![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Antimicrobial Agents |
control the growth of microbes |
|
|
Disinfection |
the destruction or removal of vegetative pathogens but not bacterial endospores used on inanimate objects |
|
|
Sterilization |
the complete removal or destruction of all viable microorganisms used on inanimate objects destroys 100% of microbes including viruses and endospores |
|
|
Antisepsis |
chemicals applied to body surfaces to destroy or inhibit vegetative pathogens |
|
|
Primary Targets |
microbes causing infection or spoilage include: vegetative bacterial cells (endospores), fungal hyphae and spores, yeast, protozoan trophozoites and cysts, worms, viruses, prions |
|
|
Microbial Control Methods |
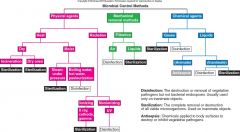
physical agents, chemical agents, mechanical removal method |
|
|
Sanitization |
mechanically removes microbes- degermation |
|
|
Factors That Affect Death Rate |
number of microbes, types of microbes- (endospores, viruses, cysts, prions), temperature, pH, concentration or dosage of agent, mode of action of the agent, presence of solvents; organic matter; or inhibitors, time of exposure |
|
|
Antimicrobial Points of Attack |
cell membrane- (soaps, topicals), cell wall- antibiotics, protein- (heat, metals, pH), DNA- mutation |
|
|
Physical Microbial Control Methods |
heat- (moist, dry), cold temp, desiccation, radiation, filtration |
|
|
Heat |
physical control method when moist it denatures proteins include: autoclave |
|
|
Autoclave |
steam under pressure moist heat under pressure used to sterilize can't autoclave plastic- it will melt |
|
|
Steam Sterilization |
stream must contact item's surface |
|
|
Thermal Death Time (TDT) |
a sterilization time shortest time to kill all test microbes at a specified temperature |
|
|
Thermal Death Point (TDP) |
a sterilization point lowest temperature to kill all microbes in sample in 10 minutes |
|
|
Boiling Water |
at 100C for 30 min to destroy non-spore forming pathogens disinfection |
|
|
Pasteurization |
mild heating to kill pathogens destroys bacteria in wine and raw milk kills pathogens and spoilage microbes heating and cooling method destroys mesophiles flash: 72C, 16 sec, then cool to 4C or 65C for 30 min |
|
|
Dry Heat |
has higher temp. than moist heat include: incineration, dry ovens |
|
|
Incineration |
form of dry heat flame or electric heating coil ignites and reduces microbes and other substances |
|
|
Dry Ovens |
150C - 180C ruins proteins |
|
|
Refrigeration and Freezing |
slows bacterial enzyme action- bacteriostatic bacteria don't divide bacteria are not killed- not bactericidal retards food spoilage |
|
|
Desiccation |
drying gradual removal of water from cells leads to metabolic inhibition no effective microbial control many cells retain ability to grow when water is reintroduced |
|
|
Lyophilization |
freeze drying preservation |
|
|
Freeze Drying |
lyophilization removes water with low temperatures keeps texture of food fibers add water and fresh food returns can preserve microbe specimens for years |
|
|
Ionization Radiation |
deep penetrating power breaks DNA, gamma rays, x-rays- destroys DNA used to sterilize medical supplies and food products |
|
|
Ultraviolet Light Non-ionizing |
poor penetration used to sterilize and disinfect food, phamaceutical products, medical and lab devices, water and packaging damages DNA lower power |
|
|
Water Disinfection System |
UV light non-ionizing prevents water borne illness |
|
|
Hospital Germicidal Lamps |
UV light sterilizes equipment, water, and air in operating rooms treats acne, psoriasis sterile hoods use UV |
|
|
Nonionizing Radiation |
for sterilizing air, water or surfaces |
|
|
Filtration |
physical removal of microbes used to sterilize heat sensitive liquids sterilizes air in hospital isolation units and industrial clean rooms |
|
|
High-level Germicides |
kill endospores may be sterilants |
|
|
Intermediate-level |
kill fungal spores (no endospores), TB, and viruses used to disinfect devices that contact mucous membranes |
|
|
Low-level |
kill vegetative bacteria, vegetative fungal cells, and some viruses clean surfaces that touch skin |
|
|
Halogens |
a germicidal include: chlorine, iodine, bromine, fluorine, At used for water |
|
|
Chlorine |
a halogen used to clean out swimming pools, drinking water, sewage, wastewater, inanimate objects |
|
|
Iodine |
a halogen an antiseptic betadine: surgical scrub milder disinfectants, ointments |
|
|
Phenolics |
a germicidal disrupts cell walls, membranes, and proteins low to intermediate level include: triclosan a chemical disinfectant (ex. lysol, chlorhexidine) |
|
|
Triclosan |
a phenolics additive to soaps |
|
|
Chlorhexidine |
a germicidal chlorine + organic rings clings to cell walls important low to intermediate level preoperative scrubs, skin cleaning, and burns dental |
|
|
Alcohols |
a germicidal denature proteins and dissolves lipids effective against most bacteria, fungi and many viruses include: medical wipes, hand sanitizer gels disinfects surfaces |
|
|
Hydrogen Peroxide |
a germicidal produces oxygen ions that damage protein and DNA forms oxygen- toxic to anaerobes antiseptic at low concentrations strong solutions are sporicidal |
|
|
Alkylating Agents |
toxic hazards found in: cidex, aldesen, hospex, sporicidin, omnicide, matricide, wavicide andothers limit the exposure of this product |
|
|
Glutaraldehyde |
an aldehyde amd alkylating agent sensitive for heat sensitive instruments used as a tissue fixative and in developing of x-rays |
|
|
Gases and Aerosols |
strong alkylating agents include: ethylene oxide, propylene oxide high level sterilize and disinfect plastics and prepackaged devices, foods |
|
|
Soaps and Detergents |
detergents: surfactants that dissolve oils and the germs that hide in them, disrupt membranes which have lots of lipids soap and water: remove most bugs, a chemical and physical agent include: quaternary ammonia compounds |
|
|
Quaternary Ammonia Compounds (Quats) |
act as surfactants poke holes in membranes very low level |
|
|
Soaps |
germicide additive? requires much contact time |
|
|
Heavy Metals |
solutions of silver and mercury (deadly and potent) kills vegetative cells in low concentrations inactivate proteins- denaturation low level include: merthiolate, silver, nitrate, silver |
|
|
Silver Nitrate |
kills gonococci excellent to treat burns |
|
|
Colloidal Silver |
began in 1800's before antibiotics drinking water and silver ions blue man |
|
|
Acid Additives |
in flour and cosmetics inhibits microbes ex. buttermilk |
|
|
Aldehydes |
high level alkylating protein and DNA include: glutaraldehyde, formaldehyde |
|
|
Formaldehyde |
an aldehyde disinfectant preservative toxicity limits use |

