![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
47 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Function of the Pancreas Gland
|
Endocrine gland
Produces hormones in the islets of Langerhans Exocrine gland |
|
|
Insulin
Definition |
Hormone produced by the beta cells of the islets of Langerhans
|
|
|
Insulin:
Action |
Released into circulation when the levels of glucose around these cells rise
Acts like a key that allows glucose to enter the cells for utilization by the body Stimulates the synthesis of glycogen, the conversion of lipids into fat stored in the form of adipose tissue, and the synthesis of needed proteins from amino acids |
|
|
List 8 Metabolic Changes Occurring When Insufficient Insulin is Released
|
Hyperglycemia
Glycosuria Polyuria Polyphagia Polydipsia Lipolysis Ketosis Acidosis |
|
|
Hyperglycemia:
|
Hyperglycemia: Increased blood sugar
|
|
|
Glycosuria:
|
Glycosuria: Sugar is spilled into the urine
|
|
|
Polyuria:
|
Polyuria: Glucose attracts water
|
|
|
Polyphagia:
|
Polyphagia: Increased hunger
|
|
|
Polydipsia:
|
Polydipsia: Increased thirst
|
|
|
Lipolysis:
|
Lipolysis: Fat breakdown
|
|
|
Ketosis:
|
Ketosis: Ketones cannot be removed effectively
|
|
|
Acidosis:
|
Acidosis: Liver cannot remove all of the waste products
|
|
|
Clinical Signs and Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
|
Fatigue
Lethargy Irritation Glycosuria Polyuria Polyphagia Polydipsia Itchy skin |
|
|
Clinical Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
|
Nervousness
Sweating Intense hunger Trembling Weakness Palpitations May have trouble speaking Can progress to confusion, drowsiness, changes in behavior, coma, seizures |
|
|
Insulin Administration
|
Consistency in timing is key for all
Most should be timed in relation to food intake to coincide with onset, peak, and duration of specific insulin. Time of administration can be from 60 minutes before, during, or up to 20 minutes after a meal Some longer acting ones need to have no relationship to meal time |
|
|
Sulfonylureas :
|
Sulfonylureas : Stimulate beta cells to make more insulin
|
|
|
Meglitinides:
|
Meglitinides: Stimulate beta cells to make more insulin
|
|
|
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs):
|
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs): Decrease glucose production in liver and increase insulin sensitivity
|
|
|
Biguanides:
|
Biguanides: Decrease glucose production in liver and increase insulin sensitivity
|
|
|
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors:
|
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: slow absorption of starches in gut by blocking an enzyme so reduced amount of glucose enters bloodstream
|
|
|
Sites of Action of Drugs Used to Treat Diabetes
|
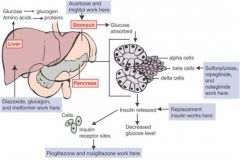
|
|
|
Regular Insulin
|
Humulin R - short acting
Onset: 30-60 min Peak: 2-4 hr Duration: 8-12 hr |
|
|
Semilente NPH
|
Humulin N - intermediate
Onset: 1-1.5 hr & 60-90 min Peak: 5-10 hr & 4-12 hr Duration: 12-16 hr & 24 hr Appearance: Cloudy |
|
|
Lispro
|
Humulog - Rapid
Onset: <15 min Peak: 30-90 min Duration: 2-5 hr |
|
|
Aspart
|
Novolog - rapid
Onset: 15 min Peak: 1-3 hr Duration: 3-5 hr |
|
|
Glulisine
|
Apidra - rapid
Onset: 2-5 min Peak: 30-90 min Duration: 1-2.5 hr ***CANNOT BE MIXED WITH ANY OTHER DRUG IN SOLUTION*** |
|
|
Glargine
|
Lantus - long
Onset: 60-70 min Duration: 24 hrs ***CANNOT BE MIXED WITH ANY OTHER DRUG IN SOLUTION*** |
|
|
Detemir
|
Levemir - long
Onset: 1-2 hours Peak: 6-8 hr Duration: 24 hr |
|
|
Lente
*might not need to know for test* |
Humulin L
Onset: 1-25 min Peak: 7-15 hr Duration: 24 hr |
|
|
PZI
|
Humulin U
Onset: 4-8 hr Peak: 14-24 hr Duration: 36 hr |
|
|
Ultralente
*might not need to know for test* |
Humulin U Ultralente
Onset: 4-8 hr Peak: 10-30 hr Duration: 20-36 hr |
|
|
Inhalational Insulin
*may not need to know for exam* |
Exubera
Onset: 10-20 min Peak: 2 hr Duration: 6 hr |
|
|
NPH and Regular
Humulin 70/30 Novolin 70/30 Humulin 50/50 Humalog 75/25 |
Onset: 30-60 min then 1-2 hr
Peak: 2-4 hr then 6-12 hr Duration: 6-8 hr then 18-24 hr |
|
|
Metformin
Type: |
non-sulfonylureas
|
|
|
Metformin
Brand Name: |
Glucophage
|
|
|
Metformin
Indications: |
Adjunct to diet and exercise for treatment of type 2 diabetics over 10 years old; extended release form for 17 and up
|
|
|
Metformin
Therapeutic actions |
May increase periferal use of glucose, increase production of insulin, decrease hepatic glucose production, alter intestinal absorption of glucose
|
|
|
Metformin
Route: Onset: Peak: Duration: |
Route: Oral
Onset: slow Peak: 2 - 2.5 hrs Duration:10-16 hrs |
|
|
Metformin
T 1/2: metabolized: excreted: |
T 1/2: 6.2 & then 17 hrs
metabolized: liver excreted: urine |
|
|
Metformin
Adverse effects |
hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, GI upseat, nausia, anorexia, diarrhea, heartburn, allergic skin reaction
|
|
|
chlorpropamide &
glyburide Type |
chlorpropamide: 1st generation sulfonylureas
glyburide: 2nd generation sulfonylureas |
|
|
chlorpropamide &
glyburide Brand Name(s) |
chlorpropamide: Diabenese
glyburide: DiaBeta, Micronase, Glynase PresTab |
|
|
chlorpropamide &
glyburide Indications |
Adjunct to diet and exercise to lower blood gluccose leves in type 2 diabetics
|
|
|
chlorpropamide &
glyburide Therapeutic actions |
stimulates the realse of insulin from functioning cells in the pancreas; may improve binding (or increase # of) insulin receptor sites.
|
|
|
chlorpropamide &
glyburide Route: Onset: Peak: Duration: |
Route: Oral
Onset: 1 hr Peak: 3-4 hrs Duration: 60 hrs |
|
|
chlorpropamide &
glyburide T 1/2: metabolized: excreted: |
T 1/2: 36 hrs
metabolized: liver excreted: urine & bile |
|
|
chlorpropamide &
glyburide Adverse effects: |
GI discomfort, anorexia, heartburn, vomiting, nausia, hypoglycemia
|

