![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
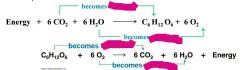
Identify the process and fill in the blanks |
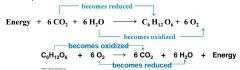
|
|
|
What type of reaction is photosynthesis (exergonic or endergonic) |
Endergonic - energy from the sun |
|
|
What are the two main phases of photosynthesis? |
1) light reactions 2) dark reactions (Calvin cycle) |
|
|
What occur during the light cycle (4)? |
- splitting of H2O - release O2 - reduce NADP+ to NADPH - generate ATP from ADP by photophosphorylation |
|
|
What occurs during dark reactions? (2) |
- uses NADPH and ATP - Fixes CO2 into organic molecules |
|
|
What type of cell are chloroplasts mainly found in? |
Mesophyll (interior tissue of the cell) |
|
|
Stomata |
Microscopic pores on the leaf that CO2 enters and O2 exits |
|
|
Where do light reactions occur? |
Thylakoid membrane |
|
|
Granum |
Stack of thylakoid |
|
|
Stroma |
Gel like substance that surrounds the thylakoids |
|
|
Pigments |
Substances that absorb the energy from visible light |
|
|
Why do leaves appear green? |
Chlorophyll doesn't absorb green light |
|
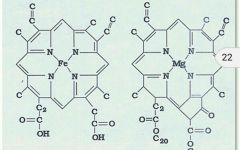
Which one is heme and which one is chlorophyll? |
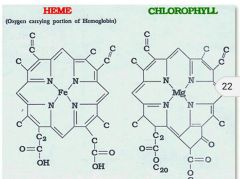
|
|
|
What is the main photosynthetic pigment? |
Chlorophyll a |
|
|
What type of pigment helps broaden the spectrum used for photosynthesis? |
Accessory pigments ex chlorophyll b |
|
|
What is an absorption spectrum? |
A graph plotting a pigment's light absorption vs wavelength |
|
|
Action spectrum |
Profiles the relative effectiveness of different wavelengths |
|
|
When a pigment absorbs light it goes from a ______ state to an unstable ______ state |
Ground, excited |
|
|
Fluorescence |
When an excited electron falls back down it gives of energy in the form of photons (giving of light and heat) (In a chloroplast, an electron acceptor is available and the potential energy represented by the excited electron is not dissipated ad light or heat) |
|
|
What are they four main parts of light reactions? |
1) Complex II 2) ETC and ATP synthase 3) Complex I 4) ETC and NADP+ reductase |
|
|
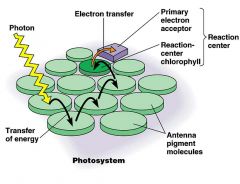
What does a photosystem consists of (2)? |
• a reaction center complex • surrounded by light harvesting complexes |
|
|
What are light harvesting complexes? |
Pigment molecules bound to proteins |
|
|
What do light harvesting complexes do? |
Transfer the energy of photons to the reaction centers |
|
|
What does the primary electron acceptor do? |
In the reaction center, accepts excited electrons and is reduced as a result. |
|
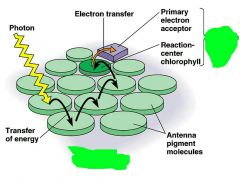
Fill in the blanks |
|
|
|
What type of phosphorylation occurs in light reactions? |
Oxidative phosphorylation (using ATP synthase) |
|
Fill in the blanks |
|
|
|
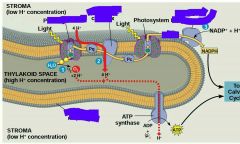
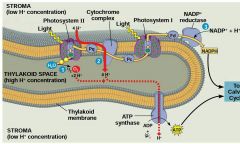
What happens in PSII? (3) |
1) A photon hits a pigment and it's energy is passed along pigment molecules until it excites P680 2) An excited electron from P680 is transferred to the primary electron acceptor (now P680+) 3) H2O is split by enzymes and its electrons are transferred from the hydrogen atoms to P680+ (reduced to P680) |
|
|
What happens in the "first" ETC of light rxns? (3) |
1) Each electron falls down an ETC from a primary acceptor of PSII to PS1 2) energy released from this falls drives the formation of a H+ gradient across the thylakoid membrane 3) Diffusion of H+ across the membrane drives ATP synthesis |
|
|
What happens in PSI (2)? |
1) Transferred light energy excites P700 which loses an electron to become P700+, an electron acceptor 2) P700+ accepts an electron from PSII passed down via ETC |
|
|
What happens in the "second" ETC of light rxns? (2) |
1) Each electron falls down the ETC from the primary electron acceptor of PSI to the protein ferredoxin (Fd) 2) the electrons are then transferred to NADP+ and reduce it to NADPH (at NADP+ reductase) • this process also removes H+ from the stroma (NADP+ + H+ + 2e- ➡ NADPH) |
|
|
What is cyclic electron flow? |
• Uses only PSI • produces surplus ATP • Does not produce NADPH • Does not release O2 |
|
|
What products of light reactions go to dark reactions? |
• NADPH • ATP |
|
|
Where do dark reactions occur? |
Stroma of chloroplasts |
|
|
What does the Calvin cycle use ATP and NADPH for? |
To reduce CO2 to sugar (G3P) |
|
|
How many times must the Calvin cycle occur to produce 1 G3P? |
3 |
|
|
What are the 3 phases of the Calvin cycle? |
1) Carbon fixation 2) Reduction 3) Regeneration (RuBP) |
|
|
What occurs in the fixation part of the Calvin cycle? |
• Inorganic carbon from CO2 is added to an organic compound (ribulose-1,6-bisphosphate - RuBP) • the enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase -RuBisCO) |
|
|
RuBisCO is the most _________ enzyme on the planet |
Abundant |
|
|
What happens in the reduction phases of the Calvin cycle? |
Phosphoglycerate is reduced to G3P (which can then be used to make glucose and other sugars) |
|
|
What happens in the regeneration phases of the Calvin cycle? |
Regeneration of RuBP |
|
|
How much energy is consumed per cycle of the Calvin cycle (1 CO2 fixed) |
- 3 ATP - 2 NADPH |
|
|
Photorespiration |
Occurs on hot, dry days when the stomata of plants close to prevent dehydration causing an increasing in O2 concentration. Consumes O2 (and ATP) instead of CO2 and releases CO2 Rubisco adds O2 instead of CO2 in the Calvin cycle, producing a 2C sugar ➡ CO2 Not good |
|
|
Under high CO2 rubisco fixes ________. However under high O2 conditions, O2 ________ |
Carbon, outcompetes CO2 for the rubisco active site |
|
|
How do C4 plants minimize the affect of photorespiration |
Separate the steps by performing them in different cells. Incorporate CO2 into 4C sugars (oxaloacetate) in mesophyll cells |
|
|
What does PEP carboxylase do? |
An enzyme that adds CO2 to PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) to form oxaloacetate in mesophyll cells of C4 plants. Acts prior to photosynthesis |
|
|
Why can PEP carboxylase work when rubisco can't? |
It has a higher affinity for CO2 there will work in environments with low CO2 concentration |
|
|
What cell do the 4C compounds made in C4 plants go? |
Bundle-shealth cells |
|
|
How do CAM plants fix carbon? |
Crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) |
|
|
How do CAM plants separate the processes and prevent dehydration? |
Open their stomata at night when there is less risk of dehydration - corporate CO2 into organic acids. During the day stomata close and CO2 is released from organic acids ➡ Calvin cycle. |
|
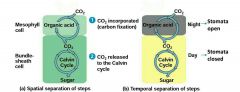
Which one is C4 and which one is CAM? |
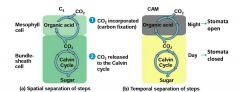
|
|
|
What affect might increased CO2 levels have on C3 plants |
Benefit C3 plants - less photorespiration |

