![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do electromagnetic interactions involve?
|
- particles that have a property called electric charge
- electrically charged objects are accelerated by electric forces. |
|
|
What does it mean by acquiring a net electric charge?
|
becoming charged
|
|
|
21.1 Experiments in electrostatics
|
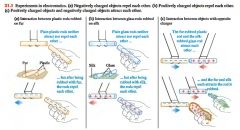
2 (+) charges or 2 (-) charges repel each other. A (+) charge and a (-) charge attract each other.
|
|
|
The structure of atoms ca be described in terms of what 3 particles:
|
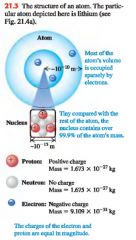
1. (-) electrons
2. (+) protons 3. neutral neutrons |
|
|
21.4 A atom can be neutral, positive or negative:
|

|
|
|
What makes a neutral atom, neutral? and does it have an net electric charge?
|
# of e- = # of protons
net electric dipole = 0 |
|
|
Atomic #:
|
# of protons or e-s in a neutral atom of an element
|
|
|
positive ion:
|
(+) charged structure
|
|
|
negative ion:
|
(-) charged structure
|
|
|
ionization:
|
gaining/ losing e-s
|
|
|
The principle of conservation of charge:
|
the algebraic sum of all the electric charges in any closed system is constant.
|
|
|
conservation of change:
|
in any charging process, charge is not created or destroyed; it is merely transferred from one body to another.
|
|
|
What is a natural unit of charge?
|
the magnitude of charge of the electron or proton
|
|
|
The chemical bonds that hold atoms together to form molecules are due to?
|
electric interactions between the atoms
|
|
|
Conductor:
|
permit the easy movement of charge through them (ex: copper wire)
|
|
|
insulator:
|
do not permit the easy movement of charge through them (ex: rubber band)
|
|
|
Charging by induction:
|

|
|
|
Polarization:
|
a slight shifting of charge w/ in the molecules of the neutral insulator
|
|
|
Columb's Law:
|

The magnitude of the electric force between 2 point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges & inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
(note: k= proportionality constant) |
|
|
What is the SI unit of electric charge?
|
Coulomb (1c)
|
|
|
Coulomb's law: force between two point charges:
|
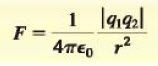
|
|
|
What does coulomb's law describe?
|
only the interaction of two point charges.
|
|
|
Principle of superposition of forces:
|
- when two charges exert forces simultaneously on a third charge, the total force acting on the charge is the vector sum of the forces that the two charges would exert individually.
- holds for any # of charges. |
|
|
Problem-Solving Strategy 21.1: Coulomb's Law
|

|
|
|
What is the best way to visualize the repulsion between A & B:
|
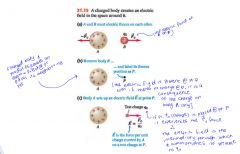
1. 1st envision that body A, as a result of the charge that it carries....
---- somehow modifies the properties of the space around it 2. then body B, as a result of the charge it carries... ---- senses how space has been modified @ its position, responds: to experience the electric force of A on B. |
|
|
Because the point charge q would experience a force at any point in the neighborhood of A, the electric field that a produces.....
|
exists at all points in the region around A.
|
|
|
A single charge produces an electric field in the surrounding space, but can the electric field exert a net force on the charge that created it?
|
no can not exert a net force on itself
|
|
|
How is the electric force on a charged body exerted?
|
by the electric field created by other charged bodies
|
|
|
How do you find out whether there is an electric field at a particular point?
|
- place a small charged body (test charge) @ that point.
---- if the test charge experiences an electric force, then there is an electric field at that point. - this field is produced by charges other than q. |
|
|
The definition of electric field as electric force per unit charge:
|
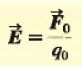
|
|
|
Force exerted on a point charge q by an electric field E:
|
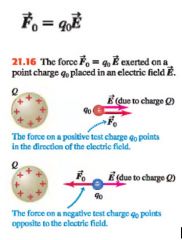
|

