![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The ECF is made up of ______ & _______ |
Plasma & interstitial fluid |
|
|
The internal environment is made up of _________ & _________ |
ECF & ICF |
|
|
What is the external environment? |
The external environment is the outside of your body |
|
|
What type of control is built into / inherent in an organ? |
Intrinsic control |
|
|
Which regulatory mechanism is initiated outside an organ to alter the activity of an organ? |
Extrinsic control |
|
|
Desired value for controlled variable |
Setpoint |
|
|
Detects changes in controlled variable |
Sensor |
|
|
Compares variable to setpoint |
Integrator |
|
|
Positive feedback is less common than negative feedback and requires a ________ |
Breakpoint
For instance in labour, the Breakpoint is birth |
|
|
The integrator is typically part of which system |
The nervous system |
|
|
Is an action potential positive or negative feedback? |
Positive |
|
|
How many neurons in the brain? |
10^11 REMRMBER THESE NEURONS ARE IN THE BRAIN |
|
|
What are the most polarized cells in biology? |
Neurons |
|
|
How long is an axon? |
10 um to 1 m |
|
|
Anterograde (via ___) is from ____ to ____ ( down or up axon) |
Kinesin, soma to terminal, down |
|
|
Retrograde (via______) from the __to ______ ( up or down the axon) |
Dynein, terminal, soma -- down |
|
|
Anterograde and retrograde are types of |
Axon transport |
|
|
How much atp does each binding and unbinding from the cytoskeleleton during axon transport use? |
1 atp |
|
|
Is dynein or kinesin bigger? |
Kinesin |
|
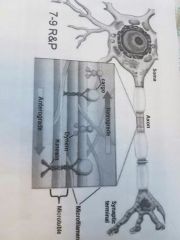
|
Know that pic |
|
|
What are the two types of control pathways? |
Rapid ( neurotransmitter) Slow ( neurohormone) |
|
|
Difference between neurotransmitter and neurohormone |
Neurotransmitter = rapid Specific target innervated (local target cell) Pathway used for reflexes and motor control Neurohormone= slow. Innervates blood stream or glands to reach distant target cell The target cell often has receptors |
|
|
About how much of the cells with in the CNS are glial cells? (%) |
90 % |
|
|
Are glial cells excitable? |
No |
|
|
Do glial cells transfer information? |
No |
|
|
How do glial cells communicate? |
Chemical signals |
|
|
Asrtrocytes function |
Structural: hold neurons together in proper spatial relationships
Important to repair of brain injuries and neural scar formation
Play a role in neurotransmitter activity ( mop up transmitters and extracellular k+) |
|
|
Oligodendrocytes |
Myelinate sheaths around axons in cns |
|
|
Microglia |
Derived from bone marrow tissue that gives rise to monocyte Release low levels of growth factors in which help neurons and other glial cells survive May contribute to alzheimer disease, multiple sclerosis and dementia |
|
|
Ependymal |
Line the CNS and produce cerebrospinal fluid |

