![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nurse obtains from observation the client has a broken arm. |
Primary objective data |
|
|
CNA tells you the client's said her shoulder is sore. |
Secondary subjective data |
|
|
Physical therapist notes indicate the client can not sit up. |
Secondary objective data |
|
|
The client tells the nurse they have a headache |
Primary subjective data |
|
|
Preliminary actions |
Introduce self
Identify patient (Name/DOB) Gather supplies Explain procedure Wash hands Provide privacy |
|
|
Good practices while performing assesment |
Offer toilet
Comfortable position Comfortable bed height Good lighting/warmth Mute TV/Radio Auscultate bare skin Holding stethoscope with “V” positioning Documentation |
|
|
Techniques used in physical assessment |
Inspection Palpation Auscultation Percussion |
|
|
Percussion sounds |
Flate Dull Resonance Tempany (musical) |
|
|
Bell of stethescope tranmists |
Low frequency |
|
|
Pain scale |
Mild pain: 1-3
Moderate pain: 4-6 Severe pain: 7-10 |
|
|
Neurological assessment focus on?
|
•Level of Consciousness
•Sensory Deficits •Movement of Extremities (MOE) •Grips •Gait •Speech •Pupils |
|
|
Thigh Blood Pressure (bladder of cuffmust be over the posterior _______ artery for the reading to be accurate)
|
popliteal |
|
|
If there is a difference of ____mmHg between arms this needs to be reportred to the physican |
10 |
|
|
Normal Temp is ___.__F - 99.5F
|
96.8 |
|
|
Pulse sites |
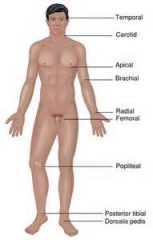
Temporal Carotid Apical Brachial Radial Femoral Popliteal Posterior tibial Dorsalis pedis |
|
|
Pulse Evaluation: Quality or amplitude
|
0 Absent (Doppler)
1 +- Thready/Weak 2 +- Normal 3 +- Increased 4 +- Bounding |
|
|
Capillary refill (Delayed return of color-arterial insufficiency)
< 3 sec in adults < __ sec in children |

2 |
|
|
Cardiacoutput
|
Volume of blood pumped into arteries |
|
|
PMI |
Point of maximum impulse (apical pulse) |
|
|
Pulse volume
Pulse rhythm Pulse deficit * |
Strenght or amplitude Pattern (equal rate) Difference between two pulse sites |
|
|
Factors affecting pulse |
Age Sex Exercise Rest and Temperature Medication Hypovolemia/dehydration (loss of blood/vol) Stress Position Pathology (Electrolyte imbalance) |
|
|
Head assesment |
•Hair •Scalp •Ears •Nose •Eyes •Lips •Mouth •Tongue |
|
Pupil Abnormalities
|
Normal size of pupils 3-7mm
|
|
|
Eupnea |
Good breathing |
|
|
Soft intensity, low pitched “gentle sighing sound” (5:2 ratio) Best heard at base of lungs
|
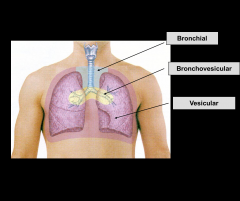
Vesicular
|
|
|
Moderate-intensity and moderately pitched “blowing sound” (1:1 ratio) Best heard 1st and 2nd ICS
|
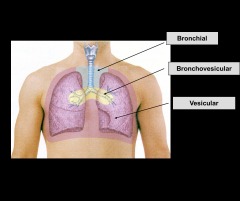
Broncho-vesicular
|
|
|
High-pitched, loud, “harsh sound" (1:2 ratio) Best heard anteriorly over the trachea (also called tracheal breath sounds)
|
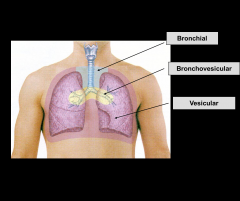
Bronchial
|
|
|
Caused by fluid that has leaked in the airways. They are characterized as discontinuous high pitched bubbling sounds |
Crackles (formally known as "Rales") |
|
|
Typically associated with secretions that are obstructing the larger airways. This causes a lower pitched vibrating sound on auscultation that is similar to snoring. May clear with cough. |
Sonorous wheeze (rhonchi) |
|
|
Characterized by a low pitched grating sound similar to the sound of walking on snow.
|
Pleural Rub
|
|
|
High pitched vibration caused by bronchispasm or asthma |
Wheezes |
|
|
formed accidentally or in an unusual anatomical position.
|
adventitious |
|
|
O 2 Sat % < 93%
|
abnormal |
|
|
Deep and labored breathing pattern often associated with severe metabolic acidosis, particularly diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) but also kidney failure.
|
Kussmaul Respiration
|
|
|
Labored or difficult breathing |
Dyspnea
|
|
|
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) that occurs when lying flat, causing the person to have to sleep propped up in bed or sitting in a chair.
|
Orthopnea
|
|
|
Slower than normal breathing < 10 bre/min |
Bradypnea |
|
|
Mixture of saliva and mucus coughed up from the respiratory tract
|
Sputum |
|
|
Measures patients likleyness of developing a pressure ulcer |
Braden Scale |
|
|
Exudate |
drainage |
|
|
Bruises
Initially appears ________ looking Day 1-2: blue or purple Day 6: _______ Day 8-9: yellowish-_________ 2-3 weeks: normal color |
Reddish Greenish Brown |
|
|
Serous |
watery yellow drainage |
|
|
Sanguineous |
More of a pure blood appearance |
|
|
consisting of, containing, or discharging pus |
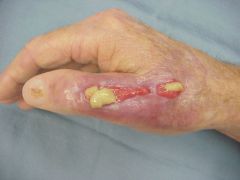
Purulent |
|
|
Containing or relating to both blood and the liquid part of blood (serum). Watery pink drainage |

Serosanguineous |
|
|
< 1cm in diameter.
Small, raised, solid pimple or swelling, often forming part of a rash on the skin and typically inflamed but not producing pus. |
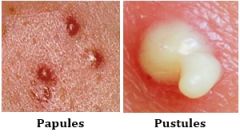
Papule
|
|
|
(ex. port wine or brown birth marks, freckles, flat moles, petechiae) they are flat and are 1 mm-1cm
|
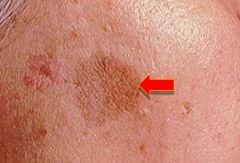
Macule
|
|
|
are dry lesions > 1 cm (ex. psoriasis)
|
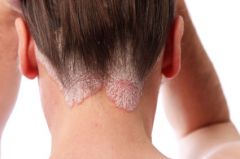
Plaques
|
|
|
(ex. mosquito bite or hives) is a reddened collection of fluid (edema of the skin), irregular in shape
|
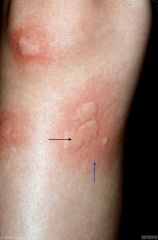
Wheal
|
|
|
are elevated solid, hard masses that extends deep into the dermis (0.5-2 cm - 0.2-0.8 in)
|
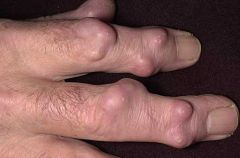
Nodules
|
|
|
are larger than 2cm and may have an irregular border (malignant melanoma).
|
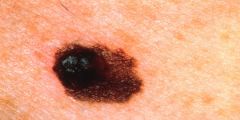
Tumors
|
|
|
thin translucent mass that is filled with serous fluid or blood. <0.5 cm (0.2 in.) (ex. Herpes simplex, early chicken pox, small burn blisters
|
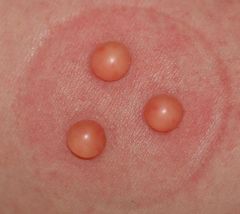
Vesicle (bulla's are large in size)
|
|
|
are vesicles filled with pus.
|
Pustule
|
|
|
pale due to inadequate circulation
|
Pallor
|
|
|
blueness
|
Cyanosis
|
|
|
Yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes
|
Icteric (Jaundice)
|
|
|
wasting away of the muscle
|
Atrophy
|
|
|
skin loss extending into the dermis or subcutaneous tissue
|
Ulcer
|
|
|
area of fibrous tissue after an injury such as a cut (laceration)
|
Scar
|
|
|
to scratch, abrade or strip off the skin by physical means, linear erosion
|
Excoriation
|
|
|
hair loss/ baldness
|
Alopecia
|
|
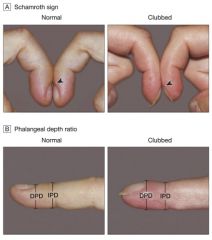
Nail beds: should be 160 degree angle
|
Clubbing
|
|
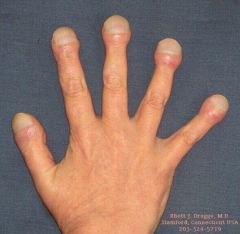
(180 degree or greater) long term lack of oxygen.
|
Clubbing of fingers
|
|
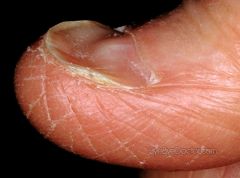
Spooning of the nail may indicate _____ deficiency _________
|
iron
anemia |
|
|
an unintentional (involuntary), rhythmical alternating movement of a muscle. Alternating contraction and relaxation of a muscle
|
Tremors
|
|
|
twitching of muscle fibers
|
Fasciculation
|
|
|
redness |
erythema |
|
|
Enlardeg pupils |
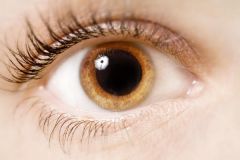
Mydriasis |
|
|
Constricted Pupils |
Miosis |
|
|
_________ auscultation involves the use of a stethoscope to amplify the sounds from within the body, like a heartbeat.
|
indicrect |
|
|
Vomiting casuses heart rate to.... |
drop (vegas nerve) |
|
|
a region of injured tissue or skin in which blood capillaries have been ruptured; a bruise
|
Contusion |
|
|
is a wound caused by superficial damage to the skin, no deeper than the epidermis.
|
abrasion |
|
|
Meaning both sides |
Bilateral |
|
|
Chest |
thoracic |
|
|
Eye test |
Direct pupil + concensual response Pen near to far 6 point extracellular muscle test |

