![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
126 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
State the basic ideas of the Cell Theory?
|
Cells are the building blocks of plants and animals.
All cells come from pre-existing cells Cells are the smallest units that perform all vital physiological functions Each cells maintain homeostasis at cellular level |
|
|
Define CYTOLOGY?
|
The study of cellular structure and function
|
|
|
What are 2 types of sex/germ/reproductive cells?
|
Sperms of Males
Oocytes of Females |
|
|
What are somatic cells?
|
Somatic cells are body cells, in which all other cell besides the sperm of males and oocytes of females
|
|
|
Define PLASMA/CELL MEMBRANE?
|
Plasma/Cell membrane separates the cell content/cytoplasm from the extracellular fluid
|
|
|
What roles does PLASMA MEMBRANE play?
|
Separates the inside of the cell from the outside because conditions are different and that is why it is necessary to maintain homeostasis
Regulates the exchange of ions and nutrients Sensitivity, because it is the first in contact with outside sources Structural support |
|
|
What is the plasma membrane mainly made up of?
|
Phospholipid bilayer
- Phosphate - hydrophilic - Lipid - hydrophobic |
|
|
True or False: Water and solutes can cross the lipid portion of the plasma membrane?
|
False, water and solute CANNOT cross the lipid portion of the plasma membrane because the lipid portion is HYDROPHOBIC
|
|
|
Define INTEGRAL/TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEIN?
|
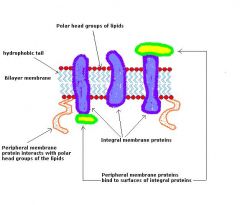
Are part of the membrane structure, that spans the width of the membrane and cannot be removed without damaging or destroying the membrane
|
|
|
Define PERIPHERAL PROTEIN
|
Are bound to the inner or outer surface of the membrane and are easily separated from it.
|
|
|
Define ANCHORING PROTEIN?
|
Anchoring proteins attach the plasma membrane to other structures and stabilize its position
|
|
|
Define ENZYME?
|
Enzymes catalyzes reactions in the extracellular fluid or in the cytosol
|
|
|
Define RECEPTOR PROTEINS?
|
Receptor proteins are found in the plasma membrane, in which they are sensitive to the presence of specific extracellular molecules.
|
|
|
Describe the relationship of a RECEPTOR PROTEIN and a LIGAND?
|
A receptor protein exposed to an appropriate ligand will bind to it and that binding may trigger changes in the activity of the cell.
|
|
|
Define CARRIER PROTEINS?
|
Carrier proteins bind solutes and transport them across the plasma membrane
|
|
|
Define CHANNELS?
|
Some integral proteins contain a central pore or channel, that forms a passageway completely across the plasma membrane that permits the movement of water and small solutes across the plasma membrane.
|
|
|
Define CHANNELS?
|
Some integral proteins contain a central pore or channel, that forms a passageway completely across the plasma membrane that permits the movement of water and small solutes across the plasma membrane.
|
|
|
Define CHANNELS?
|
Some integral proteins contain a central pore or channel, that forms a passageway completely across the plasma membrane that permits the movement of water and small solutes across the plasma membrane.
|
|
|
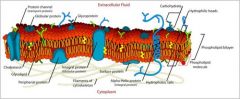
Define Glycoproteins/Glycocalyx?
|
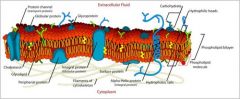
The carbohydrate portions of large molecules extend beyond the outer surface of the membrane....in which is the blue object connected to the glycoproteins
|
|
|
What are some important functions of GLYCOCALYX?
|
Lubrication and Protection
Anchoring and Locomotion Specificity in binding Recognition |
|
|
Define CYTOSOL?
|
Intracellular fluid
|
|
|
Define ORGANELLES?
|
Structures suspended within the cytosol that perform specific functions within the cell
|
|
|
Identify differences between the CYTOSOL and EXTRACELLULAR FLUID?
|
[K+] is much higher in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid.
[Na+] is much lower in the cytosol than in the extracellular fluid. Cytosol contains a much higher concentration of suspended proteins than extracellular fluid. Cytosol contains small quantities of carbohydrates and small reserves of amino acids and lipids, whereas the extracellular fluid has NO reserves |
|
|
What are two types of ORGANELLES?
|
Nonmembranous organelles: are not completely enclosed by membranes and all of their components are in direct contact with the cytosol
Membranous: isolated from the cytosol by phospholipid membranes |
|
|
Define CYTOSKELETON?
|
Cytoskeleton provides an internal protein framework that gives the cytoplasm strength and flexibility.
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton are typically made of what 3 filaments?
|
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments Microtubules |
|
|
Of the 3 filaments: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, which one is the smallest?
|
Microfilaments
|
|
|
Microfilaments are compose of what?
|
Actin
|
|
|
What are 3 major functions of Microfilaments?
|
Microfilaments anchor the cytoskeleton to integral protein of the plasma membrane
Microfilaments interacting with other proteins can determine the consistency of the cytoplasm. -Dense microfilaments form gelatinous consistency -Widely spread microfilaments forms more fluidity Actin found in microfilaments can interact with the protein myosin to produce active movement of cells |
|
|
What are some functions of INTERMEDIATE FILAMENT?
|
Strengthen the cell and help maintain its shape.
Stabilize the position of organelles Stabilize the position of the cell with respect to surrounding cells through specialize attachment to the plasma membrane |
|
|
Microtubules are form what?
|
Tubulin
|
|
|
What are some functions of MICROTUBULINS?
|
Give cell strength, rigidity, and anchorage.
Assist in cell movement Move vesicles or organelles with in the cell. |
|
|
What are thick filaments made of?
|
Myosin
|
|
|
Where are thick filament found?
|
Muscle cells, where they interact within actin filaments to produce powerful contraction
|
|
|
What are MICROVILLI?
|
Microvilli are finger-shaped projections of the plasma membrane on their exposed surface, these microvilli greatly increase the surface area of the cell exposed to the extracellular environment
|
|
|
DID NOT PUT NOTES FOR CENTRIOLES AND CENTROSOME
|
DID NOT PUT NOTES FOR CENTRIOLES AND CENTROSOME
|
|
|
Which organelles is responsible for protein synthesis?
|
Ribosomes
|
|
|
What are the 2 subunits of a functional ribosome?
|
Small ribosomal subunit
Large ribosomal subunit |
|
|
What are the two types of ribosomes?
|
Fixed and Free
|
|
|
What are PROTEASOMES?
|
Proteasomes are organelles that contain an assortment of protein digesting enzymes
|
|
|
What are PROTEASOMES responsible for?
|
Removing and recycling damage or denatured proteins, and breaking down abnormal proteins.
|
|
|
The endoplasmic reticulum is connected to what structure?
|
nuclear envelope
|
|
|
What are 4 functions of the ER?
|
Specialized regions of the ER synthesize proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
The ER can store synthesized molecules or materials absorbed from the cytosol Materials can travel from place to place in the ER Detoxification: drugs/toxins can be absorbed by the ER and neutralized by enzymes within it |
|
|
What are two types of ER?
|
Smooth
Rough |
|
|
What is the difference between smooth and rough?
|
Smooth refers to the fact that no ribosomes are associated
Rough ER contain ribosomes |
|
|
Which organelles typically consists of five or six flattened membranous discs called cisternae?
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
|
|
What is the main function of the GOLGI APPARATUS?
|
MODIFIES AND PACKAGE
|
|
|
Typically small vesicles move material from one cisterna to the next, generally arriving first at the ______ and ending at the ______
|
Forming (cis) face
Maturing (trans) face |
|
|
What are 3 types of vesicles that carry materials away from the Golgi apparatus?
|
Secretary vesicles: fuse with the plasma membrane and empty their contents in to the extracellular environment.
Membrane Renewal Vesicles: fuse with the surface of the cell and add lipids and proteins to the membrane causing the membrane to remove and recycled Lysosomes: contain digestive enzymes |
|
|
Define EXOCYTOSIS?
|
Vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and empty their contents in to the extracellular environment
|
|
|
Which organelles is responsible for energy production?
|
Mitochondria
|
|
|
How many membranes does a Mitochondria have?
|
Two
Outer surrounds the organelles Inner contain cristae |
|
|
Define Cristae?
|
Cristae are numerous folds in the mitochondria that increase the surface area exposed to the fluid matrix of the mitochondrion
|
|
|
What structure separates the nucleus from the cytosol (intracellular fluid)?
|
Nuclear Envelope
|
|
|
Is the nuclear envelope single or double layer membrane?
|
Double and is separated by the perinuclear space.
|
|
|
In order for the nucleus to direct processes in the cytosol, where does chemical communication between the nucleus and the cytosol take place?
|
Nuclear pores
|
|
|
What is the perinuclear space?
|
A space that separates the double membrane layer of the nuclear envelope
|
|
|
The fluid contents of the nucleus is call what?
|
Nucleoplasm
|
|
|
What role does the NUCLEOLUS play?
|
Synthesize ribosomal RNA
|
|
|
When the DNA strands wind around the histone, forming a complex call?
|
Nucleosome
|
|
|
Why is it necessary for the DNA strands to wind itself around the histone?
|
Such winding allows a great deal of DNA to be packaged in a small space.
|
|
|
Define NUCLEUS?
|
Contains the genetic instructions needed to synthesize the proteins that determine cell structure and function
|
|
|
Where does the nucleus stores its genetic information?
|
Chromosomes
|
|
|
What keeps the gene inactive?
|
Tightly coiled and histones keep the gene inactive, when the are tightly bound to it.
|
|
|
What is the first signal that indicates GENE ACTIVATION?
|
Removal of the histone
Temporary disruption of the weak bonds between the nitrogenous bases of the two DNA strands |
|
|
What signifies the first step in TRANSCRIPTION?
|
Enzyme, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter of the gene
|
|
|
Identify the importance of Messenger RNA?
|
DNA cannot leave the nucleus so instead its formation is copied to messenger RNA, which can leave the nucleus and carry the information to the cytoplasm
|
|
|
What is TRANSCRIPTION?
|
After the complementary strand separate and RNA polymerases binds, transcription take place and begins to copy the DNA template into RNA
|
|
|
Read the Steps in Transcription of mRNA
|
Read the steps in Transcription of mRNA (PAGE 84-85)
|
|
|
What is the difference between INTRONS and EXONS?
|
Sometimes gene includes a number of triplets that are not needed to build functional protein, thus the mRNA strand needs to be edited
Introns, nonsense regions are snipped out Exons, coding segments are splice together |
|
|
What role does anticodon play in translation?
|
Anticodon bonds complementarily with an appropriate mRNA codon.
|
|
|
What are the triplets for "START CODON?
|
AUG
|
|
|
When does TRANSLATION began?
|
mRNA strands binds to a small ribosomal subunit
|
|
|
Read the step for TRANSLATION
|
Read the steps for TRANSLATION on page 86-87
|
|
|
Passage across the membrane are in either 2 form, which are?
|
Passive processes move ions or molecules across the plasma membrane with no expenditure of energy by the cell.
Active processes require that the cell expend energy, generally in the form of ATP. |
|
|
What are 3 major transport processes?
|
Diffusion
Carrier Mediated Transport Vesicular Transport |
|
|
Is diffusion, an active or passive process?
|
Passive
|
|
|
What is DIFFUSION?
|
Passive molecular movement from an area of high concentration to an area of lower conentration
|
|
|
DIFFUSION tends to eliminate what?
|
concentration gradients
|
|
|
What are some factors that can influence diffusion rate?
|
Distance: shorter the distance, increase diffusion
Molecule size: small the molecules, rapid diffusion Temperature: higher temperature, faster diffusion Gradient size: larger the concentration gradient, the faster diffusion proceeds. Electrical forces: interior of plasma membrane is a net negative, therefore tends to attract positive molecules...rapid diffusion |
|
|
Define OSMOSIS?
|
The net diffusion of water across a membrane
|
|
|
In OSMOSIS, water flows across a membrane toward the solution that has the _______ concentration of ______ because this is where the concentration of ________ is lower?
|
Higher
Solute Water |
|
|
Define OSMOTIC PRESSURE?
|
The greater the initial difference in solute concentrations, the stronger is the osmotic flow.
Osmotic pressure of a solution is an indication of the force with which pure water moves into that solution as a result of its solute concentration |
|
|
What is the difference between osmolarity and tonicity?
|
Osmolarity refers to the solute concentration of the solution
Tonicity is a description of how the solution effects the cell. |
|
|
If a red blood cell is hypotonic, what will happen?
|
Water will flow into the cell, causing it to swell up
More water located extracellularly but more solute inside the cell, thus the water must diffuse inside |
|
|
If a red blood cell is hypertonic, what will happen?
|
Will will flow out of the cell and cause it to shrink
More water molecules located inside and more solute outside, thus water must diffuse outside |
|
|
Define Carrier Mediate Transport?
|
Carrier mediate transport requires the presence of specialized integral membrane proteins that binds specific ion or organic substrates and carry them across the plasma membrane
|
|
|
Is carrier mediate transport a passive or active transport?
|
Both, because it depends on the substance transported and the nature of the transport mechanism.
|
|
|
Define Vesicular transport?
|
Vesicular transport involves the movement of materials within small membranous sac (vesicles).
|
|
|
Is vesicular transport active or passive transport?
|
Active
|
|
|
What are some characteristics of Carrier Mediated Transport?
|
Specificity: each carrier protein in the plasma membrane will bind and transport only certain substances.
Saturation Limits: when all available carrier proteins are operating at maximum speed, the carrier are said to be saturated and cannot increase transportation any further. Regulation: Hormones can affect the activity of carrier proteins thus it is an important means of coordinating carrier protein activity throughout the body |
|
|
Define COTRANSPORT/SYMPORT?
|
The carrier transports two substances in the same direction simultaneously, either into or out of the cell.
|
|
|
Define COUNTERTRANSPORT/ANTIPORT?
|
One substance moves into the cell and the other moves out
|
|
|
Give some examples of CARRIER MEDIATED TRANSPORT?
|
Facilitated diffusion
Active Transport |
|
|
Describe the process of how facilitated diffusion transport glucose into the cytoplasm?
|
Glucose must first bind to a receptor site on the protein. The protein will then change shape and move glucose across the plasma membrane where it meets a carrier protein and release it into the cytoplasm.
|
|
|
What is the difference between CHANNEL MEDIATED DIFFUSION and FACILITATED DIFFUSION?
|
Unlike channel mediated diffusion, once the carrier proteins are saturated, the rate of transport cannot increase regardless of further increase in the concentration gradient.
|
|
|
What is an advantage of ACTIVE TRANSPORT compare to any other transports?
|
Not dependent on a concentration gradient as a result the cells can import/export specific substrates, regardless of the intracellular or extracellular concentrations.
|
|
|
What is one disadvantage of ACTIVE TRANSPORT?
|
Expends a lot of energy
|
|
|
What are ION PUMPS?
|
Carrier proteins that transport additional cations (+)
|
|
|
What are the two major cations found in the body fluids? Which one is found mainly in the extracellular? Which one is found mainly intracellular?
|
Sodium – extracellular
Potassium – intracellular |
|
|
Describe the Sodium-Potassium Exchange Pump?
|
Exchanges sodium that are located intracellular and move them outside.
Whereas potassium that are located outside are exchange and move inside |
|
|
What are two main categories of VESICULAR TRANSPORT?
|
Endocytosis
Exocytosis |
|
|
Define ENDOCYTOSIS?
|
A process where extracellular materials can be packaged in vesicles at the cell surface and imported into the cell
|
|
|
What are 3 major types of ENDOCYTOSIS?
|
Receptor –mediated endocytosis
Pinocytosis Phagocytosis |
|
|
What are the differences of Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis, Pinocytosis, and Phagocytosis?
|
Receptor –mediated endocytosis: selective and the targets are ligands; produces endosomes
Pinocytosis (cell drinking) – not selective and the target is usually some fluid; produces endosomes Phagocytosis (cell eating) – not selective and target is solidify materials; produces phagosomes |
|
|
Define EXOCYTOSIS?
|
Exocytosis is when a vesicle created inside the cell fuses with the plasma membrane and discharges its contents into the extracellular environment
|
|
|
What is TRANSMEMBRANE POTENTIAL?
|
Transmembrane potential occurs because the insides of cells are slightly negative charge, but outside the cell there is a slight positive charge. Normal these two opposite charge would rush together, however they are separated by the phospholipid bilayer and thus produce a potential difference across the membrane
|
|
|
What is RESTING POTENTIAL?
|
Resting potential is when the transmembrane potential in a cell is undisturbed….-10 mV
|
|
|
What is cell division?
|
The division of a sing cell produces a pair of daughter cell, each half the size of the original.
|
|
|
What terms is identify as the genetically controlled death of cells?
|
Apoptosis
|
|
|
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
|
Mitosis is the division of somatic cells, whereas meiosis is the production of sex cells
|
|
|
What occur in interphase of Mitosis?
|
Normal functions and prepared to divide
|
|
|
G1, S, and G2, are phases found in which of mitosis?
|
Interphase
|
|
|
In which phase, G1, S, or G2, does the cell get ready to be divided?
|
G1
|
|
|
What happens in G1?
|
Development of organelles
Centrioles replicate |
|
|
What happens in the S phase of mitosis?
|
DNA replication
|
|
|
What purpose does DNA polymerase served?
|
As the double stranded DNA unwinds by enzyme helicases, DNA polymerase bind to the exposed nitrogenous bases, in which it promotes binding between the nitrogenous bases of the DNA strand.
|
|
|
What happens during G2 phase?
|
Last minute protein synthesis and completion of centriole replication
|
|
|
What happens after G2 phase is complete?
|
Mitosis occurs
|
|
|
List the stages mitosis?
|
Interphase
Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase |
|
|
Describe what will happen during Prophose of Mitosis
|
Chromosomes coil so tightly that they become visible.
Nucleoli disappear 2 Pair of centrioles move to opposite poles of the nucleus Nuclear envelope disappears |
|
|
Describe what will happen during Prophose of Mitosis
|
Chromatids move to a narrow central zone called the metaphase
|
|
|
Describe what will happen during Anaphase of Mitosis
|
Chromatids pair splits and pulled to opposite ends.
|
|
|
Describe what will happen during Telophase of Mitosis
|
Nuclear membrane reforms
Chromosomes gradually uncoil |
|
|
What is another word for tumor?
|
Neoplasm
|
|
|
Between benign and malignant tumor, which one is more severe?
|
Malignant
|

