![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
9 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
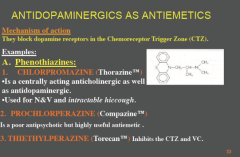
How can antidopaminergics be used as anti emetics?
What is a centrally acting anticholingeric as well as antidopaminergic that is used?
Which drug is a poor antipsychotic but highly useful antiemetic?
Which drug inhibits the CTZ and VC? |
|
|
|
What drug is a butyophenone derivative that blocks dopaminergic receptors in the CTZ? Used clinically post operatively for nausea and vomiting? |
Droperidol |
|
|
What are the two benzamide derivatives? MOA of each? |

|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of the serotonin (5-HT) antagonists? What receptors do they block in the stomach and in the small intestine?
Are these agent the most effective anti emetics? |

|
|
|
What are some examples of antiemetic serotonin agonists?
Which one is effective for preventing emesis by high dose of cytotoxic drugs?
Which one is more potent? Which has a longer half life? Which available IV?
Administration of 5HT3-receptor blockers with which drug increases their potency? |

|
|
|
What drugs are used only when patients fail to respond to other anti emetics? |

|
|
|
Do corticosteroids enhance the overall antiemitic effect? How? |

|
|
|
How does Aprepitant prevent emesis induced by cytotoxic chemotherapeutic agents? Does it cross the BBB?
Any CYP metabolism? |

|
|
|
What type of vomiting is benzodiazepene used for? |

|

