![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
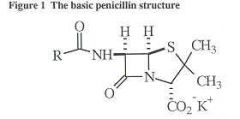
What drug can go with this following structures
|
-Need to be accompany by a + charged molecule when it in ionized form:
1. Procaine +: 24 hrs 2. Benzthine +: 1 week |
|
|
What drugs are refered to as Depot forms?
|
-Procaine, Penzathine penicillin
|
|
|
How is Pen G. metabolized?
|
-Metabolism: minimal
-Kidney excreted: 10% Glomerular 90% Tubular secretion |
|
|
What is the usage of Probenecid?
|
-Inhibit tubuler secretion: help to maintain blood level of Pen G longer
-Treatment of gout- inhibit uric acid uptake |
|
|
What is the toxicitiy relating to Pen G.?
|
-Hepersensitivity
-Neurotoxicity |
|
|
How does hypersensitivity occur with Pen G.?
|
-Protein in the body form a covalent bond w/ Pen G.
|
|
|
What causes Immediately hypersensitivity?
|
-RXN that temporary occur w/in 20min-1hr (Most serious)
-Occurs of anaphylaxis, caused by minor determinants -IgE causes this: If not treated --> Death will occur |
|
|
What is the Treatment of Immediate Hypersensitivity?
|
-Epi --> Repeated IM for 15 at thigh
-2nd: Give antihistamine or Glucocorticoids |
|
|
What is minor determinant?
|
-Less concentration w/in blood and will RXN with the side chain of the thiazolidine ring.
|
|
|
What causes Non-immediate hypersensitivity?
|
-Happen b/t 1hr -weeks
-Caused by Major determinants -IgG + IgM -Manifested by rash & hives |
|
|
What is major determinant?
|
-Occur in highest [ ] w/in blood and will RXN with the B-lactam bond of Pen. G. to cause Non-Immediate Hypersensitivity
|
|
|
What dosage of Pen G. must be given to induce Neurotoxicity (convulsions)?
|
-20-60 million unit
|
|
|
What is Pen G. used for on the Gram Positive Cocci and Gram Positive Bacilli?
|
Gram Positive Cocci:
-Streptococcus Groups A (pyogenes), B, C, G -Streptococcus enterococcus (endocarditis) -Streptococcus pneumoniae Gram Positive Bacilli: -Bacillus anthracus-anthrax -Clostridium perfringens -Clostridium tetani (not Clostridium difficile) |
|
|
What is Pen G. used for on the Gram Negative Cocci, Enteric Gram Negative Bacilli and other?
|
Gram Negative Cocci
-Neisseria meningitidis -Neisseria gonearrhea Gram Negative Bacilli -Bacteroides of oropharynx (oral cavity but not of GI tract) Other -Treponema pallidum (syphilis): Bacteria have NOT develop resistance. One shot is enough -Borellia burgdorfiri: Lyme disease |
|
|
Most Staph. aureus infection is resistant to Pen G. (T/F)
|
True
|
|
|
How does Staph. aureus become resistant to Pen G.
|
-Production of B-Lactamase (Penicillinase): This enzyme break up the B-lactam bond by forming an unstable bond with C=0 and being replaced by H2O (hydrolyze)
|
|
|
What are some drugs of choose if bacteria resistant to Pen G.
|
Penicillinase-Resistant Pen
-Methicillin: acid-labile, Parentally ONLY -Nafcillin: parentally, 90% excreted by Bile -Oxacillin, Cloxacillin, Didoxacillin: acid stable, given orally |
|
|
How does Gram + bacteria develop Methicillin resistant?
|
-Change the shape of Pencillin Binding Protein. So it can't block Transpeptidase from removing the 5th a.a and linking two NAM-NAG strand
-Or make B-Lactamase |
|
|
How does Gram - bacteria develop Methicilin resistant?
|
-B-lactamase
-Penase -Change shape of PBP. |

