![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Many DNA damaging agents are
(electophiles/nucleophiles) Alkylating reagents chemically modify DNA specifically at the reactive (nucleophilic/electrophilic) centers Form covalent adducts that disrupt DNA secondary structure and/or processing by repair enzymes |
electrophiles
electrophilic |
|
|
What can all DNA alkylating agents covalently modify?
|
-The nucleophilic centers of purine and pyrimidine.
-The phosphate backbone. -DNA associated proteins. primarily target guanine residues in DNA inter-strand, intra-strand or DNA-protein cross-linking seems to be the major mechanism of toxicity guanine alkylation can result in multiple mechanisms of DNA damage that lead to cell death. |
|
|
Match these drugs to the description: (thiopeta, chlorambucil, mechloretamine, melphalan, and cyclophosphamide)
__(a) and __(c) are very reactive and can not be administered orally, can be very effective for in situ use. Other alkylating reagents are less reactive and can be administered orally __(c), __(d), and __(e) |
mechlorethamine and thiopeta are very reactive and can not be administered orally, can be very effective for in situ use.
Other alkylating reagents are less reactive and can be administered orally chlorambucil, melphalan, and cyclophosphamide |
|
|
__(1)- developed to target melanoma since these tumors use Phe to produce melanin,
more active against multiple myeloma |
Melphalan
|
|
|
designed to target breast cancer that
express estrogen receptor used to treat prostate cancer |
Estramustine
|
|
|
pro-drug that is converted by cytochrome p450 in the liver
|
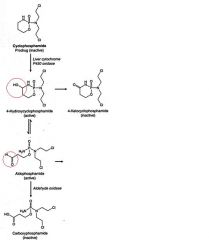
Cyclophosphamide
|
|
|
CYCLOPHOSPHAMIDE
-aldophosphamide is also converted into toxic acrolein and phosphoramide mustard -acrolein is toxic to the bladder epithelium. -hemorrhagic cystitis -can be prevented by aggressive hydration and/or __(1) which binds to acrolein. Cyclophosphamide is primarily used in combination therapy in the treatment of lymphomas, some forms of leukemia and some solid tumors |
(1) mesna
|
|
|
-Can act in a similar way to other alkylating agents but also can attach a carbamoyl group to DNA.
-unclear if carbamoylation contributes to bioactivity require bioactivation able to cross the blood/brain barrier and are used to treat brain tumors, non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, multiple myeloma, and malignant melanoma Lomustine (CCNU) is a non bis-alkylating __(1) |
Nitrosourea
|
|
|
used in combination therapy for Hodgkin's disease
|
Dacarbazine
|
|
|
-Orally active drug used for Hodgkin's disease.
-MAO inhibitor and can induce tyramine senstivity and hypotension. |
Procarbazine
|
|
|
-refractory ovarian cancer
-although structurally related to thiopeta, unclear if alkylation is main mechanism of action. |
Altretamine
|
|
|
__(1) is less nephrotoxic than cisplatin and has replaced it.
- most active drug used to treat testicular cancer, effective against lung cancer. acts as bis-alkylating reagent cis conformation of drug is critical to bioactivity as trans isomer is not potently anti-tumorigenic. -Somewhat nephrotoxic but can be lessened with amifostine |
Carboplatin
|
|
|
used in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin for the treatment of colorectal cancer
combination known as FOLFOX. |
Oxaliplatin
|
|
|
a glycosylated nonribosomal peptide antibiotic from Streptomyces verticillus.
-Binds to DNA and chelates iron, free radical formation leads to strand cleavage. -Chemotherapeutic forms are primarily bleomycin A2 and B2 used in the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma as a component of the ABVD regimen (adriamycin, bleomycin, vinblastine and dacarbazine) -Also used against squamous cell carcinomas, testicular cancer, pleurodesis (production of adhesions between the parietal and visceral pleura) and plantar warts |
Bleomycin
|
|
|
Glycopeptide-based Antitumor Antibiotics.
Treats: Wilms' tumor rhabdomyosarcoma Ewing's sarcoma trophoblastic neoplasms testicular carcinoma |
Dactinomycin, generally called Actinomycin D.
|
|
|
-Alkylating antibiotic that target hypoxic tumors.
-Requires bioreductive activation which readily occurs in hypoxic environment in center of solid tumors. -Causes delayed bone marrow toxicity. -Usually administered at 6-weekly intervals since prolonged use may result in permanent bone-marrow damage. |
Mitomycin C
|
|
|
-Specifically inhibit topoisomerase I by blocking the religation of the single strand.
-Other replication enzymes bind to drug-DNA complex and lead to double strand breakage. -Cancer cells often can not repair the strand break. |
Camptothecins
|
|
|
-Used in treating metastatic ovarian cancer and small cell lung carcinoma.
|
Irinotecan and Topotecan
|
|
|
-Intercalate with duanosamine residue directed toward the minor groove.
-Highest preference for two adjacent G/C base pairs flanked on the 5' side by an A/T base pair. -Effectively binds to every 3 base pairs and induces a local unwinding which interferes with topoisomerase II, leads to strand scission and cell death. Both cause myelosuppression and alopecia __(2) is associated with induction of congestive heart failure, dexrazoxane. |
Daunorubicin and Doxorubicin.
(2) Doxorubicin. |
|
|
-Inhibits religation reaction.
-Cells often develop resistance by increasing efflux via upregulation of P-glycoprotein. -Used against leukemia, lung and testicular cancer -Combined with carboplatin and/or bleomycin provides powerful combination to damage tumor cell DNA via distinct mechanisms. |
Etoposide
|
|
|
-Inhibits religation reaction.
-Cells also develop resistance by increasing efflux via upregulation of P-glycoprotein. -Mainly used against childhood lymphocytic leukemia. -Strongly decrease WBC and platelet count within 1-2 weeks, raises risk of infection |
Teniposide
|
|
|
Mechanism of action.
Both __(1) and __(2) bind specifically to the microtubule proteins and blocks polymerization. The dissolution of the mitotic spindle interferes with chromosome segregation and leads of mitotic arrest. |
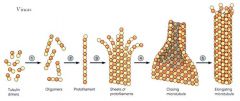
(1) Vincristine
(2) Vinblastine |
|
|
-Inhibits microtubule depolymerization.
-Relatively toxic and hypersenstivity reactions occur. -All these drugs can induce peripheral neuropathies since long peripheral nerves in legs require an intact microtubule system for normal transport of proteins. |
Paclitaxel(Taxol)
Docetaxel(Taxotere) |

