![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Reasons for using the rectal and/or vaginal route of drug Delivery |
Patient is not able to make use of the oral route Dash nauseous, post operative [unconscious], young or old or mentally disturbed The drug is not well-suited for oral administration – unstable at pH of G.I. tract, And activated by enzyme, Destroyed by first pass metabolism The patient is not well-suited to the drug – Unacceptable taste, drugs of abuse – suicide Localized treatment required |
|
|
Disadvantages of rectal and vagina route |
Sexual associations Slow and incomplete drug absorption Uncomfortable poor patient adherence |
|
|
Rectal route therapy |
Local action - local treatment of pain and itching - hemorrhoids mainly [painful swollen veins in the lower part of the rectum and anus], local anesthetics, anti-inflammatory, some laxatives Systemic action – anti asthmatic, anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs |
|
|
Anatomical factors affecting absorption from the rectum |
Anatomically, rectum is part of the colon- the final 150 to. 200 mm of the G.I. tract. Rectum can be considered as a hollow organ with a flat wall surface without villi and with three major folds [the rectal valves] The Epithelium is glandula – contains a cylindrical and goblet cells that secrete mucus Dash 3 mL spread over surface area of 300 cm² PH 7.5 With little buffering capacity |
|
|
Physiological factors affecting absorption from the rectum |
Quantity of fluid available - three ML , Thus the dissolution of poorly water soluble drugs is slow Properties of rectal mucus – pH 7.5 and no buffer capacity Motility of the rectal wall – exerts a pressure on the suppository Circulation rate – lower hemorrhoidal veins receive the absorb truck and bypass the liver circulation/ First pass effect Contents of the rectum: empty rectum has great absorption, little enzyme activity resulting greatest ability of peptides like drugs |
|
|
Physicochemical/formulation factors |
Drug solubility in vehicle - less soluble means more release - Partition coefficient between Vehicle and rectal fluids Particle size.Smallest size is fast the dissolution Nature of the base. Base must melts softener or dissolve to release drug components and non-irritating mucus membrane Spreading capacity Spreading surface area |
|
|
Examples of traditional rectal dosage forms |
Suppositories– Cocoa butter, hard fats, macro goals, gelatinous mixtures Rectal capsules Rectal solutions, emulsion, suspensions Powders and tablets Semi solid preparations – ointments creams and gels Rectal foams and tampons |
|
|
Suppositories |
Suppositories are solid dosage forms intended for insertion into the body or face with a melt, softener or dissolve and exert an effect. They contain active substance disbursed in a suitable base that maybe soluble in water on me melt a body temperature Can administer large or small volumes 1-4g, torpedo shaped item |
|
|
Suppository base requirements |
Melt at body temperature or-dissolve in bodily fluids The non-toxic and non-irritating Pharmacologically and nuts Compatible with the drug - Lipophilic drugs are usually incorporated into water soluble bases and hydrophilic drugs are incorporated into fatty ones Chemical and physically stable Consistent to handle |
|
|
Yellowish white solid, smells like chocolate and is a mixture of Saturated and unsaturated triglycerides Advantages: MP 30-35. Degrees – solid at room temperature Rapid melting and rapid solidification and cooling Miscible with many ingredients non-irritating Disadvantages Polymorphism when melted or cooled- into different crystalline forms - alpha, beta and gamma Adherence to the mold – does not contract sufficiently to loosen from the mold – needs lubrication Rancidity on storage due to oxidation of unsaturated crossroads Poor water absorbing ability Expensive – natural |
Yellowish white solid, smells like chocolate and is a mixture of Saturated and unsaturated triglycerides Advantages: MP 30-35. Degrees – solid at room temperature Rapid melting and rapid solidification and cooling Miscible with many ingredients non-irritating Disadvantages Polymorphism when melted or cooled- into different crystalline forms - alpha, beta and gamma Adherence to the mold – does not contract sufficiently to loosen from the mold – needs lubrication Rancidity on storage due to oxidation of unsaturated crossroads Poor water absorbing ability Expensive – natural |
|
|
Fatty suppository base - Synthetic hard fat (suppocire) |
Synthetic, hydrogenated vegetable oil,Mainly saturated mono, diet and triglycerides Advantages: contraction, good resistant to oxidation Disadvantages: brittleness if cooled quickly Lower viscosity so risk of sedimentation leading to lack of distribution uniformity and localized irritation |
|
|
Water-based suppositories - glycerol gelatin |
Glycerol - gelatin bases And macrogol bases mainly used for a laxative purposes and for vaginal Disadvantages Osmosis occurs – laxative effect Can cause rectal irritationDo you to dehydrating effect Have a unpredictable solution time Hygroscopic so should be packaged in tight containers Requires use of preservative Lubrication essential |
|
|
polyethylene (macrogol) base |
Polymers of Etheline dioxide and water – different chain links and molecular weights Hardness increases with increase in molecular weight average - over 1000 equals white solid, 600-1000 are semi solid And MP equals 50°But Chucta solution dependent on dissolving Advantages: no laxative effect, No lubricant necessary, stable at room temperature on storage, good solvent High viscosity so Less leakage Disadvantages Hygroscopic and may irritate mucosa (dip in water) Poor bio availability because good solvent may retain drug Incompatible with some drugs – benzocaine and packaging e.g. plastic Brittle ifcooled too quick
|
|
|
Rectal absorption From suppository |
1.melting points or dissolution time of cocoa butter : 3-7 mins For glycerin 30-40 mins 2. Diffusion of drug from suppository into mucus layer - Particle size, solubility of drugging vehicle, temperature, spreading capacity 3. Transport wall- pH, pKa |
|
|
Advantages and disadvantage is of rectal administration |

Advantages: Safe and painless means of administration |
|
|
Describe an ideal vaginal dosage form |
• Ease of insertion and removal (appropriate applicator)• Maintain pH close to vaginal pH (4)• Adequate (rheological) properties– to spread and distribute the drug into the vaginal lumen– to retain: no leakage, messiness and excessive wetness toavoid poor patient compliance• No local side effect– no disruption to the normal vaginal flora– non-irritant or toxic to the vaginal epithelium– free from producing any physical discomfort• Compatibility with:– other treatment (contraception)– daily life, sexual activity…• Stable at different conditions (tropical climate/HIV!)• Simple to manufacture and cost-effective |
|
|
Describe the various aspects and potential of vaginal drugdelivery |
Drug absorption from the vagina is via passive diffusion. The vaginal wall is very well suited for the systemic absorption of drugs because of its vast network of blood vessels, and avoids the hepatic portal system A number of physiological factors such as volume, viscosity and pH of vaginal fluid can influence drug absorption. |
|
|
Anatomy of VDD |
Uterus=protect and nourishembryo/foetus+ expulsion baby Vagina=receive malereproductive cells+ birth canal +Excretory canalof products ofmenstruation + lubrication mucus or cervico vaginal fluids. (mucins, pH3.5-4.5, microflora bacteria convert glycogen to lactic acid) Vagina is a fibro-muscular tube that connects the uterus to the external environment. Internal structure of vagina: epithelium, visceral muscel and adventitia. lubricated by bartholins glands Can also be affected by infection |
|
|
Formulation factors affecting VDD |
Drug-related factors that influence absorption include drug solubility in vaginal fluid, ionization behaviour at vaginal pH, characteristics of release from the formulation and pKA molecular weight, as this will affect the diffusion/partition coefficient via the vaginal membrane. permeability |
|
|
Advantages/Disadvantages VDD |
Advantages: Easy access - Self administrationReasonable S area 60cm2 <150m2GITRich Blood supply (rapid absorption)No hepatic 1st pass effectLow metabolic activity (+ for proteins)Permeability (++ luteal phase)Prolonged retentionZero-order controlled releaseUterus targeting Disadvantages Gender specificityVariable - Inconsistent DDLife/cycle constraints (hormones, age,menstruation, coϊtus, pregnancy,ATB…)Compliance?Leakage-stainingLocal side effects (itching, burning)Acceptability (better but culturalissues, social taboo, unawareness) |
|
|
Menstruation |
When the follicular phase begins, levels of estrogen and progesterone are low. As a result, the top layers of the thickened lining of the uterus (endometrium) break down and are shed, and menstrual bleeding occurs. About this time, the follicle-stimulating hormone level increases slightly, stimulating the development of several follicles in the ovaries. Each follicle contains an egg. Later in this phase, as the follicle-stimulating hormone level decreases, only one follicle continues to develop. This follicle produces estrogen. The ovulatory phase begins with a surge in luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone levels. Luteinizing hormone stimulates egg release (ovulation), which usually occurs 16 to 32 hours after the surge begins. The estrogen level peaks during the surge, and the progesterone level starts to increase. During the luteal phase, luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone levels decrease. The ruptured follicle closes after releasing the egg and forms a corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. During most of this phase, the estrogen level is high. Progesterone and estrogen cause the lining of the uterus to thicken more, to prepare for possible fertilization. If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum degenerates and no longer produces progesterone, the estrogen level decreases, the top layers of the lining break down and are shed, and menstrual bleeding occurs (the start of a new menstrual cycle). |
|
|
• Give some example of traditional vaginal dosage forms |
• ‘Pessaries’ Vaginal pessaries are solid or semisolid, oval-shaped, single-dose preparations for vaginal insertion, and encompass formulations such as suppositories, tablets and capsules. SOLID: Pessaries* = moulded (suppository type - fatty and water soluble bases (PEG))Tablets* = compressed formsOvules = shell pessaries or vaginal (soft) capsules*Films(medicated)Tampons*Sponge, DiaphragmIntravaginal ring (IVR) Liquid and semisolid forms:creams, gels (jelly), solution (douches), foamimprecise dose, leaks, difficult application… good coverage |
|
|
Why VDD? Local disorders |
To treat local disorders TReat - Vaginosis / Vaginitis Vaginal infections (bacterial, viral, genital herpes, allergy) STD - New microbicides (prevention STDs - HIV) -Enhancers of vaginal acidity or natural vaginal bacteria• Detergents that break down the outer coats of bacteria or viruses -- Contraceptives & Spermicidal agents(Nonoxynol-9) - Hormone Replacement Therapy HRT (Oestrogen) - Induction of Abortion and Labor(synthetic prostaglandin: misoprostol) - Topical Chemotherapyvaginal intraepithelial neoplasia (VAIN) eg fluorouracil (5-FU) |
|
|
Why VDD? - systemic disorders |
- steroid sex hormones HRT- peptides and proteins low hepatic first pass effect |
|
|
Physiological factors |
Vaginal pH: Drug ionisation!!??????Lactobacillus + cellular glycogen (or carbohydrates) --> lactic acid. pH depends on cycle changes = oestrogen status (age, pregnancy-birth controlmethod) + menstruation, infection-ATB, hygiene products, sexual arousal, presence ofsemen Some enzymatic activity in in outer & basal vaginal cell layer:β-glucuronidase. some activity but lower than GIT!Depends on oestrogen: menstrual cycle (high infollicular phase but fall before ovulation), Age , ATB,Birth control method (microbicides), Sexual intercourseTrauma. affect bioavailability -Transport route Drug absorption!!Changes in vaginal epithelium Alter Trans and Para cellular drug uptakei.e. hydrophilic compoundsmenstrual cycle - oestrogen / age / pregnancy |
|
|
Skin Structure |
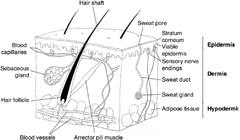
Strateum corneum 15mcm (top layer) Epidermis - viable epidermis 150mcm Stra Dermis, 3-5 mm HYPODERMIS: Subcutaneous layer - adipose tissue - |
|
|
Physiology and Function of Skin |
largest organ in body, Total SA 2m squared Function: protection from external environment, Maintain stable conc within body of materials, in and out. Water, temp regulation Communication with external stimuli - heat, pain touch etc.
|
|
|
Topical Route of administration |
Major barrier is stratum corneum Trancellular or intercellular, follicular (hair) and eccrine (sweat glands) |
|
|
Herpes Zoster - Shingles |
ReActivation of varicella zoster virus from dormant state, in dorsal root ganglion due to stress Virus migrates down sensory nerve Symptoms: numbness, itchiness, burning pain, clusters of blisters or vesicles. small blisters on a red base with blisters following a ray-like distribution More common in elderly and immunosupressed. Pain may persist for months after lesions have healed = Post herpetic neuralgia (PHN) |
|
|
Treatment for Post-Hepetic Neuralgia |
Lidocaine HCl injection - Nerve Block Therapy, ointment, Lidocaine in propylene glycol solution applied to skin. Centrally acting analgesics Antidepressants |
|
|
Clinical Need of the lidocaine |
Pain relief in nerve endings in dermis Controlled release formulation of lidocaine controlled area of delivery of lidocaine formulation must not irritate the skin non-occlusive - allow the skin to breathe |
|
|
patch Technology |
Matrix or reservoir patches for transdermal delivery Matrix (contain silicone or acrylate), Reservoir (contain alcohol) Both patches are occlusive and associated with skin irritation |
|
|
Cataplasms |
A soft moist mass, often warm and medicated, that is spread over the skin to treat an inflamed, aching or painful area, to improve the circulation, etc. (like a clay mask) Used for the delivery of drugs (e.g. NSAIDS, BBlockers), and lidocaine cataplasm. popular in asia with a hydrogel formula |
|
|
Formulation challenges of lidocaine |
1. Lidocaine base will precipitate out of water (from the hydrogel swelling polymer or gelling agent in water) - need to use co-solvent 2. Skin of patients with PHN very sensitive to touch, heat, wind and clothing - need non-irritating and non-occlusive formulation - thus need to use high water content and non-woven backing layer for hydrogel 3. need controlled release of lidocaine from hydrogel, cross linking of polymers to ensure uniform release. pH must be controlled as lidocaine ionises. About 50 formulations developed - Versatis 3 patches applied daily for 12 hours for 3 days, |
|
|
Versatis formulation components |
Propylene glycol - co-solvent to dissolve insoluble lidocaine base. Also a skin penetration enhancer -sodium polyacrylate, gelatin etc - gel forming substances -dihydroxyaluminium aminoacetate - cross linking agent for polymers, ensures defined pore network in the hydrogel which is important for controlled drug release. |
|
|
OTC patch ibuprofen |
Nurofen joint and muscular pain relief medicated patch. Occlusive patch, no breathable backing layer. prepared with non-aqueous adhesives, |
|
|
Important physicochemical properties in topical delivery |
Partition Co-efficient Diffusion coefficient molecular size, shape, hydrogen bonding ability, solubility oils and water melting point |

