![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is ionization
|
Ionization occurs when an electron is ejected from a neutral atom, leaving behind
a positive ion. |
|
|
What is ionizining radiation
|
Electromagnetic radiation with sufficient energy to remove electrons is called ion-
izing radiation. |
|
|
Are X-rays and gamma rays considered ionizing radiation
|
yes
|
|
|
What are 2 types of ionizing radiation
|
Radiation may be directly ionizing (involving charged particles) or indirectly ion-
izing (involving uncharged particles such as neutrons, x-rays, and gamma rays). |
|
|
What is the amount of energy needed to generate one electron-ion pair in air
|
33 eV
|
|
|
How do charged particles loss energy
|
Charged particles lose energy when passing through matter by interacting with
electrons in nearby atoms. |
|
|
Name 5 types of ionizing particles
|
Electrons, positrons, protons, neutrons, and alpha particles are examples of ioniz-
ing particles |
|
|
What is linear energy transfer
|
Linear energy transfer (LET) measures the loss of energy of a charged particle in
thousands of electron volts for each micrometer of distance traveled by the particle. |
|
|
What increases the loss of energy by a charged particle
|
increasing charge
increasing mass decreasing velocity |
|
|
What are considered low-LET radiation
|
electrons and positrons
|
|
|
How much energy is lost by electrons and positrons when traveling through1um of soft tissue
|
0,5 keV
|
|
|
How much energy does an alpha particle loss when traveling through 1um of soft tissue
|
100 keV
|
|
|
Is an alpha particle considered to be a high LET radiation
|
yes
|
|
|
Where does the loss or radiation go
|
Ionizing radiation transfers energy to electrons in the absorbing medium.
|
|
|
What happens to the energy once is absorbed by the absorbing medium
|
The energy deposited in the absorbing medium by ionizing radiation can result in
deleterious chemical modifications to molecules such as DNA. |
|
|
Do protons and neutrons have a LET that is inbetween a electron/positron and alpha particle
|
yes
|
|
|
What is a nuclide
|
Nuclei having different numbers of protons, neutrons, or both are called nuclides.
|
|
|
What is a radionuclide
|
Unstable nuclides are called radionuclides, and atoms with unstable nuclei are
called radioisotopes. |
|
|
What is a radioisotope
|
an atom with an unstable nuclei
|
|
|
What is the mass number
|
A (the sum of protons and neutrons)
# of nucleons |
|
|
What is a nucleon
|
a proton or neutron
|
|
|
What is the mass of iodine 131
|
131
|
|
|
What is the symbol for proton
|
Z
|
|
|
What are 3 types of nuclides
|
isobArs
isotoPes isotoNes |
|
|
What is an isobar
|
Nuclides having the same mass number (A) are called isobArs.
|
|
|
What is an isotope
|
Nuclides having the same atomic number (Protons) are called isotoPes
|
|
|
What is an isotone
|
Nuclides having the same number of Neutrons are called isotoNes.
|
|
|
What are isobars, isotones and isopes
|
nuclides
|
|
|
What is a radionuclide
|
an unstable nuclide
|
|
|
What is an isomer
|
an excited state of a nucleus
|
|
|
What are the isotopes of hydrogen
|
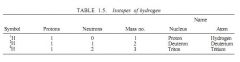
|
|
|
What is a general characteristic of stable and low mass number nuclides
|
the number of neutrons is approximately equeal to the number of protons
|
|
|
What is a general characteristic of high mass number nuclides
|
the neutrons excedd the number of protons (tungsten 74 protons and 110 neutrons)
|
|
|
Is a element has the same number of neutrons what is it called
|
an isotone
|
|
|
Are heavy nuclei generally stable
|
no
|
|
|
What is considered the mass of a heavy nuclei
|
Z>82
|
|
|
What are 3 ways an unstable nuclide can obtain stability
|
alpha, beta and gamma decay
|
|
|
What is the transformation from unstable to stable called
|
radioactive decay
|
|
|
When a nuclide undergoes decay what is the original nuclide called
|
parent and the product is called the daughter
|
|
|
What happens to mass number, energy and electric charge in nuclear transformation
|
they are conserved
|
|
|
What is a half life
|
the time for half the material to decay
|
|
|
What is the activity
|
number of transformations per unit of time
|
|
|
How is activity expressed
|
Activity is expressed mathematically as dN(t)/dt, where N(t) is the number of atoms
at time (t). |
|
|
How is activity related to lamda
|
Lambda (λ) is the decay constant, and dN(t)/dt = N(t) x λ.
|
|
|
What is current
|
Electric current is the rate of charge flow past a given point in an electric circuit, measured in Coulombs/second which is named Amperes
|
|
|
What is voltage
|
Voltage is the potential energy that makes the electrical current flow in a circuit by pushing the electrons around
|
|
|
How is current and voltage related
|
Voltage attempts to make a current flow, and current will flow if the circuit is complete. Voltage is sometimes described as the 'push' or 'force' of the electricity, it isn't really a force but this may help you to imagine what is happening. It is possible to have voltage without current, but current cannot flow without voltage
|
|
|
What is the mathematically equation for activity
|
Activity is expressed mathematically as dN(t)/dt, where N(t) is the number of atoms
at time (t). |
|
|
What is the mathematically equation for activity
|
Activity is expressed mathematically as dN(t)/dt, where N(t) is the number of atoms
at time (t). |
|
|
What is another formula for activity with the used of a decay constant
|
Lambda (λ) is the decay constant, and dN(t)/dt = N(t) x λ.
|
|
|
What is another formula for activity with the used of a decay constant
|
Lambda (λ) is the decay constant, and dN(t)/dt = N(t) x λ.
|
|
|
What is the symbol for a decay constant
|
lambda
|
|
|
What is the symbol for a decay constant
|
lambda
|
|
|
What is the formula for activity
|
N x λ, where N is the number of atoms.
|
|
|
What is the relationship of lambda and the half-life of radioactivity
|
The relation between λ and the half-life of the radioactivity (T1/2)
λ = loge(2)/T1/2 = 0.693/T1/2. |
|
|
What is the formula for activity
|
N x λ, where N is the number of atoms.
|
|
|
What is the relationship of lambda and the half-life of radioactivity
|
The relation between λ and the half-life of the radioactivity (T1/2)
λ = loge(2)/T1/2 = 0.693/T1/2. |
|
|
How is the rate of radioactive decay expressed
|
The rate of radioactive decay is typically expressed in terms of either the radioactive half-life, or the radioactive decay constant.
|
|
|
What are the SI unit of activity
|
The SI unit of activity is the becquerel (Bq), and the non-SI unit is the curie (Ci).
|
|
|
What are the units used to describe a quanity of radioactivity
|
Bq or Ci
|
|
|
What are the SI unit of activity
|
The SI unit of activity is the becquerel (Bq), and the non-SI unit is the curie (Ci).
|
|
|
What are the units used to describe a quanity of radioactivity
|
Bq or Ci
|
|
|
What is 1 becquerel
|
One becquerel is 1 transformation per second.
|
|
|
What is 1 curie
|
One curie is 3.7 x 10e10
transformations per second. |
|
|
What is a conversion of
|
One mCi = 37 MBq; 1μCi = 37 kBq.
|
|
|
What is meant by transformation
|
Nuclear transformation is what happens to unstable atom nuclei in while striving to reach stability. The nucleus of any element atom should have specific neutron/proton ratio to be a stable nucleus. In addition, the absolute number of protons should not exceed certain limit.
|
|
|
What is activity
|
the number of transformations per unit of time
|
|
|
What is an example of nuclear transformation
|
For a nucleus with neutron/proton is higher than the stability ratio, two nuclear transformations may occur to decrease the ratio in the nucleus in order to reach stability:
neutron transformation to proton plus electron where the proton remains in the nucleus and the electron is emitted from the nucleus as beta radiation emitting neutron from the nucleus as neutron radiation (this transformation is relatively rare. Example of this transformation is the unstable Krypton-87) |
|
|
Give an example of a half life an element
|
For example, the applet will tell you that the halflife of beryllium 11 is 13.81 seconds. Let's say you start with, oh, 16 grams of 11Be. Wait 13.81 seconds, and you'll have 8 grams left; the rest will have decayed to boron 11. Another 13.81 seconds go by, and you're left with 4 grams of 11Be; 13.81 seconds more, and you have 2 grams...you get the idea.
|
|
|
Can you predict when a certain atom is going to decay
|
no, You'll also notice that the pattern of atoms in the top picture is random-looking, and different each time you run the applet, but the graph below always has the same shape. It's impossible to predict when a specific atom is going to decay, but you can predict the number of atoms that will decay in a certain time period.
|

