![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition, unit and symbol of heat? |
Heat is a form of energy that causes a rise in temperature when added or fall when withdrawn. Its unit is joules (J). Its symbol is Q. |
|
|
What is the definition, unit and symbol of heat capacity? |
Heat capacity of an object is the heat required to change its temperature by 1 kelvin. Its unit is J K-1. Its symbol is C. |
|
|
What is the formula of heat capacity? |

|
|
|
What is the definition, unit and symbol of specific heat capacity? |
Specific heat capacity of a substance is the amount of heat energy needed to change 1 kg of a substance by 1 kelvin. Its unit is J kg-1 K-1. Its symbol is C. |
|
|
What is the formula of specific heat capacity? |
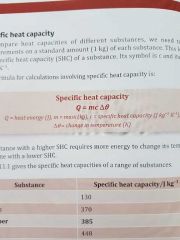
|
|
|
What is the definition and unit of latent heat? |
Latent heat of a substance is thr heat energy required to change its state without a change in temperature. Its unit is joules (J). |
|
|
What is the definition and unit of specific latent heat? |
Specific latent heat of a substance is the amount of heat energy required to change the state of 1 kg of the substance without a change in temperature. Its unit is J kg-1. |
|
|
What is specific latent heat of vaporisation? |
Specific latent heat of vaporisation of a substance is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of the substance from a liquid to a gas without a change in temperature. |
|
|
What us specific latent heat of fusion? |
Specific latent heat of fusion of a substance is the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of the substance from a solid to a liquid without a temperature change. |
|
|
What is the formula of specific latent heat? |

|
|
|
Name 2 heat pumps. |
Perspiration (sweating) and refrigerator. |
|
|
How does perspiration work? |
The body releases water on the skin, causing the water to absorb the heat from the body causing it to change state, without a change in temperature (latent heat). |
|
|
How does the refrigerator work? |
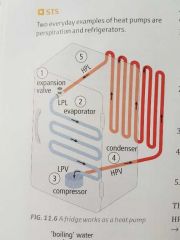
1. High-pressure liquid (HPL) enters an expansion mechanism. The mechanism lowers the pressure of the liquid by moving its particles apart. The liquid becomes a low-pressure liquid (LPL). 2. Liquids dont like being at low pressure, causing the LPL to change state to a low-pressure vapour (LPV). To do this it needs energy, where the heat energy is absorbed from inside the fridge. 3. The LPV then enters a compressor that forces the vapours particles to come closer together. Changing it to a High-Pressure Vapour (HPV). 4. Vapours dont like being at high pressure, causing it to change to a HPL, which releases heat energy at the back of the fridge. 5. The HPL re-enters the expansion mechanism and the cycle begins again. |
|
|
What is conduction? |
Conduction is the transfer of heat in a solid by passing kinetic energy from molecule to molecule. |
|
|
What is convection? |
Convection is the transfer of heat energy by the circulation of the heated parts of a liquid or gas. |
|
|
What is radiation? |
Radiation is the transfer of heat energy as electronagnetic (EM) waves, without the need of a medium. |
|
|
What is the solar constant? |
The amount of energy striking 1 m2 of the earths atmosphere every second. |
|
|
What is u-value? |
The u-value of a material is the amount of heat energy that can be transmitted across 1 m2 of its surface every second, so long as there is a temperature difference of 1 K each side of the material. |

