, skin texture, moisture, edema Percussion: talking, vibration especially useful for abdomen and lungs Auscultation: the use of hearing/listening olfaction: use of smellp |
|
|
When to position clients |
Upright: assess gait, cerebellum function, neurological, musculoskeletal functions
Sitting upright: vitals, breasts, cardiovascular Supine: abdomen, breasts, extremities, pulses (lying flat on back) Fowler/semi Fowler: head is elevated 60/45 degrees Dorsal recumbent: flexing the knees . Abdominal assessment Lithotomyw: dorsal recumbent position with feet in stirrups for female pelvic exams Lithotomy; dorsal recumbent position for female pelvic exams but feet in stirrups |
|
|
|
Supine |
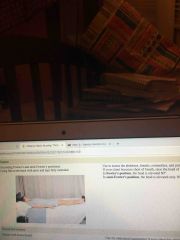
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Dorsal recumbent |
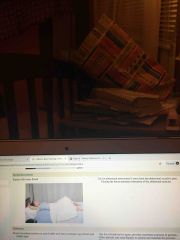
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Lithotomy |
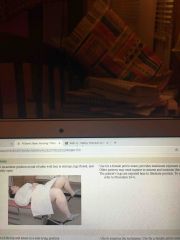
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Sims |
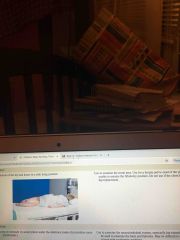
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Prone |
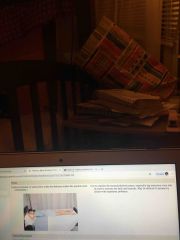
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Lateral recumbent |
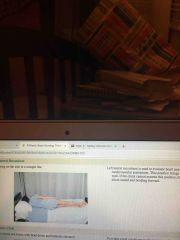
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is Ptosis |
Drooping of the lid seen in a client who experience a stroke |
|
|
|
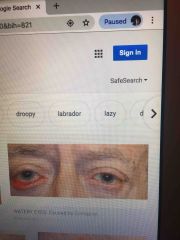
Ectropian |
An everted eyelid commonly seen in an older adults secondary to loss of skin |
|
|
|
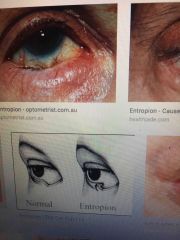
Entropion eye |
An inverted eyelid which can lead to corneal damage |
|
|
|
What do you do to assess hearing |
The Weber and Rinne tests Weber year: using the vibrating tuning fork to assess vibrations Rinne test: use of tuning fork to compare air conduction and bone conduction. Romberg test: assess equilibrium |
|
|
|
What areas do listen the heart |
All people enjoy time magazine |
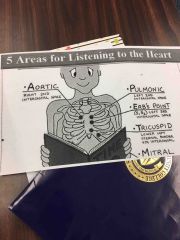
|
|
|
What do you hear in the heart |
Heart sounds such as first heart sounds: lub, s1 Second: dub, s2 |
|
|
|
Arteries carry blood |
Away from the heart |
|
|
|
Veins carry blood |
Pulmonary bones transport oxygenated blood from lungs to left atrium. Systemic veins return oxygenated blood from periphery to right atrium |
|
|
|
What is the Glasgow coma scale |
Evaluated eye opening response, Motor response Verbal response |
|
|
|
How to check LOC |
Time, place and person |
|
|
|
Cerebral functions |
Alert: follows commands in timely fashion Lethargic: appears drowsy, drifts asleep Stuporous: requires vigorous stimulation before responding Comatose: does not respond to verbal or painful stimili |
|
|
|
Normal pulse |
60-100 bpm |
|
|
|
Normal respiratory rate |
12-20 breaths/min |
|
|
|
Normal temperature |
97.3-98.6 degrees Fahrenheit or 36.3-37 degrees Celsius |
|
|
|
Normal blood pressure |
120/80 |
|
|
|
How to measure bmi |
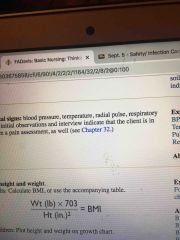
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
How to check skin turgor |
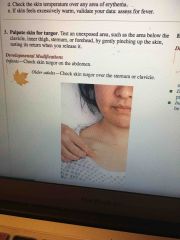
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
To check for moisture |
Palpate skin for moisture/hydration using the dorsum of your hand |
|
|
|
How to inspect for edema |
Press with fingertip for 5 sec over a bony area, feet etc |
|
|
|
How to assess capillary refill |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Why do we do the 6 cardinal points |
To assess extra ocular movements |
|
|
|
Name some abnormal lung sounds |
Crackles/rales |
Cracking, popping for pneumonia, congestive heart failure, bronchitis, emphysema |
|
|
Abnormal lung sounds |
Crackles, rhonchi, wheezes, stridor, friction rub, grunting |
|
|
|
Describe rhonchi |
Course, snoring due to mucus secretions in the large airways |
|
|
|
Wheezes |
High pitched musical squeaking sounds due to asthma, emphysema |
|
|
|
Stridor |
High pitch honking sound due to acute respiratory distress |
|
|
|
Grunting |
High pitch tubular sound heard on expiration due to emphysema |
|
|
|
What order is physical assessment done |
Inspection, palpitation, percussion, auscultation |
|
|
|
What is pulse pressure |
Difference between systolic and diastolic pressure readings |
|
|
|
To assess pedal pulse what is location |
Top of foot |
|
|
|
Normal urine output |
1500 ml |
|
|
|
Where is the apical pulse |
Fifth intercostal space at left mid clavicle line |
|
|
|
Vesicular sounds |
Soft and low pitched breezy sound heard over most of the peripheral lung fields |
|
|
|
Cheyne stroke respiration |
Irregular patterns of rapid waxing and waning breaths with periods of apnea |
|
|
|
Snellen chart |
Bottom value eg 20/60, is given credit because it is distance at which the client with normal vision can read the chart |
|
|
|
Capillary refill |
Greater than 3 seconds indicates poor perfusion |
|
|
|
Blak |
Bbabanb |
Bbb |

