![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what characteristic is responsible for the branching off of sponges from the other animals? |
no true tissue |
|
|
what level of organization do they demonstrate? |
cell level |
|
|
what does the word "porifera" mean? |
pore bearers |
|
|
what is the name of the flagellated cells seen in sponges? |
choanocytes |
|
|
what characteristics are used to divide this phylum into classes? |
canal systems, flagellated cells and skeletal structure |
|
|
what is the name of the central cavity of sponge body types and skeletal structures? |
spongocoel |
|
|
what is the name of the large opening at the top of the sponge? |
osculum |
|
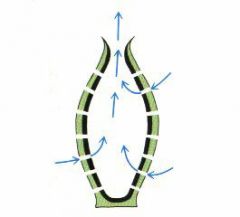
what is this body type and where are the flagellated cells? |
asconoid: flagellated spongocoel
|
|
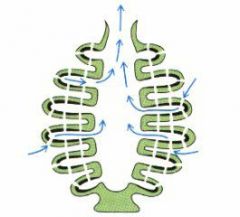
what is this body type and where are they flagellated cells? |
syconoid:flagellated canals |
|
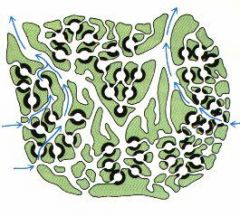
what is this body type and where are the flagellated cells? |
leuconoid: flagellated chambers |
|
|
what are the name of the skeletal structures seen in sponges? what are they made of? |
spicules: made of calcium carbonate or silica
made of spongins (protein) |
|
|
type of digestive system? |
none, intracellular digestion |
|
|
type of excretory system? |
none |
|
|
type of circulatory system? |
none |
|
|
type of respiratory system? |
none |
|
|
type of nervous system? |
none, local reactions
|
|
|
type of body cavity? |
none |
|
|
type of asexual reproduction? |
budding or gemmules |
|
|
type of sexual reproduction? |
egg and sperm |

