![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using tags, tapes and collars V spot ons and pour ons
|
tags- adv. less work, but resistance when run low and poor release
pour- non invasive but may over dose |
|
|
organophosphate MOA
|
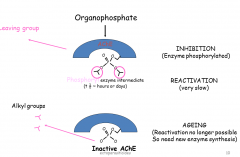
the leaving group permanently inhibits AChE selectively but not specific to ectoparasites.
normally the AChE is inhibited by an ACh for a short time before being hydrolysed ( reactivated). Organophosphates eventually bind permanently ( called aging) and they phosphorylate the AChE |
|
|
organophosphate spectrum
|
broad. flies/fleas/lice/ticks/mites
|
|
|
organophosphate toxicity and antidote and any percautions.
|

narrow margin for man and animals -high risk of acute toxicity for animals and man, with muscarinic, nicotinic and central effects because of the excess ACh. seen more in humans eg Muscarinic - DUMBELS- Diarrhoea, Urination, Miosis, Bronchoconstriction, Emesis, Lacrimation, Salavation
atropine and oxmides as antidote. LIKE AandE ! except o! time restriction- warble flies overwinter in SC and oeso. so only use in summer. age restriction ( young / old more S) other drugs ( AChE inhibitiors eg carbamates) care with handling ( people and environment) resistance LIKE AN OP JUST WANTS TO STAY FOR EVER AND TALK! |
|
|
organophosphate use and administration
|
sheep dips ( scab and flies)- long 70 day withdrawl
cat/dog flea collar ( only a GSL) fish ( sea lice) topical (dips/sprays) systemic ( pour on /spot on) collars/tapes/tags |
|
|
organophosphate antidotes and MOA of these
|
Atropine- non specific muscarinic antagonist
oxmides- speeds up reactivation of AChE - esp important with drugs which cause AChE to age quickly eg Parathion. ( it transfers the phosphate away from the AChE ) |
|
|
carbamates MOA and difference/ simularities to organophosphates
|
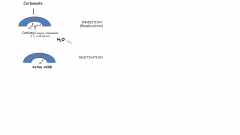
binds reversibly to AChE in certain parasites only and more persistent in insests ( unlike organophosphates) Enzyme intermediate is also caused by phosphorylation but the half like before reactivation is only around 20 mins V days in orrganophosphates also there is no aging of the enzyme.
|
|
|
carbamates spectrum
|
broad ( ticks/mites/lice/fleas)
|
|
|
carbamates toxicity and antidotes
|
carcinogenic. However less toxic than organophosphates as its phosphorylated intermediate has a shorted half life and its binding is reversible. also not presistant in the environment.
antidotes - only atropine |
|
|
why is atropine used by it self as anantidote for carbamates whereas it is used with oxmides for organophosphates
|
AChE can regenerate so does not need oxmides
|
|
|
carbamates use
|
cats/dogs ( lice/ fleas/ticks/mites)( GSP- general sales list. collar or sprays -less)
|
|
|
pyrethrins and pyrethroids MOA
|

binds to Na channel at presynaptic membrane and keeps it open, allowing an AP to form causing spastic paralysis. Quick penetration but quickly broken down by enzymes so needs to be given with PBO which inhibits its metabolism so allows it to have a longer exposure time to have its lethal effect
|
|
|
pyrethrins and pyrethroids Spectrum
|
broad. ( lice/fleas/flies/keds)
pyrethroids also do ticks and mites |
|
|
pyrethrins and pyrethroids toxicity
|
selective toxicity - humans met. it quickly so not toxic.
low if given orally ( except some sp.). V.Toxic if injected. fish and some aquatic vertebrates are succeptible. pyrethroids- type 1 and type 2 type 1... if there is no alpha cyano group present- 't syndrome' whole body tremor, exagerated startle reflex, muscle twitch. type 2 ... if alpha cyano group is present met. will be slowed and toxic effects will be salavation, uncordination, spasms, apnea, seizures and death note the pyrethroids Cis isomer is more toxic ( there will be a mixture of CIs and trans) degree of toxicity will depend on the age, species, fasting status. CATS- susceptible to permethrin type 1 syndrome as they cant metabolism it properly. this may occur if dog collars are used on cats- treated with methocarbamol IV ( a muscle relaxant ) |
|
|
Avermectins and milbemycins spectrum
|
some are endectosides. eg dextomax for cattle sheep and pigs. sucking lice/some mange mites/warbles
|
|
|
avermectins and Milbemycins MOA
|

peripheral Glutamate and or GABA gated chloride channels which cause flacid paralysis due to influx of chloride. ( note these channels are central in Humans).
|
|
|
avermectins and Milbemycins toxicity
|
some dog breeds, kittens, some bird sp. and turtles fish and reptiles.
Ivermectin- toxocosis symdrome ( mydriasis, depression, tremor, ataxia, emesis, salavation and coma.dogs with MDR1 mutation who lack the pump. ( collies, german s, auz. S and others...) other avermectins are largly free of these porblems |
|
|
Amidines ( amitraz) MOA
|

octopamine receptor antagonist ( affects behaviour of the ectoparasite so it does not seek the host) also alpha 2 receptor agonist. This inhibits tick MAO leading to hyperactivity and detaching behavior .... decreased fecundity, inhibits ovi-position and egg hatch-ability
|
|
|
Amidines adverse effects and treatment
|
transient sedation about 12-14 hrs after treatment
puritis in some dogs.high exposure- depression andsedation , polyurea and bradycardia, GI stasis ( horses- not licenced) cats - countraindicated ( as cant metabolise) note only for dogs.also contraindicasted in chihuahuas and dogs with heat stress treatment is with an alpha 2 agonist |
|
|
cyromazine and methoprene MOA
|
IGR -insect growth regulators. effect the deposition of chitin in cuticle or juvenile insect hormone
|
|
|
benzoyl urea derivative MOA
|
inhibits chitin synthesis. systemic so require flea to bite
|
|
|
benzoyl urea derivatives spectrum
|
fleas. larvicidal and ovicidal
|
|
|
benzoyl urea derivatives distribution
|
food increases Ab.
builds up in fat as highly lipophilic |
|
|
Fipronil MOA
|
antagonist to GABA and glutamate gated chloride channels ( peripheral NS of insect and in our central NS so safe).lipophilic so reservoir in skin.
|
|
|
fipronil spectrum
|
fleas/ticks and mites in SAs.
kills the adults before they lay eggs |
|
|
fipronil toxicity
|
mod. in rabbits.
highly toxic to some birds/fish/aquatic invertebrates |
|
|
neonicotinoids MOA
|
Block ACh nicotinic receptors- paralysis.
needs to be ingested by insect. |
|
|
neonicotinoids spectrum
|
fleas in SAs/ rabbits/ferrets
|
|
|
neonicotinoids toxicity
|
low
|
|
|
metaflumizone MOA and spectrum
|
Block voltage dependant Na channels causing paralysis- fleas
|
|
|
oxadiazine insecticides MOA and spectrum
|
Na channel blocker. ( activated in gut).
fleas |
|
|
name 3 drug combinations used as endectosides ( active compounds and trade name) and which species they are used for.
|
frontline combo- (SAs, fipronil and methoprene)
Advantix ( dogs NOT cats, Imidacloprid and permethrin) Adovocate ( SAs, Imidacloprid and moxidectin ) |

