![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How does V/Q mismatch effect induction?
|
Slows down
|
|
|
Which induction medications does V/Q mismatch effect more?
|
Effects the fast ones more (the more insoluble)
|
|
|
How does increased CO effect the speed of induction?
|
Slows down
|
|
|
Which induction medications does increased CO effect more?
|
The slow ones (more soluble)
|
|
|
How much of sevo is metabolized?
|
5-7%
|
|
|
Pharmaceutics
|
the formulation and preparation of drugs
|
|
|
Pharmacognosy
|
the study of the medicinal uses of naturally occurring compounds
|
|
|
Pharmacodynamics
|
Physiological and biochemical mechanism of action of dugs
|
|
|
What kind of binding does asprin do?
|
noncompetitive (non reversible)
|
|
|
What are the chemical bonds strongest to weakest?
|
Covalent
Ionic Hydrogen Hydrophobic van der Waals |
|
|
What are 4 things you can ascertain from a drug dose response curve?
|
Affinity (potency)
Efficacy Variability Slope |
|
|
Define up regulation
|
Increase of receptors due to chronic use of antagonist
|
|
|
Define down regulation
|
Down regulation is from chronic agonist administration
|
|
|
What is potentiation?
|
1 + 0 = 3
|
|
|
what is antagonism?
|
1 + 1 = 0
|
|
|
what is synergism?
|
1 + 1 = 3
|
|
|
What is ionization?
|
the degree of water solubility
|
|
|
what is non-ionized?
|
the degree of lipid solubility
|
|
|
What is enzyme induction?
|
an increase in drug metabolizing enyzmes, faster metabolism
|
|
|
What is enzyme inhibition?
|
a decrease in drug metobolizing enyzmes, slower metbolism
|
|
|
Neurotransmitters
|
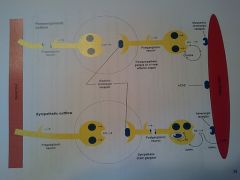
|
|
|
How are MAC and O/G solubility related?
|
Inversely proportional
|
|
|
What is diffusion hypoxia?
|
When N2O rapidly diffuses into the lungs causing dilution of O2
|
|
|
What are some differences in pediatrics and adults related to induction?
|
- Sleep faster (breath faster)
- Higher MAC used - Use Sevo primarily |
|
|
What are some anesthesia effects during pregnancy?
|
- increased CO = SLows anesthesia
- Increased RR = Speeds anesthesia |
|
|
What are some anesthesia effects of obesity?
|
Same induction slower emergence
|
|
|
How does hypothermia effect anesthesia?
|
Slower emergence
|
|
|
How does increased Cardiac Output effect induction?
|
- Delayed due to prevention of rise in alveolar concentration
- The more soluble the anesthetic the longer the induction |
|
|
What is the calculation for therapeautic window?
|
LD50/ED50
|
|
|
What are the pH's of different body systems?
|
● Gastric Juices 1-3 pH → Small Intestines 5-6 pH → Ileum 8 → Large Intestine 8 → Blood 7.4 pH → CSF 7.3 → Urine 4-8 pH.
|
|
|
What does O/G coefficient mean?
|
The more lipid-soluble (or INSOLUBLE) the gas anesthetic is the more POTENT it is.
|
|
|
Pre-synaptic parasympathetic neurotransmitter
|
ACH
|
|
|
Post-synaptic parasympathetic neurotransmitter
|
ACH
|
|
|
Pre-synaptic parasympathetic receptor
|
Nicotinic cholinergic
|
|
|
Post-synaptic parasympathetic receptor
|
Muscarinic cholinergic
|
|
|
Pre-synaptic sympathetic neurotransmitter
|
ACH
|
|
|
Presynaptic sympathetic receptor
|
Nicotinic cholinergic
|
|
|
Post-synaptic sympathetic receptor
|
Adrenergic
|
|
|
Post-synaptic sympathetic neurotransmitter
|
NE
|

