![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Chromosomes replicate
Each replicated chromosome contains 2 genetically identical sister chromatids connected at the centromere Centrosome replicates, forming 2 centrosomes |
Takes up more than 90% of time
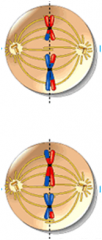
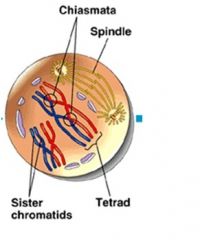
Chromosomes condense Homologous chromosomes pair along their lengths DNA molecules in nonsister chromatids break at corresponding places and then rejoin during crossing over In synapsis, a protein structure forms between homologues holding them tightly together Protein disassembles and each chromosome pair is seen as a group of 4 chromatids Nuclear envelope begins to break down The homologous pairs move toward the metaphase plate |
|
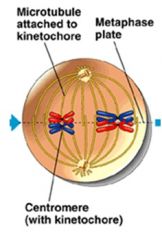
Pairs of homologous chromosomes are arranged on the metaphase plate
Both chromatids of a homologue are attached to kinetochore microtubules from one pole |
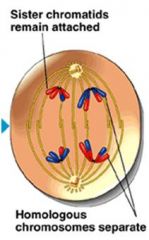
Chromosomes move toward the poles
Sister chromatids remain attached at the centromere and move toward the same pole Homologous chromosomes move toward opposite poles |
|
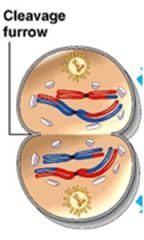
Cytokinesis forms 2 haploid duaghter cells
In animal cells a cleavage furrow is formed In some cells the nuclear envelope and nucleoli re-form No chromosome replication occurs |
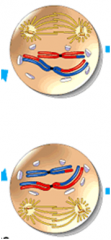
A spindle apparatus forms
Chromosomes composed of 2 chromatids move toward the metaphase II plate |
|
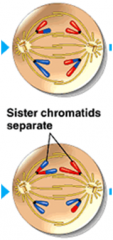
Chromosomes are positioned on the metaphase plate
The kinetochores of sister chromatids are attached to microtubules extending from opposite poles |
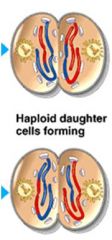
Centrosomes of each chromosome finally separate and the sister chromatids come apart
Sister chromatids move individually towards opposite poles |

