![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
319 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
LEVOTHYROXINE |
INDICATIONS:
hypothyroidism pituitary TSH suppression CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity recent MI recent thyrotoxicosis uncorrected adrenal insufficiency use with caution if elderly, cardiovascular disease, swallowing disorders do not use for weight control MOA: unknown ADVERSE AFFECTS: • fever • headache • nausea • vomiting • diarrhea • stomach cramps • sensitivity to heat • excessive sweating • increased appetite • nervousness • irritability • tremor • insomnia • temporary hair loss • weight loss • changes in menstrual cycle INTERACTIONS: increases effect of vitamin K anatagonists PATIENT EDUCATION: take with 8oz of water on empty stomach 30-60min before breakfast may take several weeks for symptoms to improve requires 6-8 weeks for full effect continue taking even if feel well call immediately if experience rapid HR or chest pain |
|
|
|
What are the indications for aspirin?
|
analgesic
antipyretic anti-inflammatory anti-platelet → prevention of MI, TIA, CVA; current MI; post-MI; revascularization procedures |
Pharmacology p504
|
|
|
PROPRANOLOL
|
INDICATIONS:
unlabeled/investigational use for thyrotoxicosis HTN angina pectoris V-tach arrhythmias essential tremor MI prevention migraine prevention CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity severe bradycardia 2nd or 3rd-degree heart block uncompensated CHF cardiogenic shock asthma COPD pheochromocytoma use with caution if DM (may mask hypoglycemia), hyperthyroidism (may mask thyrotoxicosis), myasthenia gravis or psychiatric disease (may cause CNS depression), renal or hepatic dysfunction MOA: non-selective B-adrenergic blocker → competitively blocks B1 and B2 adrenergic stimulation → decrease in BP, HR, myocardial contractility and O2 demand ADVERSE EFFECTS: • fatigue • dizziness • rash • upset stomach • vomiting • constipation • diarrhea • insomnia INTERACTIONS: increased or decreased with alcohol PATIENT EDUCATION: take same time everday do not stop abruptly → may result in HTN, tachycardia or ischemia call immediately if experience • hypotension, arrhythmia, sore throat, SOB, chest pain, unusual bleeding, swelling of the feet or hands, unusual weight gain |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of penicillins?
|
inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis by disrupting synthesis of peptidoglycan
|
|
|
|
PROPYLTHIOURACIL (PTU)
|
INDICATIONS:
hyperthyroidism (palliative treatment prior to radioactive iodine therapy or surgery) thyrotoxic crisis only give if allergic or can't tolerate methimazole or in 1st trimester of pregnancy CONTRAINDICATIONS: pregnancy breast feeding hypersensitivity use with caution if bone marrow depression or liver dysfunction MOA: inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones by blocking oxidation of iodine in thyroid gland ADVERSE EFFECTS: • dizziness • nausea • vomiting • difficulty tasting food • hair loss • neck swelling • myalgias • arthralgias • parasthesias INTERACTIONS: decreases effect of vitamin K anatagonists PATIENT EDUCATION: take same time everyday in relation to meals (i.e. always with meals or always without meals) take even if feel well requires periodic monitoring of CBCDP, HFP, TSH, FT4, PT |
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of aspirin?
|
IRREVERSIBLY inhibits COX-1 → preventing thromboxane A2 production
COX-1 normally converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2 → prostaglandin is converted to thromboxane A2 |
Pharmacology p233, 502
|
|
|
METHIMAZOLE
|
INDICATIONS:
hyperthyroidism (palliative treatment prior to radioactive iodine therapy or surgery) thyrotoxic crisis CONTRAINDICATIONS: pregnancy breast feeding hypersensitivity use caution if bone marrow depression or hepatic dysfunction MOA: inhibits synthesis of thyroid hormones by blocking oxidation of iodine in thyroid gland ADVERSE EFFECTS: INTERACTIONS: decreases effect of vitamin K anatagonists PATIENT EDUCATION: take same time every day in relation to meals (i.e. always with meals or always between meals) requires periodic monitoring of CBCDP, HFP, TSH, FT4, PT |
|
|
|
List drug classes used to treat lung disease.
|
short-acting beta agonists → all asthma, COPD; bronchodilator
inhaled corticosteroids → mild, moderate, severe asthma; anti-inflammatory long-acting beta agonists → moderate, severe asthma; bronchodilator systemic corticosteroids → severe asthma; anti-inflammatory mast cell stabilizer → asthma prophylaxis; inhibitts histamine release anticholinergics → COPD; inhibits Ach → bronchodilation phosphodiesterase inhibitors → do not prescribe; bronchodilator leukotreine modifiers → asthma prophylaxis; inhibits arachidonic acid pathway |
|
|
|
What is the starting regimen and monitoring for levothyroxine in a newly diagnosed patient with hypothyroidism?
|
starting dose and rate of adjustment dependent on age, weight, chronic disease (especially CAD), symptom duration, and TSH level
if young and healthy: start at 50-100 mcg/d if >50y/o or comorbidities: start at 25-50 mcg/d to avoid angina, arrhythmias or HF symptomatic improvement occurs in 2-4 weeks full effect occurs 6-8 weeks monitor TSH and adjust dose after 6-8 weeks if young and healthy → adjust in 25-50 mcg increments until euthyroid if >50y/o or comorbidities → adjust in 25 mcg increments until euthyroid decrease dose if cardiac symptoms if pregnant → refer to endocrinologist → requires increase up to 50% in 25-50 mcg increments every 4-6 weeks |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of aspirin?
|
prolonged bleeding time
GI problems → distress, ulcer, hemorrhage, iron-deficiency anemia sodium and water retention → edema, hyperkalemia hemorrhagic stroke |
Pharmacology p233, 502
|
|
|
List available thyroid replacement therapies.
|
levothyroxine (T4)
levotrix (T4/T3 combination) |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of quinolones?
|
inhibit bacterial DNA replication by interfering with DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) and topoisomerase IV enzymes
|
Pharmacology p387
|
|
|
What are the pros and cons of thyroid replacement therapies?
|
LEVOTHYROXINE (T4):
well tolerated LIOTRIX (T4/T3 combo): unecessary since body converts T4 into T3 in appropriate amounts does not improve outcomes compared to T4 data insufficient to support use potential side effects can easily take too much side effects rapid due to short half-life can cause HTN, tachycardia, angina especially avoid in elderly switch to levothyroxine |
|
|
|
Why may aspirin cause GI bleeding?
|
↑ gastric acid secretion
↓ mucus production |
Pharmacology p502
|
|
|
LIOTRIX
|
INDICATIONS:
hypothyroidism T4/T3 combination does not improve outcomes cost not justified |
|
|
|
What are diuretics?
|
medications that increase urine flow
|
Pharmacology p261
|
|
|
What is Amour thyroid and why shouldn't it be prescribed?
|
Amour thyroid
brand of dessicated thyroid from pigs should not be used due to large variation in amount of thyroid from batch to batch |
|
|
|
If an NSAID causes GI bleeding, and continued NSAID treatment is necessary, what should you prescribe?
|
proton pump inhibitor (PPI) or misoprostol
|
Pharmacology p502
|
|
|
What is the MOA of sulfonamides?
|
inhibit folate synthesis preventing cell division
|
|
|
|
Toxic doses of aspirin cause?
|
respiratory depression
|
|
|
|
List short acting beta agonists.
|
albuterol
pirbutelol terbutaline levalbuterol metaproterenol |
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of aspirin toxicity?
|
HA, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, mental confusion, tinnitus, hyperventilation → restlessness, delirium, hallucinations, convulsions, coma, respiratory and metabolic acidosis, death from respiratory failure
|
Pharmacology p505
|
|
|
What is the MOA of cephalosporins?
|
inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis by disrupting synthesis of peptidoglycan
|
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for aspirin?
|
<15y/o
pregnancy and breast-feeding surgery within 1 week probenecid, sulfinpyrazone increase uric acid secretion (whereas aspirin decreases uric acid secretion) |
Pharmacology p505, 506
|
|
|
What is psyllium?
|
AKA metamucil
bulk-forming laxative used to treat constipation |
|
|
|
Why must aspirin be avoided in adolescents <15y/o?
|
aspirin + viral infection = potential Reye's syndrome
|
Pharmacology p504
|
|
|
Sildenafil Citrate (Viagra): indications, contraindications, patient education
|
INDICATIONS:
erectile dysfunction pulmonary arterial HTN CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity to sildenafil concurrent use of nitrates PATIENT EDUCATION: take 1 tablet 1 hour before sexual activity do not take >1 tablet per day absorption delayed by consumption of food (especially high-fat) avoid excessive alcohol consumption → may cause hypotension do not take nitrates may experience HA, flushing, vision changes, nasal congestion, epistaxis, dyspepsia, myalgia, insomnia discontinue if serious side effects → erection >4hr, vision change, hearing changes |
Pharmacology p341
Lexi-Comp p1368 |
|
|
What is the patient education for aspirin?
|
1. take with fluids and food to decrease dyspepsia
2. do not take concurrently with other salicylates 3. do not take 1 week prior to surgery 4. do not take with probenecid or sulfinpyrazone 5. may need to lower warfarin, phenytoin, or valproic acid etc. since aspirin causes higher plasma concentrations of those drugs |
Pharmacology p233, 506
|
|
|
What is the MOA of short acting beta agonists?
|
B2 agonists → binding causes relaxation of airway smooth muscle → bronchodilation
effective in 5-30 minutes last 4-6 hours |
|
|
|
What is the dosing for aspirin?
|
prevention of MI → 81-162 mg/d
prevention of stroke → 50-325 mg/d acute MI → 162-325mg OA or RA → 3g/d |
Pharmacology p505
|
|
|
Tadalafil (Cialis): indications, contraindications, patient education
|
INDICATIONS:
erectile dysfunction CONTRAINDICATIONS: concurrent use of nitrates PATIENT EDUCATION: take 1 tablet 1 hour before sexual activity do not take >1 tablet per day avoid excessive alcohol consumption → may cause hypotension do not take nitrates may experience HA, flushing, nasal congestion, dyspepsia discontinue if serious side effects → erection >4 hours, vision changes, hearing changes |
Pharmacology p341
Lexi-Comp p1422 |
|
|
What type and dose of aspirin should be given for acute MI?
|
162-325mg of nonenteric coated aspirin chewed and swallowed immediately
|
Pharmacology p505
|
|
|
What are the classes of diuretics?
|
carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
osmotic diuretics loop diuretics thiazide diuretics potassium-sparing diuretics |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ibuprofen?
|
analgesic
antipyretic anti-inflammatory anti-platelet |
Pharmacology p507
|
|
|
Compare sildenafil citrate (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis).
|
SILDENAFIL CITRATE:
quicker onset (<1 hour) shorter duration (4 hours) absorption delayed by food consumption TADALAFIL: slower onset (1 hour) longer duration (36 hours) absorption NOT delayed by food consumption |
Pharmacology p341
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action for ibuprofen?
|
REVERSIBLY inhibits COX-1 → preventing synthesis of prostaglandins (but not leukotrienes)
|
Pharmacology p507
|
|
|
What is the MOA of long acting beta agonists?
|
B2 agonists → binding causes relaxation of airway smooth muscle → bronchodilation
*analogs to albuterol but possess lipophilic side chain that increases affinity for B2-adrenoreceptors → increasing duration last 12 hours |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of ibuprofen?
|
GI → dyspepsia, bleeding
CNS → HA, dizziness, tinnitus |
Pharmacology p507
|
|
|
Alprostadil (Caverject, Muse): indications, contraindications, patient education
|
INDICATIONS:
erectile dysfunction CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity to alprostadil anatomical deformity of penis conditions predisposing to priapism → sickle cell disease, multiple myeloma, leukemia penile implant pregnancy PATIENT EDUCATION: get trained on how to inject into penis or urethra only use appropriate dose do not use >1 time per day do not use >3 times per week do not reuse needles avoid concurrent alcohol use may experience penile pain, urethral burning or bleeding, testicular pain, HA, dizziness, HTN discontinue if serious side effects → erection >4hr, signs of penile fibrosis (angulation, fibrosis, peyronie's disease) |
Lexi-Comp p70
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action for indomethacin?
|
REVERSIBLY inhibits COX-1
|
Pharmacology p507
|
|
|
Define analgesia.
|
loss or modulation of pain perception
can be local, regional, or systemic |
|
|
|
What are the indications for indomethacin?
|
OA of hip
ankylosing spondylitis acute gout *analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory effects but use limited to above conditions due to toxicity |
Pharmacology p507
|
|
|
List drugs to treat erectile dysfunction and whether they are oral or injections.
|
ORAL:
sildenafil citrate tadalafil INJECTION: alprostadil (may be injected into corpus carvernosum or urethra) |
|
|
|
What are the indications for meloxicam?
|
OA
RA ankylosing spondylitis |
Pharmacology p507
|
|
|
What is are the indications for SABA?
|
prevention or treatment of bronchospasm in asthma
prevention of exericise-induced asthma |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ketorolac?
|
potent analgesic → short-term relief of moderate to severe pain up to 5 days after first dose administered via IV or IM
*only moderate anti-inflammatory |
Pharmacology p508
|
|
|
Describe the male sexual response cycle.
|
sexual stimulation → increased production of nitric oxide → increased acitivity of guanylyl cyclase → increased cGMP → increased relaxation of smooth muscle of corpus cavernosum → increased blood flow → erection
|
Pharmacology p342
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for ketorolac?
|
pediatrics
|
Pharmacology p508
|
|
|
List classes of diuretics in order of most effective to least effective.
|
loop diuretics < thiazide diuretics < potassium sparing diuretics
|
Pharmacology p261
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of ketorolac?
|
GI bleeding
stomach or intestinal perforation fatal peptic ulcer |
Pharmacology p508
|
|
|
What are risks of UTI in women?
|
young or >65 y/o
sexually active use of diaphragm or spermicide cream |
|
|
|
What is the patient education for ketorolac?
|
if mild or chronic pain → do not exceed 40mg/d
|
Pharmacology p508
|
|
|
What is methycellulose?
|
used to treat constipation
|
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action for celecoxib?
|
reversible inhibition of COX-1 but mostly COX-2
|
Pharmacology p508
|
|
|
List sulfonamides used to treat UTIs.
|
sulfamethoxazole
trimethoprim |
|
|
|
What are the indications for celecoxib?
|
pain
OA RA *no anti-platelet function |
Pharmacology p508
|
|
|
List types of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.
|
acetazolamide
|
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of celecoxib?
|
HA, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, diarrhea
*less GI bleeding than aspirin |
Pharmacology p508
|
|
|
Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim (Bactrim): MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
inhibits folate synthesis INDICATIONS: UTIs acute otitis media in children acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis in adults due to H. flu or S. pneumo prophylaxis and treatment of pneumocystic jiroveci pneumonitis (PCP) traveler's diarrhea due to entertoxigenic E. coli enteritis due to Shigella flexneri or Shigella sonnei CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivitiy to any sulfa drug infants <2 m/o pregnancy breast feeding megaloblastic anemia due to folate deficiency severe hepatic or renal disease ADVERSE EFFECTS: rash, urticaria nausea, vomiting, anorexia DOSING PARAMETERS FOR UTI: 1 double-strength tablet PO q12 hours x 3-5 days if uncomplicated x 7-10 days if complicated x 14 days if pyelonephritis x 2 weeks if acute prostatitis x 2-3 months if chronic prostatitis PATIENT EDUCATION: take with 8oz of water wear sunscreen and avoid prolonged sun exposure to prevent photosensitivity |
Lexi-Comp p1407
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for celecoxib?
|
sulfonamide allergy
severe heart disease severe hepatic disease severe renal disease may increase levels of some B-blockers, antidepressants, antipsychotics |
Pharmacology p509
|
|
|
How do you convert lbs to kg?
|
lbs/2.2 = kg
|
|
|
|
What is the generic name for Motrin?
|
ibuprofen
|
|
|
|
List quinolones used to treat UTIs.
|
ciprofloxacin
norfloxacin |
|
|
|
What is the generic name for Vicodin?
|
hydrocodone
|
|
|
|
List antitubercular drugs.
|
isoniazid
rifampin pyrazinamide ethambutol |
|
|
|
What is the generic name for Valium?
|
diazepam
|
|
|
|
List cephalosporins used to treat UTIs.
|
cephalexin
|
|
|
|
What is the generic name for Percocet?
|
oxycodone
|
|
|
|
What is the MOA for carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (acetazolamide)?
|
inhibition of HCO3- reabsorption in proximal convoluted tubule
|
Pharmacology p261
|
|
|
What is the generic name for Demerol?
|
meperidine
|
|
|
|
List penicillins used to treat UTIs.
|
procaine penicillin G
ampicillin amoxicillin + clavulanic acid (Augmentin) |
|
|
|
What are the indications for acetominophen?
|
analgesic → pain, OA
antipyretic *no anti-inflammatory effects |
|
|
|
What is the treatment protocol for TB?
|
1. if latent TB → treat with isoniazid x 9 months
2. if active TB → treat with isoniazid + rifampin + ethambutol + pyrazinamide x 2 months → then isoniazid + rifampin x 4 months 3. add more drugs if previous TB or suspected resistant TB |
Pharmacology p400
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of opioids?
|
sedation
respiratory depression constipation tolerance withdrawal addiction |
|
|
|
Quinolones
|
bactericidal
effective against gram-negative organisms ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin: 2nd generation effective against aerobic gram-negative and atypical |
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for morphine?
|
respiratory depression
renal failure |
|
|
|
When should diarrhea NOT be treated with antidiarrheals?
|
bloody stool
high fever systemic toxicity d/c if worsening diarrhea okay if mild to moderate diarrhea with none of the above |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of colchicine?
|
1. bind and depolymerizes tubulin, a protein involved in mobilization of neutrophils → decreasing their accumulation in gout affected sites
2. blocks cell division by binding to myotic spindles 3. inhibits leukotriene synthesis |
|
|
|
Ciprofloxacin: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis and reproduction INDICATIONS: systemic infections CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATION: |
|
|
|
What are the indications for colchichine?
|
pain relief in acute gout
prevention of acute gout attacks |
Pharmacology p516
|
|
|
What is the MOA for isoniazid?
|
inhibits enoyl acyl carrier protein reductase (InhA) and B-ketoacyl-ACP synthase (KasA) → inhibiting mycolic acid synthesis → inhibiting mycobacterial cell wall synthesis
|
Pharmacology p400
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for colchicine?
|
pregnancy
|
|
|
|
Norfloxacin: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis and reproduction INDICATIONS: effective against gram-neg and gram pos in treating: uncomplicated UTIs complicated UTIs prostatitis CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATION: |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of colchicine?
|
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain
|
|
|
|
What are the indications for acetazolamide?
|
prophylaxis for mountain sickness
↓ intraocular pressure of open-angle glaucoma |
Pharmacology p272
|
|
|
List ucosuric medications.
|
probenecid
sulfapyrazone |
|
|
|
Leuprolide: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
agonist of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone → inhibiting gonadotropin secretion → decreasing testosterone INDICATIONS: palliative treatment of advanced prostate cancer endometriosis anemia caused by uterine fibroids central precocious puberty CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity abonormal vaginal bleeding pregnancy breast feeding ADVERSE EFFECTS: altered mood, depression, memory HA, weakness, pain, depression, insomnia, fatigue, dizziness, vertigo skin reaction edema nausea, vomiting, weight change hot flashes, testicular atrophy, hyperlipidemia, decreased libido vaginitis, urinary disorder flu-like syndrome DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATION: if treating for prostate cancer, initial rise in serum testosterone may cause worsening of symptoms |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of ucosurics (probenecid and sulfapyrazone)?
|
inhibits urate-anion exchanger in proximal tubule → inhibiting resorption → increasing renal clearance of uric acid
|
|
|
|
What are the indications for isoniazid?
|
latent TB
active TB |
Drug Information Handbook p820
|
|
|
What are the indications for probenecid or sulfapyrazone?
|
prevention of gout where uric acid is undersecreted
|
|
|
|
Flutamide: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
INDICATIONS: metastatic prostate cancer CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity severe hepatic impairment ADVERSE EFFECTS: gynecomastia decreased libido impotence nausea and vomiting increase AST and LDH DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATIONS: |
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for probenecid or sulfapyrazone?
|
renal insufficiency
kidney stones high dose aspirin therapy |
|
|
|
Define anesthesia.
|
total loss of sensory perception
may include loss of consciousness |
|
|
|
List xanthine oxidase inhibitors.
|
allopurinol
|
|
|
|
Finasteride: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
INDICATIONS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATIONS: |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of allopurinol?
|
inhibits xanthine oxidase which normally catalyzes uric acid synthesis
|
|
|
|
What are the side effects of isoniazid?
|
hypersensitivity
peripheral neuritis (parasthesias of hands and feet) hepatitis and idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity inhibits metabolism of phenytoin → potentiating side effects of phenytoin → nystagmus, ataxia |
Pharmacology p401
|
|
|
What are the indications for allopurinol?
|
prevention of chronic gout if:
1. overproducer of uric acid 2. undersecreter of uric acid + renal insufficiency |
|
|
|
Prazosin: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
INDICATIONS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATIONS: |
|
|
|
List natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic opiods.
|
natural → morphine, codeine
semi-synthetic → hydromorphone, hydrocodone, oxycodone synthetic → tramadol, methadone, meperidine |
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for acetazolamide?
|
hepatic cirrhosis
|
Pharmacology p272
|
|
|
List the indications for opioid analgesics.
|
mild to moderate pain → tylenol with codeine,
moderate to severe pain → morphine, hydromorphone, hydrocodone, oxycodone, meperidine, tramadol opioid detox → methadone |
|
|
|
Terazosin: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing parameters, patient education
|
MOA:
INDICATIONS: CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS: DOSING PARAMETERS: PATIENT EDUCATIONS: |
|
|
|
What are the most common adverse effects of opioids?
|
constipation, sedation, respiratory depression
|
|
|
|
What is the MOA of rifampin?
|
inhibits mRNA synthesis (transcription)
|
Pharmacology p402
|
|
|
Urinary retention is a common side effect of meperidine (demerol), true or false?
|
true
|
|
|
|
When should a 3 day regimen vs a 7 day regimen be used for acute uncomplicated UTI?
|
3 day regimen if:
uncomplicated cystitis 7 day regimen if cystits + diphragm use >65 y/o DM symptoms >7 days recurrent infection |
|
|
|
What is the clinical presentation of laxative abuse syndrome?
|
dehydration
electrolyte imbalance prolonged use causes constipation laxative dependency → larger doses of laxative needed to produce same effect on colon intestinal paralysis, colonic infection, IBS, colon cancer, liver damage bloody stool → anemia if recovering → water retention, edema, weight gain |
|
|
|
What are the most common pharmacologic agents associated with nephrotoxicity?
|
acetaminophen
NSAIDS → high dose ASA antibiotics → penicillins, cephalosporins, sulfonamides, vancomycin antivirals → acyclovir antifungals → amphotericin B antituberculosis → rifampin antineoplastics → cisplatin, carboplatin diuretics ACE inhibitors and ARBs allopurinol lithium contrast dye gold ethylene glycol (found in radiator fluid) |
|
|
|
What are the indications for rifampin?
|
active TB
meningitis prophylaxis OFF LABEL: h. flu prophylaxis legionella pneumonia leprosy |
Drug Information Handbook p1315
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of pyridium in acute UTI?
|
symptomatic relief of urinary itching, burning, urgency, or frequency
|
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of acetazolamide?
|
hypokalemia
metabolic acidosis renal stone formation drowsiness paresthesia |
Pharmacology p272
|
|
|
Nitrofurantoin: MOA, indications, contraindications,
adverse effects, dosing, patient education |
MOA:
inhibits several bacterial enzymes → interfering with metabolism and cell wall synthesis INDICATIONS: prevention and treatment of UTI caused by E. coli, klebsiella, enterobacter, S. aureus, enterococcus CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity pregnancy at term breastfeeding renal impairment DOSING: 7 day regimen PATIENT EDUCATION: take with food requires monitoring of LFTs if for prophylaxis, take at bedtime |
|
|
|
What are the side effects of rifampin?
|
nausea
vomiting rash hepatitis (rare) liver failure (rare) *beware if elderly, alcoholic, or chronic liver disease *make cause flu-like syndrome with fever, chills, myalgias *sometimes associated with acute renal failure, hemolytic anemia, and shock |
Pharmacology p402
|
|
|
Discuss the use of nitrofurantoin in the use of UTIs.
|
rarely used due to narrow-spectrum and toxicity
useful against E. coli and gram-pos cocci other organisms may be resistant causes GI upset, acute pneumonitis, neurologic problems |
|
|
|
What is the brand name of warfarin?
|
coumadin
|
Drug Information Handbook p1846
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of nitrofurantoin?
|
GI disturbances
acute pneumonitis neurologic problems |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of ethambutol?
|
inhibits arabinosyl transferase → inhibiting mycoplasma cell wall
|
Pharmacology p403
|
|
|
What are the pharmacologic agents used to treat BPH?
|
finasteride
prazosin terazosin |
|
|
|
List types of osmotic diuretics.
|
mannitol
|
|
|
|
What are the pharmacologic agents used to treat prostate cancer?
|
treatment → flutamide
palliative treatment → leuprolide |
|
|
|
What are the indications for ethambutol?
|
adjunctive treatment of active TB
other mycobacterial diseases |
Drug Information Handbook p573
|
|
|
Tolterodine tartrate: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing, patient education
|
MOA:
antagonist of muscarinic receptors → increasing residual urine volume and decreases detrusor muscle pressure INDICATIONS: overactive bladder with sxs of frequency, urgency, or urge incontinence CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity urinary retention gastric retention uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma ADVERSE EFFECTS: dry mouth HA constipation DOSING: PATIENT EDUCATION: may cause drowsiness or blurred vision |
|
|
|
Antibiotics are not recommended in diarrhea caused by?
|
salmonella
campylobacter E coli O157:H7 Yersinia Aeromonas |
|
|
|
Oxybutynin: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing, patient education
|
MOA:
direct antispasmotic effect on smooth muscle → increases bladder capacity, decreases uninhibited contractions, delays desire to void INDICATIONS: antispasmodic for neurogenic bladder (frequency, urgency, urge incontinence) CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity urinary retention gastric retention untreated glaucoma ADVERSE EFFECTS: dry mouth constipation DOSING: PATIENT EDUCATION: |
|
|
|
What are the side effects of ethambutol?
|
optic neuritis → decreased visual acuity and loss of ability to discriminate red and green
decreased uric acid secretion → gout |
Pharmacology p403
|
|
|
Trospium chloride: MOA, indications, contraindications, adverse effects, dosing, patient education
|
MOA:
antagonist of muscarinic receptor → reducing smooth muscle tone of bladder INDICATIONS: overactive bladder with frequency, urgency, incontinence CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity urinary retention gastric retention uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma ADVERSE EFFECTS: dry mouth constipation HA DOSING: PATIENT EDUCATION: take 1 hour prior to meals or on empty stomach |
|
|
|
What is the MOA for osmotic diuretics?
|
cause increased water secretion (not increased Na+ excretion like other diuretics)
|
Pharmacology p272
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of finasteride?
|
decreased libido
sexual dysfunction |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of pyrazinamide?
|
unknown
|
Pharmacology p403
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of prazosin and terazosin?
|
vertigo
orthostatic hypotension tachycardia sexual dysfunction |
|
|
|
PYSCHOSOCIAL SUPPORT & CHILDBIRTH CLASSES:
|
adjunctive therapy to medications
involves relaxation, suggestion, concentration, and motivation techniques which help reduce anxiety, tension, and fear increases knowledge of process of labor and delivery increases communication between patient and partner effects dependent on provider and patient commitment |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of flutamide?
|
decreased libido
sexual dysfunction gynecomastia |
|
|
|
What are the indications for pyrazinamide?
|
adjunctive treatment of active TB
|
Drug Information Handbook p1270
|
|
|
What are the indications for mannitol?
|
maintain urine flow following:
increased ICP due to shock acute renal failure due to shock drug toxicity trauma prevents kidneys from failing |
Pharmacology p272
|
|
|
What are the side effects of pyranizamide?
|
fatigue, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, myalgia, arthralgia
liver dysfunction decreased uric acid secretion → gout |
Pharmacology p403
|
|
|
Why is ipecac no longer used to induce vomiting?
|
only causes partial evacuation
delays or prevents use of activated charcoal increases risk of pulmonary aspiration increases risk of toxic effects on heart |
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of acute theophylline overdose?
|
MILD INTOXICATION:
nausea vomiting tachycardia tremors SEVERE INTOXICATION: hypotension seizures supraventricular tachy arrhythmias ventricular arrhythmias ACUTE OVERDOSE: hypokalemia hyperglycemia hypercalcemia hyperphosphatemia metabolic acidosis |
Current ch38
Pharmacology p325 http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/818847-treatment |
|
|
What are the adverse effects of mannitol?
|
extracellular water expansion and dehydration
hypo and hypernatremia |
Pharmacology p272
|
|
|
What is the management of acute theophylline overdose?
|
1. activated charcoal
2. if large ingestion involving sustained release preparations → whole bowel irrigation in addition to charcoal 3. benzodiazepines for seizures 4. B-blockers for hypotension and tachycardia |
Current ch38
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/818847-treatment |
|
|
How do you calculate a pediatric dosage of a given medication based on weight (lbs or kg)?
|
pediatric doses usually available as mg/kg/dose or mg/kg/day
if no pediatric dosing available: 1. Clark's Rule for 2-17y/o: pediatric dose = adult dose x [weight (kg)/70] pediatric dose = adult dose x [weight (lb)/150] 2. Fried's Rule for <2y/o: pediatric dose = adult dose x [age (months)/150] |
|
|
|
What are the indications for varenicline (Chantix)?
|
aid in smoking cessation
|
Drug Information Handbook p1548
|
|
|
List types of loop diuretics.
|
furosemide
torsemide bumetanide ethacrynic acid |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of varenicline?
|
partial neuronal alpha4 beta2 nicotinic cholinergic receptor agonist → preventing nicotine stimulation of meso-limbic dopamine system associated with nicotine addiction
*stimulates dopamine secretion but too much smaller degree than nicotine → resulting in decreased craving and withdrawal symptoms |
Drug Information Handbook p1548
|
|
|
List type of drugs used to treat diarrhea.
|
antiperistaltic agents
absorbents bismith subsalicylate polycarbophil bile acid sequestrants |
|
|
|
What are the contraindications of varenicline?
|
none
|
Drug Information Handbook p1548
|
|
|
What is the MOA for loop diuretics?
|
inhibition of Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransport in ascending loop of Henle → retention of Na+, Cl-, and water in tubule
|
Pharmacology p261
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects and interactions of varenicline?
|
fatigue
HA nausea GI symptoms insomnia abnormal dreams/vivid nightmares mood changes suicidal thoughts no interactions |
Pharmacology p119
|
|
|
What is regional anesthesia vs general anesthesia?
|
REGIONAL ANESTHESIA:
local analgesia GENERAL ANESTHESIA: requires loss of consciousness |
|
|
|
What is the patient education for varenicline?
|
may cause sedation so do not drive or operate heavy machinery
if experience any behavioral or mood changes stop treatment and contact provider immediately |
Drug Information Handbook p1548
|
|
|
What are the indications for loop diuretics?
|
acute pulmonary edema due to HF
hypercalcemia hyperkalemia |
Pharmacology p269
|
|
|
What are the indications for prescribing buproprion?
|
major depressive disorder
seasonal affective disorder adjunct in smoking cessation |
Drug Information Handbook p223
|
|
|
bismuth subalicylate (AKA pepto-bismol)
|
antidiarrheal
MOA: INDICATIONS: symptomatic treatment of mild nonspecific diarrhea adjunct for traveler's diarrhea adjunct for H pylori CONTRAINDICATIONS: children recovering from viral illness due to risk of Reye's syndrome breast feeding ADVERSE EFFECTS: black tongue black stool DRUG INTERACTIONS DOSING: PATIENT EDUCATION: |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of buproprion?
|
inhibits reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine
|
Pharmacology p145
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of loop diuretics?
|
ototoxicity → especially ethacrynic acid
hypokalemia hypomagnesemia hyperuricemia → furosemide and ethacrynic acid hypotension |
Pharmacology p269
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for buproprion?
|
children
pregnancy lactation hypersensitivity seizure disorder anorexia/bulemia use of MAO inhibitors with 14 days abrupt discontinuation of alcohol or sedatives |
Drug Information Handbook p224
|
|
|
What is the brand name of valproic acid?
|
depakote
|
Drug Information Handbook p1846
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects and interactions of buproprion?
|
HA
tachycardia insomnia dizziness weight loss nausea pharyngitis dry mouth sweating nervousness tremor sexual dysfunction seizures (increased risk at high doses) |
Pharmacology p145
|
|
|
List types of thiazide diuretics.
|
hydrochlorathiazide
chlorothiazide metolazone |
|
|
|
What are the indications for prescribing buproprion?
|
major depressive disorder
seasonal affective disorder adjunct in smoking cessation |
Drug Information Handbook p223
|
|
|
List antiperistaltic agents.
|
loperamide
diphenoxylate paregoric |
|
|
|
Describe chlorothiazide.
|
thiazide diuretic
MOA → inhibits Na+/Cl cotransporter in ascending loop of Henle indications → mild-to-moderate HTN; adjunctive therapy for edema contraindications → renal failure |
Drug Handbook p308
|
|
|
What are the indications and contraindications for regional analgesia?
|
INDICATIONS:
labor analgesia C-section other OB procedures CONTRAINDICATIONS: infection valvular heart disease progressive neurologic disease coagulopathy hypovolemia patient refusal |
|
|
|
What is the MOA for thiazide diuretics?
|
inhibition of Na+/Cl- cotransporter in distal convoluted tubule → retention of water in tubule
|
Pharmacology p261
|
|
|
What type of drug is cromolyn?
|
mast cell stabilizer
|
|
|
|
loperamide
|
antiperistaltic agent
MOA: acts on opioid receptor to inhibit peristalsis and prolong transit time INDICATIONS: chronic diarrhea associated wtih IBD acute nonspecific diarrhea traveler's diarrhea CONTRAINDICATIONS: children <2 breast feeding abdominal pain w/out diarrhea bloody diarrhea diarrhea with high fever acute dysentary bacterial enterocolitis pseudomembranous colitis acute ulcerative colitis ADVERSE EFFECTS: constipation nausea abdominal cramps dizziness DRUG INTERACTIONS DOSING: PATIENT EDUCATION: |
|
|
|
What are the indications for cromolyn?
|
inhaled → prophylaxis for allergic disorders including asthma; prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm
nasal → prevention and treatment of allergic rhinitis |
|
|
|
What are the indications for thiazide diuretics?
|
HTN
mild-to-moderate HF (if thiazide fails → prescribe loop diuretic) hypercalciuria diabetes insipidus |
Pharmacology p267
|
|
|
What are the contraindications for cromolyn?
|
hypersensitivity
acute asthma attacks |
|
|
|
Define pharmacokinetics.
|
what the body does to a drug
A = absorption D = distribution M = metabolism E = elimination |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of cromolyn?
|
inhibits degranulation after contact with antigens → preventing mast cell release of histamine and leukotrienes
|
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of thiazide diuretics?
|
hypokalemia
hyperuricemia hyponatremia hypomagnesemia hypercalcemia hyperglycemia volume depletion → hypotension hyperlipidemia hypersensitivity |
Pharmacology p267
|
|
|
What is the adverse effects and interactions of cromolyn?
|
side effects low due to poor absorption
bitter taste irritation of pharynx and larynx |
|
|
|
List categories of drugs used to treat constipation.
|
bulk forming agents
surfactants/stool softeners lubricants osmotic agents stimulants enemas sugar alcohol/synthetic sugar |
|
|
|
What is the patient education for cromolyn?
|
only for prophylaxis!
not for acute asthma attacks! |
|
|
|
List the thiazide diuretics from most effective to least effective?
|
metolazone < hydrochlorothiazide < chlorothiazide
|
Pharmacology p265
|
|
|
What is the patient education for use of metered dose inhalers?
|
inhale SLOWLY and DEEPLY
if improperly inhaled → 80-90% deposited in mouth, pharynx, or swallowed → systemic absorption → increase in adverse effects To use an MDI: Shake the inhaler well before use (3 or 4 shakes) Remove the cap Breathe out, away from your inhaler Bring the inhaler to your mouth. Place it in your mouth between your teeth and close you mouth around it. Start to breathe in slowly. Press the top of you inhaler once and keep breathing in slowly until you have taken a full breath. Remove the inhaler from your mouth, and hold your breath for about 10 seconds, then breathe out. If you need a second puff, wait 30 seconds, shake your inhaler again, and repeat steps 3-6. After you've used your MDI, rinse out your mouth and record the number of doses taken. |
|
|
|
List types of regional analgesia.
|
lumbar epidural block
caudal epidural block |
|
|
|
What is the patient education for use of dry powder inhalers?
|
inhale QUICKLY and DEEPLY
"swish and spit" after use to prevent deposition on oral and laryngeal mucosa which can lead to hoarseness and candidiasis |
|
|
|
How does the strength of metolazone compare to the other thiazide diuretics?
|
more potent
causes Na+ excretion even in advanced renal failure |
Pharmacology p268
|
|
|
What type of drug is theophylline?
|
phosphodiesterase inhibitor
|
|
|
|
Castor oil should be avoided in what patient population?
|
pregnant women → may stimulate contractions
|
|
|
|
Describe theophylline.
|
bronchodilator
narrow therapeutic window lots of side effects and drug interactions overdose may cause seizures and arrhythmias |
|
|
|
List types of potassium sparing diuretics.
|
spironolactone
triamterene amiloride hydrochloride |
|
|
|
List leukotriene modifiers.
|
zarfirlukast
montelukast zileuton |
|
|
|
What is the brand name of phenytoin?
|
dilantin
|
Drug Information Handbook p1846
|
|
|
What are the indications for leukotriene modifiers?
|
prophylaxis of asthma
NOT for acute asthma |
|
|
|
What is the MOA for potassium-sparing diuretics?
|
occurs in collecting duct and tubule
spironolactone → aldosterone agonist → inhibits aldosterone-mediated Na+ resorption/K+ secretion triamterene and amiloride → block Na+ channels |
Pharmacology p261
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects and drug interactions of leukotriene modifiers?
|
elevated liver enzymes → requires monitoring
Churg-Strauss HA dyspepsia |
|
|
|
List bulk forming agents.
|
psyllium
methylcellulose polycarbophil |
|
|
|
What are the indications for anticholinergics?
|
oral inhalation → anticholinergic bronchodilator used in brochospasm associated with COPD
use in conjunction with SABA! may cause reflexive bronchospasm use with caution if myasthenia gravis, narrow-angle glaucoma, prostatic hyperplasia, or bladder neck obstruction |
|
|
|
What are the indications for spironolactone?
|
adjunctive therapy to prevent hypokalemia
HF hepatic cirrhosis secondary hyperaldosteronism |
Pharmacology p270
|
|
|
What is the MOA of anticholinergics?
|
inhibits action of Ach at parasympathetic sites in bronchial smooth muscle → bronchodilation
|
|
|
|
LUMBAR EPIDURAL BLOCK
|
analgesic technique used for labor, vaginal delivery, or C-section
placed once labor established inject 3mL of 1.5% aqueous solution of lidocaine into catheter as test dose (if anesthesia does not occur after 5-10 minutes, inject another 5mL), inject total of 10mL of anesthetic solution (usually Bupivacaine + fentanyl), then continuously infuse 10-12mL/h given via bolus injections or continuous infusion dosing can be altered throughout labor and delivery eradicates pain between T10 and L1 during first stage of labor and between T10 and S5 during 2nd stage of labor supplemented with narcotics prolongs 2nd stage of labor increases use of outlet forceps but does not affect fetal outcomes monitor maternal BP due to predisposition to venous pooling and impaired venous return |
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of spironolactone?
|
GI upset → nausea, peptic ulcer
gynecomastia menstrual irregularities hyperkalemia → lethargy, mental confusion |
Pharmacology p270
|
|
|
Polycarbophil can be used to treat diarrhea and constipation, true or false?
|
true
|
|
|
|
What are the indications for triamterene and amiloride hydrochloride?
|
adjunctive therapy to prevent hypokalemia
|
Pharmacology p271
|
|
|
Define pharmacodynamics.
|
what a drug does to the body
|
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of triamterene?
|
leg cramps
hyperkalemia hyperuricemia ↑ BUN |
Pharmacology p271
|
|
|
psyllium
|
Bulk-producing laxative
antidiarrheal MOA: Soluble fiber Absorbs water in intestine to form viscous liquid which promotes peristalsis and reduces transit time INDICATIONS: Dietary fiber supplement Treatment of constipation lasting <1 week CONTRAINDICATIONS: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain Fecal impaction, GI obstruction Use caution in elderly, swallowing disorders, esophageal disorders ADVERSE EFFECTS: Abdominal cramps, constipation, diarrhea, esophageal or bowel obstruction DRUG INTERACTIONS None DOSING: PATIENT EDUCATION: Take with 8oz water to prevent choking |
|
|
|
What is the effect of adrenergic stimulation on heart, lungs, and blood vessels?
|
heart → increase HR, contractility, and conduction velocity
lungs → bronchiole dilation (relaxing smooth muscle) blood vessels → vasoconstriction in skin and mucous membranes; dilation to liver and skeletal muscle |
|
|
|
CAUDAL EPIDURAL BLOCK
|
type of epidural block approached through caudal space
can provide selective sacral block for 2nd stage of labor rarely used d/t complications (transfixing rectum, puncturing of fetal skull) lumbar epidural is safer |
|
|
|
What is the effect of cholinergic stimulation on heart, lungs, and blood vessels?
|
heart → decreases HR, contractility, and conduction velocity
lungs → bronchiolar constriction, increase in mucus secretion blood vessels → vasodilation |
|
|
|
What type of drug is docusate?
|
stool softener
|
|
|
|
What are the indications for carbamazapine?
|
seizures
|
Drug Information Handbook p252
|
|
|
dronabinol (THC)
|
marijuana derivative
antiemetic appetite stimulant INDICATIONS: chemotherapy-related nausea and vomiting AIDs-related anorexia CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity history of schizophrenia, mania, depression caution if elderly, hepatic disease, seizures, history of substance abuse ADVERSE EFFECTS: sedation, dysphoria, vertigo, disorientation, vertigo PATIENT EDUCATION: use caution when performing taks that require mental alertness potential for abuse may cause withdrawl with abrupt discontinuation psychiatric monitoring |
|
|
|
What class of drug is epinephrine?
|
catecholamine → adrenergic receptor agonist
|
Pharmacology p71
|
|
|
SPINAL BLOCK
|
first-line for C-section
performed more quickly than epidural analgesia occurs within 5-10 minutes dense sensory and motor block ideal for surgery give saline beforehand mother remains conscious may cause spinal HA |
|
|
|
What are the indications for epinephrine?
|
1. cardiac arrest
2. brochoconstriction → acute asthma, anaphylactic shock 3. glaucoma 4. anesthetics 3. |
Pharmacology p71
|
|
|
metoclopramide
|
INDICATIONS:
symptomatic treatment of GERD or diabetic gastric stasis MOA: blocks dopamine receptors in CNS blocks seratonin receptors enhances response to Ach in upper GI tract → enhanced motility and accelerated gastric emptying ADVERSE EFFECTS: extrapyrimidal symptoms → restlessness, |
|
|
|
*What are the adverse effects of epinephrine, norepinephrine, and isoproterenol?
|
adverse effects → CNS disturbances (HA, tremor, tension, anxiety, fear), cardiac arrhythmia, pulmonary edema, cerebral hemorrhage
NE also causes blanching and skin sloughing at site of injection due to extreme vasoconstriction |
Pharmacology p71
|
|
|
List medications that are contraindicated in children.
|
aspirin/salicylates (d/t potential Reye's syndrome)
tetracyclines (d/t potential discoloration of teeth enamel) sulfonamides (d/t potential kernicterus) ceftriaxone (3rd generation cephalosporin; d/t potential kernicterus) ciprofloxacin (2nd generation fluoroquinolone; d/t potential tendon and ligament rupture) chloramphenicol (d/t potential grey baby syndrome) benzoalcohol (d/t potential gasping syndrome) use caution with SSRIs (d/t increased risk of suicide) |
|
|
|
What are the clinical uses of norepinephrine?
|
shock → NE causes vasoconstriction → increase in vascular resistance → increase BP
*though metaraminol preferred b/c it does not reduce blood flow to kidneys |
Pharmacology p74
|
|
|
What is the brand name for carbamazapine?
|
tegretol
|
Drug Information Handbook p252
|
|
|
What class of drug is norepinephrine?
|
catecholamine → adrenergic agonist
|
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects, contraindications, and toxicities of norepinephrine?
|
same as epinephrine + blanching and skin sloughing along injected vein (due to extreme vasoconstriction)
|
Pharmacology p75
|
|
|
What class of drug is isoproterenol?
|
synthetic catecholamine → B1- and B2-adrenergic receptor agonist
|
Pharmacology p75
|
|
|
What are the clinical use of isoproterenol?
|
1. stimulation of heart in emergency situations
2. rarely used as brochodilator in asthma |
Pharmacology p75
|
|
|
fluconazole
|
antifungal used to treat:
candidiasis |
|
|
|
What class of drug is phenylephrine?
|
synthetic noncatecholamine → primarily binds alpha1 receptors
causes vasoconstriciton → raising BP no effect on heart |
Pharmacology p77
|
|
|
mabendazole
|
antihelmintic used to treat:
pinworms hookworms roundworms tapeworms flukes |
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of phenylephrine?
|
nasal decogestant
increase BP terminate supraventricular tachycardia |
Pharmacology p77
|
|
|
albendazole
|
antihelmintic
|
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of phenylephrine?
|
hypertensive HA
cardiac irregularities |
Pharmacology p77
|
|
|
ferrous sulfate
|
iron deficiency anemia
|
|
|
|
What class of drug is ephedrine?
|
noncatecholamine → mixed action adrenergic agonist
|
Pharmacology p79
|
|
|
ferrous bisglycinate
|
iron deficiency anemia if ferrous sulfate not tolerated
|
|
|
|
What are the clinical uses of ephedrine?
|
raise BP
treat asthma via bronchodilation nasal decongestant |
Pharmacology p79
|
|
|
warfarin
|
anticoagulant used to treat:
DVT PE |
|
|
|
What class of drug is ephedrine?
|
noncatecholamine → mixed action adrenergic agonist
|
Pharmacology p79
|
|
|
terbinafine
|
antifungal used to treat:
onychomycosis |
|
|
|
vancomycin
|
antibiotic used as last resort to treat:
penicillin-resistant gram-pos bacteria → MRSA |
|
|
|
What is the MOA and clinical use of B-blockers?
|
MOA → B-adrenergic agonists → diminsh phase 4 depolarization → depressing automaticity, prolonging AV conduction, and decreasing HR and contractility
clinical use → atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, AV-nodal reentrant tachycardia, prevention of ventricular arrhythmia following MI |
|
|
|
What do you prescribe if penicillin-allergic?
|
erythromycin
|
Current p204
|
|
|
What is the MOA and clinical use of digoxin?
|
MOA → cardiac glycoside → shortens refractory period in atrial and ventricular myocardial cells while prolonging refractory period and decreasing conduction velocity in AV node
clinical use → atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, HF *digoxin toxicity → can lead to ventricular fibrillation |
|
|
|
If severe penicillin allergy, what other antibiotics should be avoided due to cross-reaction?
|
cephalosporins
*cross-reaction occurs in 8% |
Current p205
|
|
|
What is the MOA and clinical use of CCBs?
|
MOA →
clinical use → atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, HTN, angina |
|
|
|
What is atropine used for?
|
to increase HR (AKA bradycardia)
|
|
|
|
What is the MOA and clinical use of quinidine?
|
MOA → Na+ channel blocker → binds to Na+ channels → prevents Na+ influx → slows phase 0 depolarization in ventricular muscle fibers
clinical use → atrial, junctional, and ventricular tachyarrhythmias; maintain sinus rhythm following cardioversion of atrial flutter or a-fib; prevent frequent ventricular tachycardia |
|
|
|
What category of drug is amidorone?
|
antiarrhythmic
|
|
|
|
What is the MOA and clinical use of lidocaine?
|
MOA → Na+ channel blocker → shortens phase 3 repolarization and decreases duration of AP
clinical use → ventricular arrhythmias arising during myocardial ischemia |
|
|
|
What are the indications for amidorone?
|
ventricular tachycardia
atrial fibrillation ventricular fibrillation |
|
|
|
What should be prescribed for atrial fibrillation?
|
first line → B-blocker
second line → CCBs, digoxin if ≥1 risk factor for stroke → long-term warfarin with INR 2.0-3.0 |
|
|
|
What is gingko biloba used for?
|
memory
dementia intermittent claudication http://nccam.nih.gov/health/ginkgo/ |
|
|
|
List 2 Na+ channel blockers.
|
lidocaine
quinidine |
|
|
|
What are the side effects of ginko biloba?
|
thrombocytopenia which increases risk of bleeding
use caution if taking anticoagulants, have bleeding disorder, or having surgical/dental procedure http://nccam.nih.gov/health/ginkgo/ |
|
|
|
What is lidocaine?
|
Na+ channel blocker used to treat ventricular arrhythmias often associated with MI
|
|
|
|
What is St. John's Wort used for?
|
sleep disorders
anxiety depression http://nccam.nih.gov/health/stjohnswort/ataglance.htm |
|
|
|
What is quinidine?
|
Na+ channel blocker used to treat atrial, junctional, or ventricular arrhythmias
|
|
|
|
What drugs does St. John's Wort interact with?
|
oral contraceptives
anticoagulants; warfarin cyclosporine digoxin antidepressants HIV meds; indinavir cancer meds; irinotecan http://nccam.nih.gov/health/stjohnswort/ataglance.htm |
|
|
|
List arrhytmias treated by B-blockers, CCBs, digoxin, quinidine, and lidocaine.
|
BBs:
-atrial flutter -atrial fibrillation -supraventricular tachycardia -ventricular tachycardia CCBs: -atrial flutter -atrial fibrillation -paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia DIGOXIN: -atrial flutter -atrial fibrillation -paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia QUINIDINE: prevention of atrial, junctional, and ventricular arrhythmias -atrial fibrillation -paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia -premature atrial contraction -ventricular tachycardia -premature ventricular contraction -following cardioversion for atrial flutter or fibrillation LIDOCAINE: -ventricular arrhythmias (often due to MI) |
|
|
|
What is echinacea used for?
|
stimulate immune system to fight cold/flu/infection
http://nccam.nih.gov/health/echinacea/ataglance.htm |
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of nitroglycerin and isosorbide dinitrate for angina and how does it effect myocardial O2 demand?
|
clinical use → stable angina, prinzmetals
MOA → vasodilator 1. dilation of large veins → decreased venous return → decreased preload → decreased work of heart → decreased myocaridal O2 demand 2. dilation of coronary arteries → increased blood supply to myocardium |
|
|
|
What are the side effects of echinacea?
|
GI
allergic reaction http://nccam.nih.gov/health/echinacea/ataglance.htm |
|
|
|
What is nitroglycerin?
|
vasodilator
|
|
|
|
What is black cohosh used for?
|
hot flashes and other menopausal symptoms
http://dietary-supplements.info.nih.gov/factsheets/blackcohosh.asp#h1 |
|
|
|
List nitrates.
|
nitroglycerin
isosorbide dinitrate |
|
|
|
Who should avoid black cohosh?
|
pregnancy
breast cancer liver disorders http://dietary-supplements.info.nih.gov/factsheets/blackcohosh.asp#h1 |
|
|
|
What is isosorbide dinitrate?
|
vasodilator
|
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of ranozaline and how does it effect myocardial O2 demand?
|
clinical use → chronic angina
*does not relieve acute angina MOA → |
|
|
|
What type of nitrate should be given for prompt relief of ongoing stable angina attack?
|
sublingual nitroglycerin
|
Pharmacology p210
|
|
|
What are the routes of administration, onset, and duration of nitroglycerine and isosorbide dinitrate?
|
NITROGLYCERIN:
1. sublingual tablet or spray -onset → 2 min -duration → 25 min 2. transdermal patch -onset → 30 min -duration → 8-14 hrs 3. oral sustained release tablet -onset → 35 min -duration → 4-8 hrs ISOSORBIDE DINITRATE: 1. sublingual -onset → 5 min -duration → 1 hr 2. oral slow-release tablet -onset → 30 min -duration → 8 hrs |
Pharmacology p211
|
|
|
What should you prescribe for newly diagnosed stable angina?
|
nitroglycerin or isosorbide dinitrate sublingual tablet or spray
take if angina attack can also take before activities that may precipitate angina attack |
Current ch10
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of nitrates?
|
HA!!!
facial flushing postural hypotension tachycardia |
Pharmacology p211
|
|
|
Discuss tolerance to nitrates.
|
tolerance develops rapidly where blood vessels become desensitized to vasodilation
TO AVOID TOLERANCE: -schedule daily 8-12 hr nitrate-free interval to restore sensitivity -remove transdermal patch at night -if prinzmetal's angina → remove transdermal patch in afternoon since angina worsens early in morning |
Pharmacology p211
|
|
|
Nitrates are contraindicated if taking what drug?
|
sildenafil (Viagra) → potentiates action of nitrates → may cause extreme hypotension
*can prescribe ranolazine instead |
Pharmacology p211
|
|
|
List drugs for treatment of angina.
|
acute → nitrates
chronic → -first line → B-blockers, ranozaline -third line → CCBs |
|
|
|
List antiplatelets, anticoagulants, and thrombolytics used in the treatment of thrombotic/embolic cardiopulmonary disorders.
|
ANTIPLATELETS:
aspirin clopridogrel (Plavix) ticlodopine (Ticlid) ANTICOAGULANTS: heparin LMWH warfarin THROMBOLYTICS: alteplase (Activase) |
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of pentoxifylline (Trental)?
|
MOA → reduces blood viscosity
clinical use → symptomatic treatment of intermittent claudication due to chronic occlusive arterial disease of limbs |
Drug Handbook p1173
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of clopridogrel (Plavix)?
|
MOA → antiplatelet
clinical use → reduces rate of atherothrombotic events -unstable angina -NSTEMI -STEMI -PAD -stroke *risk of bleeding |
Drug Handbook p356
|
|
|
What is the pharmological treatment following MI?
|
1. immediate chewable aspirin → 162mg or 325mg
2. if aspirin allergy → clopridogrel 300mg or 600mg 3. if STEMI → aspirin + clopridogrel 4. if STEMI (not NSTEMI) → thrombolytic therapy or coronary angioplasty 5. thrombolytic therapy → streptokinase or tissue plasminogen activator 6. continued aspirin 81mg and heparin 7. long term → aspirin 81mg, clopridogrel or both |
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of warfarin?
|
MOA → anticoagulant
clinical use -thrombosis/embolism → DVT, PE -reduce risk of embolic complications from atrial fibrillation or valve replacement -reduce risk of systemic embolism following MI |
Drug Handbook p1570
|
|
|
What does HMG COA reductase inhibitors stand for?
|
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors
|
Pharmacology p253
|
|
|
What is the common name for HMG COA reductase inhibitors?
|
statins
|
Pharmacology p253
|
|
|
What are the indications for prescribing HMG COA reductase inhibitors?
|
1. elevated LDL
2. hyperlipidemias *not familial hypercholesterolemia |
Pharmacology p253
|
|
|
What are the first-line agents for elevated LDL?
|
HMG COA reductase inhibitors
|
Pharmacology p253
|
|
|
HMG COA reductase inhibitors are effective in patients who are homozygous for familial hypercholesterolemia, true or false?
|
false → since these patients lack LDL receptors
|
Pharmacology p253
|
|
|
What is the MOA for HMG COA reductase inhibitors?
|
inhibition of HMG COA reductase → decreased cholesterol synthesis → decreased [intracellular cholesterol] →
1. increased LDL receptor synthesis→ increased number of LDL receptors → increased internalization of LDL → decreased plasma cholesterol 2. decreased VLDL secretion → decreased plasma cholesterol |
Pharmacology p253
|
|
|
What are the contraindications of HMG COA reducatse inhibitors?
|
adolescents
pregnancy breast-feeding renal insufficiency |
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of HMG COA reductase inhibitors?
|
1. liver failure → monitor LFTs
2. myopathy and rhabdomyolysis → usually associated with renal insufficiency or drug interaction → monitor CK |
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What is rhabdomyolysis?
|
disintegration of muscle
|
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What are the drug interactions for HMG COA reductase inhibitors?
|
increase in warfarin → monitor INR
|
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What is the patient education for HMG COA reductase inhibitors?
|
1. do not take if pregnant or breast-feeding
2. must periodically get blood drawn to monitor LFTs and CK 3. if taking warfarin → must periodically get blood drawn to monitor INR |
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What are other names for niacin?
|
nicotinic acid
vitamin B3 |
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What are the indications for niacin?
|
1. decreased HDL
2. increased LDL 3. hypercholesterolemias 4. familial hyperlipidemias |
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What is the most effective agent for increasing HDL levels?
|
niacin
|
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What is the MOA of niacin?
|
inhibition of lipolysis in adipose tissue → decreased plasma levels of cholesterol and triglycerides
|
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of niacin?
|
*cutaneous flush
*pruritus nausea and abdominal pain hyperuricemia and gout → niacin inhibits uric acid secretion impaired glucose tolerance hepatotoxicity |
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
What are the drug interactions of niacin?
|
alcohol → may increase cutaneous flushing
gout meds → allopurinol, probenecid, sulfinpyrazone DM meds |
|
|
|
What is the patient education for niacin?
|
if experience cutaneous flushing:
1. usually lasts 15-30min 2. may be accompanied by pruritus, especially in clothing-covered areas 3. take 300mg aspirin 30min before niacin to reduce flushing 4. flushing is usually self-limited after several weeks of a consistent dose |
Pharmacology p256
|
|
|
Which HMG COA reductase inhibitors are most effective at decreasing LDL, increasing HDL, and decreasing triglycerides?
|
decreasing LDL → atorvastatin, rosuvastatin
increasing HDL → pravastatin, simvastatin decreasing triglycerides → atorvastatin |
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
List HMG COA reductase inhibitors in order of most effective to least effective at reducing LDL.
|
atorvastatin = rosuvastatin > pravastatin = simvastatin > lovastatin = fluvastatin
|
Pharmacology p255
|
|
|
Name 5 HMG COA reductase inhibitors.
|
atorvastatin
simvastatin pravastatin lovastatin fluvastatin |
|
|
|
Name 2 bile-acid sequestering agents
|
cholestyramine
colestipol |
|
|
|
What are the indications for prescribing bile-acid sequestering agents?
|
1. elevated LDL
*though not as effective as statins |
Pharmacology p257
|
|
|
What is the MOA of bile-acid sequestering agents?
|
bind negatively charged bile acids and bile salts in small intestine → complex secreted in feces → preventing bile acids from returning to liver → lowering [bile acid] → causing hepatocytes to increase conversion of cholesterol to bile acids → decreasing[intracellular cholesterol] → increasing LDL uptake into cell → decreasing plasma LDL
|
Pharmacology p257
|
|
|
List the categories of drugs used to treat elevated LDL, decreased HDL, and elevated TRIG in order of most effective to least effective.
|
elevated LDL → HMG CoA reductase inhibitors > bile acid sequestrants > niacin > fibrates
decreased HDL → niacin > fibrates > HMG CoA reductase inhibitors > bile acid sequestrants elevated TRIG → fibrates > niacin > HMG CoA reductase inhibitors > bile acid sequestrants |
Pharmacology p259
|
|
|
List statins and how they effect LDL, HDL, and TRIG.
|
lovastatin → decreases LDL, increases HDL
pravastatin → decreases LDL and TRIG fluvastatin, simvastatin, and atorvastatin → decreases LDL and TRIG, increases HDL |
|
|
|
Which is the cheapest statin?
|
lovastatin (but also least potent)
|
|
|
|
What is the first-line agent for treatment of DM type II?
|
metformin
|
|
|
|
METFORMIN
|
INDICATIONS:
DM type II CONTRAINDICATIONS: hypersensitivity renal dysfunction hepatic dysfunction chronic metabolic acidosis MOA: decreases hepatic glucose production → decreasing intestinal absorption of glucose increases insulin sensitivity → increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization ADVERSE EFFECTS: GI symptoms nausea vomiting diarrhea flatulence INTERACTIONS: increased effect if cephalexin, cimetidine, pegvisomant, iodinated contrast decreased effect if corticosteroids, LHRH, somatropin PEAK LEVEL AND DURATION: if immediate release → peak within 2-3 hours if ER → peak within 4-8 hours duration up to 2 weeks PATIENT EDUCATION: take with meals to reduce GI symptoms take same time everyday GI symptoms normally at start of therapy and usually subside after few weeks avoid alcohol (may cause lactic acidosis) self-monitor glucose requires periodic monitoring of GLUC, A1C, CBC, RFP, B12/FOL |
|
|
|
An adverse effect of metformin is hypoglycemia, true or false?
|
false
hypoglycemia rarely occurs |
|
|
|
List biguanides.
|
metformin
|
|
|
|
What is the peak and duration of the insulin preparations used to treat diabetes?
|
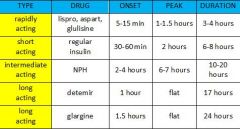
|
|
|
|
When should rapidly acting insulins be administered?
|
20 mintues prior to meals
|
|
|
|
When should regular insulin be administered?
|
60 minutes prior to meals
|
|
|
|
Are sulfonylureas indicated for type I or type II DM?
|
type II
sulfonylureas require intact B-cells of islet of langerhans of pancreas |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of sulfonylureas?
|
stimulate insulin release
bind to pancreatic B-cell receptors → K+ channels close → depolarization → Ca2+ influx → insulin release |
|
|
|
List 2nd generation sulfonylureas.
|
glyburide
glipizide glimepiride |
|
|
|
List 2nd generation sulfonylureas.
|
glyburide
glipizide glimepiride |
|
|
|
List 1st generation sulfonylureas.
|
tolbutamide
tolazamide cholorpropamide |
|
|
|
List A1C results that correlated with mono and dual therapy for DM.
|
A1C 6.5-7.5% → monotherapy
A1C 7.6-9.0% → dual therapy |
|
|
|
What is the MOA of alpha-glucose inhibitors?
|
delay intestinal glucose absorption
|
|
|
|
List nonsulfonylurea insulin stimulators.
|
repaglinide
|
|
|
|
List alpha-glucose inhibitors.
|
acarbose
|
|
|
|
List incretins.
|
exenatide
sitagliptin |
|
|
|
List thiazolidinediones.
|
pioglitazone
rosiglitazone |
|
|
|
REPAGLINIDE
|
INDICATIONS:
DM II – adjunctive therapy if not adequately controlled by metformin CONTRAINDICATIONS: hepatic or renal dysfunction MOA: nonsulfonylurea insulin stimulator similar to sulfonylureas causes brief but rapid impulse of insulin ADVERSE EFFECTS: weight gain hypoglycemia INTERACTIONS: PEAK LEVEL AND DURATION: PATIENT EDUCATION: |
|
|
|
ACARBOSE
|
INDICATIONS:
Type II DM – adjunctive therapy CONTRAINDICATIONS: diabetic ketoacidosis cirrhosis GI tract disorders MOA: competitive inhibitor of pancreatic a-amylase and intestinal brush border a-glucosidases → delayed digestion of carbs and absorption of glucose ADVERSE EFFECTS: flatulence diarrhea abdominal pain increased liver enzymes INTERACTIONS: PEAK LEVEL AND DURATION: PATIENT EDUCATION: take with first bite of meal flatulence tends to decrease in frequency and intensity over time |
|

