![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Types of cholinesterase |

|
|
|
|
Types of muscuranic receptors |

|
|
|
|
Types of nicotinic receptors |

|
|
|
|
Cholinergic agonist s |

|
|
|
|
Main activator and blocker of muscuranic and nicotinic receptors |
M - act by muscuraine and blocked by atropine N - act by nicotine and blocked by tubocuraine or hexamethonium |
|
|
|
Action of ach on eye |

|
|
|
|
Pilocarpine intro uses adverse effects |

|
|
|
|
Bethanechol |

. |
|
|
|
Muscuraine |

Mushroom poisoning |
|
|
|
Physostigmine kinetic and uses |

Kinetics - rapidly absorbed from git and parenteral routes.. Crosses cornea and bbb easily |
|
|
|
Pyridostigmine |
Similar to neostigmine but longer acting and less potent.. Thus more tolerant by mg patients and preferred more |
|
|
|
Edrophonium uses |

1 diagnosis of mg - ameliorative test 2 differentiate bw myastenia and cholinergic crisis 3 preferred in curare poisoning bcoz of its rapid onset of action |
|
|
|
Drugs for treatment of glaucoma |

Osmotic agents Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor diuretics B blocker a agonist Anticholinesterases as miotics Prostaglandins |
|
|
|
Role of a agonist in glaucoma treatment |

Apraclonidine and dipiverfrine |
|
|
|
Compare physostigmine and neostigmine |

As neostigmine has structure similar to ach, it directly acts at Nm receptors of NMJ and thus improve muscle power in patients of myastenia gravis |
As neostigmine has structure similar to ach, it directly acts at Nm receptors of NMJ and thus improve muscle power in patients of myastenia gravis |
|
|
Mechanism of action of anticholinesterases |

|
|
|
|
Atropine pharmacological actions |
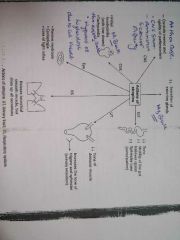
Competitive antagonist of muscuranic receptors |
|
|
|
Classify cholinergic drugs |

|
|
|
|
Adrenergic receptors and their functions |

|
|
|
|
Antimuscuranic drugs |

|
|
|
|
Effects of atropine and ephedrine on eye |

|
|
|
|
Why ipatropium bromide and tiotropium bromide is prefered over atropine in COPD and bronchial asthma |

|
|
|
|
Use of scopolamoline |
For motion sickness as by blocking cholinergic fibres it surpress vestibular disturbances |
|

