![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
88 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most inferior region of the pharynx?
|
larynx (hypopharynx)
|
|
|
What group of muscles pull trachea up and away during swallowing to let food go into esophagus?
|
infrahyoid muscles
|
|
|
The 3 concha of the nasal cavity are lined with what epithelium?
|
pseudostratefied ciliated columnar epithelium
|
|
|
What is the main function of the meati (sp?) or choanae between the 3 concha of the nose?
|
to filter, warm, and humidify air as it enters
|
|
|
How do choanae warm air as it enters?
|
blood vessels very near the surface
|
|
|
What region of the pharynx equilibrates air pressure in the head?
|
auditory tube
|
|
|
What nerve of what CN has parasympathetic fibers to nasal glands?
|
greater petrosal nerve of CN VII
|
|
|
What artery supplies blood to the nasal region through the IFT and pterygomaxillary fissure?
|
maxillary artery
|
|
|
What 3 things make up the nasal septum?
|
1. septal cartilage
2. perpendicular plate of ethmoid 3. vomer |
|
|
Which concha is its own bone?
|
inf. concha
|
|
|
What region of the pharynx equilibrates air pressure in the head?
|
auditory tube
|
|
|
What nerve of what CN has parasympathetic fibers to nasal glands?
|
greater petrosal nerve of CN VII
|
|
|
What artery supplies blood to the nasal region through the IFT and pterygomaxillary fissure?
|
maxillary artery
|
|
|
What 3 things make up the nasal septum?
|
1. septal cartilage
2. perpendicular plate of ethmoid 3. vomer |
|
|
Which concha is its own bone?
|
inf. concha
|
|
|
What 2 concha are parts of the ethmoid bone?
|
mid and sup. concha
|
|
|
Where does the pituitary gland sit?
|
sella terseca
|
|
|
Where is the opening to the auditory tube from the nasopharynx?
|
just posterior to the inf. concha
|
|
|
What are the 4 nasal air sinuses?
|
1. frontal
2. maxillary 3. sphenoid 4. ethmoid |
|
|
What branches provide sensory innervation to the 4 nasal air sinuses?
|
branches nasociliary of V1
branches of V2 |
|
|
Where does the sphenoid sinus drain to and into what region of the nasal cavity?
|
spheno-ethmoidal recess just posterior to sup. concha (so the sinus drains anteriorly)
|
|
|
Where do the ethmoid air cells drain to and into what region of the nasal cavity?
|
ethmoid bulla in the middle meatus
|
|
|
What does the frontal sinus drain through and into what region of the nasal cavity?
|
frontonasal duct drains the frontal sinus into the middle meatus
|
|
|
What duct drains the tears from your eyes, and into what region of the nasal cavity?
|
nasolacrimal duct drains into the inf. meatus
|
|
|
What drains the maxillary sinus and into what region of the nasal cavity?
|
Hiatus semi-lunaris into the middle meatus
|
|
|
What is the largest sinus and what drains it?
|
maxillary sinus drained by Hiatus Semi-lunaris
|
|
|
Where is the Hiatus Semi-lunaris located in regards to the maxillary sinus, and what does this mean?
|
Hiatus semi-lunaris is at the most superior end of the maxillary sinus, so the sinus doesn't drain until it's full or you are lying down
|
|
|
Where is the pterygopalatine fossa located in relation to the maxillary sinus?
|
the pterygopalatine fossa is just posterior to the maxillary sinus
|
|
|
V2 and the pterygopalatine ganglion (parasympathetic fibers from greater petrosal n) are located in what distinct region just posterior to maxillary sinus?
|
pterygopalatine fossa
|
|
|
What nerve has GVE components that innervate nasal glands from post-ganglionic fibers after the pterygopalatine ganglion?
|
greater petrosal n. of CN VII
|
|
|
What branches of CN V innervate the internal nasal regions with GSA?
|
V1 -> nasociliary -> ant. and post. ethmoidal
V2 -> pterygopalatine -> nasopalatine |
|
|
What CN has SVA to posterior palate for some taste buds there?
|
CN VII
|
|
|
What canal opens into inf. meatus?
|
nasolacrimal canal
|
|
|
What 3 canals open into middle meatus?
|
1. frontonasal duct
2. Hiatus Semi-lunaris 3. openings to ant. ethmoidal air cells |
|
|
What 2 canals open into superior meatus?
|
1. opening to sphenoid sinus
2. openings to post. ethmoidal air cells |
|
|
What are the 3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles?
|
sup, mid, inf
|
|
|
What group of muscles begins peristalsis?
|
3 pharyngeal constrictor muscles
|
|
|
What are the 3 longitudinal muscles of the posterior pharyngeal wall?
|
1. salpingopharyngeus
2. palatopharyngeus 3. stylopharyngeus |
|
|
What is the largest pharyngeal constrictor muscle?
|
inf. constrictor
|
|
|
What muscle lifts the soft palate up?
|
levator palatini
|
|
|
What muscle puts lateral tension on the soft palate by reaching around the pterygoid hamulus?
|
tensor palatini
|
|
|
What is another name for the velum?
|
soft palate
|
|
|
What are the 4 papillae of the tongue and their shapes?
|
1. fungiform - mushroom
2. filiform - hair 3. foliate - fold 4. vallate - trench |
|
|
What is the largest and 2nd most numerous papillae?
|
vallate
|
|
|
Taste buds are associated with what papillae?
|
1. fungiform
2. foliate 3. vallate |
|
|
What innervates all the intrinsic muscles of the tongue and all extrinsic tongue muscles except the palatoglossus?
|
CN XII (hypoglossus)
|
|
|
What are the 4 extrinsic muscles of the tongue and their innervations?
|
3 by CN XII
styloglossus, hyoglossus, genioglossus 1 by CN X palatoglossus |
|
|
What 2 CNs make up the pharyngeal plexus?
|
CN IX and CN X
|
|
|
What structure divides the tongue into ant 2/3 and post 1/3?
|
sulcus terminalis (vallate papillae)
|
|
|
Through what foramen does the Chorda Tympani run?
|
petrotympanic fissure
|
|
|
What are 2 components of Chorda Tympani?
|
SVA (taste)
GVE |
|
|
What gland secretes through Wharton's Duct into ant. of mouth under the tongue?
|
sub-mandibular
|
|
|
What is the autonomic ganglion for parasympathetic fibers going to the sub-mandibular and sub-lingual glands?
|
sub-mandibular ganglion
|
|
|
What is the relationship of the Lingual Nerve to Wharton's Duct from post. to ant?
|
in posterior, lingual n. is superior and lateral to Wharton's Duct
in anterior, lingual n. is inferior and medial to Wharton's Duct |
|
|
What 3 CNs have SVA for taste?
|
VII, IX, X
|
|
|
Where are filiform palillae located?
|
all throughout tongue but mostly in ant. 2/3
|
|
|
Where are foliate papillae located?
|
sides of tongue
|
|
|
What 2 CNs provide innervation to ant 2/3 of tongue and what are their components?
|
1. CN V - GSA
2. CN VII - SVA |
|
|
What 1 CN innervates post 1/3 of tongue and what are its 2 components?
|
CN IX - GSA, SVA
|
|
|
What 1 CN innervates the root of tongue and what are its 2 components?
|
CN X - GSA, SVA
|
|
|
What innervates the geniohyoid?
|
cervical plexus C1
|
|
|
What are the 3 unpaired laryngeal cartilages from sup to inf?
|
sup: epiglottis, thyroid, cricoid: inf
|
|
|
What are the 4 paired laryngeal cartilages?
|
1. arytenoid
2. corniculate 3. cuneiform 4. triticeal |
|
|
All of the intrinsic muscles of the larynx are innervated by what?
What is the only muscle that is not an intrinsic muscle of the larynx, and what innervates it? |
recurrent laryngeal branch of CN X innervates intrinsic laryngeal muscles
external portion of sup. laryngeal branch of CN X innervates the cricothyroid |
|
|
What is the primary function of the larynx?
|
protect the airway
|
|
|
What is the flat area at the superior region of the larynx called?
|
vallecula
|
|
|
What are the 2 vocal folds?
|
1. true vocal folds
2. vestibular (false) vocal folds |
|
|
What is located between the true and false (vestibular) vocal folds?
|
the sinus/ventricle of the larynx
|
|
|
What is the only external muscle of the larynx and what is its innervation?
|
cricothyroid: ext. portion of sup. laryngeal branch of CN X
|
|
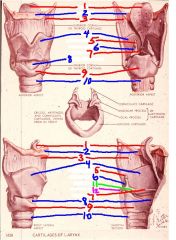
1
|
epiglottis
|
|
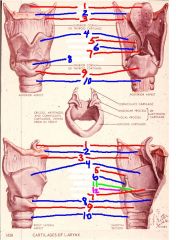
2
|
hyoid bone
|
|
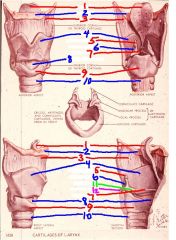
3
|
thyrohyoid membrane
|
|
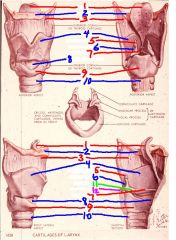
4
|
thyroid cartilage
|
|
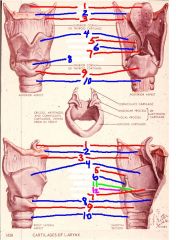
5
|
Corniculate cartilage
|
|
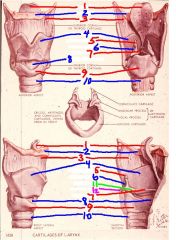
6
|
arytenoid cartilage
|
|
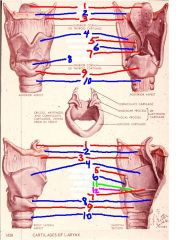
7
|
vocal ligament
|
|
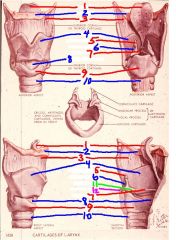
8
|
cricothyroid membrane (ligament)
|
|
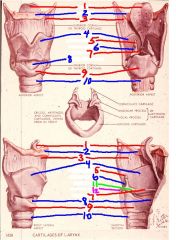
9
|
cricoid cartilage
|
|
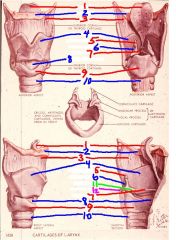
10
|
trachea
|
|
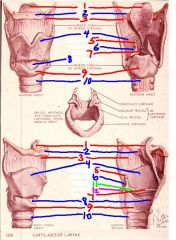
11
|
vocal process of arytenoid cartilage
|
|
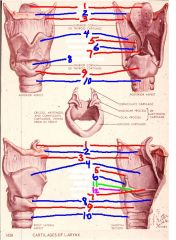
12
|
muscular process of arytenoid cartilage
|
|
|
What is another name for the conic ligament?
|
cricothyroid ligament (membrane)
|
|
|
What is the only muscle that can abduct (open) the vocal folds?
What is its innervation? |
posterior crico-arytenoid muscle
recurrent laryngeal branch of CN X because it's an intrinsic muscle |
|
|
What is the process of vocal fold adduction?
|
bringing them closer together
|
|
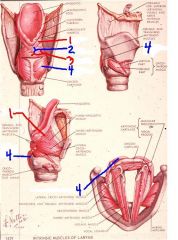
1
|
aryepiglottic muscle
|
|
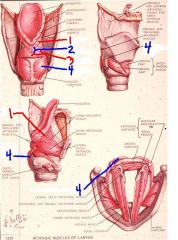
2
|
oblique arytenoid muscle
|
|
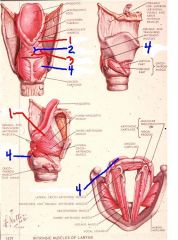
3
|
transverse arytenoid muscle
|
|
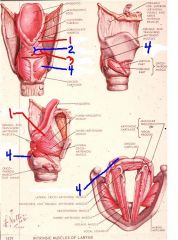
4
|
posterior crico-arytenoid muscle
|

