![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Purpose of vasoconstrictors in local anesthetic |

|
|
|
What is the max dose of vasoconstrictors in local anesthetic |

|
|
|
What is the max dose of: articaine Lido Mepivicaine Prilocaine |
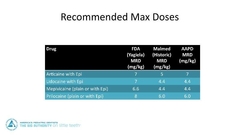
|
|
|
What are symptoms of local anesthetic overdose |

|
|
|
How would you mange local anesthetic overdose |

|
|
|
What drugs would you use to manage local anesthetic overdose and why |

|
|
|
What is the allergic potential of dental cartridge Which allergy can cause cross allergenicity with the dental cartridge |

Sulfa allergy can use local anesthetics |
|
|
What are stages of anesthesia |

|
|
|
How is nitrous oxide eliminated |

|
|
|
What are the anesthetic properties Of nitrous |
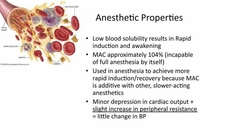
|
|
|
Contraindications of use of nitrous |

|
|
|
When do you need to get a med consult when planning to use nitrous |

|
|
|
What are the emergency oxygen requirements for your office |

|
|
|
What are the greatest risk factor for adverse sedation events |

|
|
|
What are the anatomic difference of the child verse adult airway |
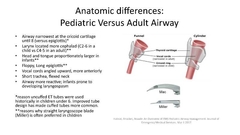
Narrow nasal passage ( Obligate nasal Breathers) Significant Lymphoid tissue Less developed mandible |
|
|
How does the pulse oximeter work |

|
|
|
What is the first pass phenomenon |
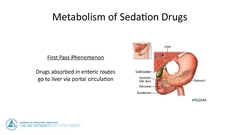
|
|
|
How does sedation work in the brain |
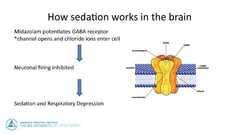
|
|
|
Which nerve supplies the mandible,maxilla tongue and teeth |
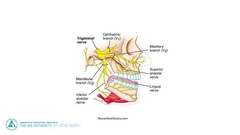
|
|
|
How does local anesthetic work |
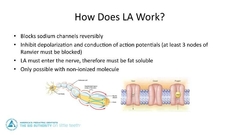
|
|
|
What is the composition of local anesthetics |

|
|
|
How does Ph and pka affect local anesthetics effectiveness |

The lower the pka the more nonionized molecules =more effective |
|
|
How does tissue pH change the effectiveness of a local anesthetic |

|
|
|
Mental nerve block - what teeth are affected - what nerve is blocked - where is the site of injection |
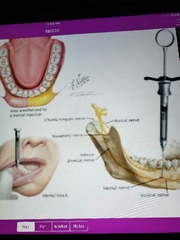
Mental and incisive nerve |
|
|
PSA block - what nerve is blocked - what teeth are numb - where is the site of injection |
1- Post superior alveolar nerve 2- The Maxillary molar teeth may not get the mesio buccal root of the 1st Maxillary molar In all buccal soft tissue adjacent to molars 3- Behind the last molar |
|
|
Where is the site of injection for a IA block |
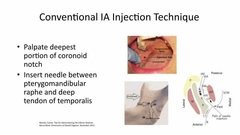
|
|
|
What can the long buccal nerve anesthetize and where is the site of injection |
-The long buccal nerve will sometimes innervate primary and permanent molars --the site of injection is buccal to the last tooth to be treated |
|
|
How does the mandibular foramen in the child differ from an adult And how is growth of the mandible characterized in a child |

|
|
|
Gow Gates block - what teeth are numb -where is the site of injection - what nerves are blocked |
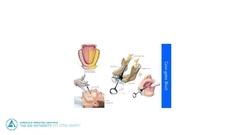
|
|
|
What is the cause of injection pain |

|
|
|
What are some characteristics of a larger needle gauge |

|
|
|
What determines the effectiveness of your anesthesia |
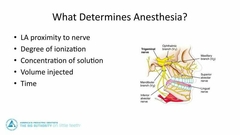
|
|
|
What are the types of local anesthetics and where are they metabolized |

|
|
|
What topical anesthetic has been known to cause issues in children and what is the issue |

|
|
|
What is the duration of pulpal and soft tissue anesthesia of Lidocaine |
45 minutes for pulpal anesthesia two to three hours for soft tissue anesthesia |
|
|
Which injectable anesthetic has been associated with meth hemoglobinemia |

|
|
|
What is the treatment for methemoglobinemia |
Methylene blue injection |
|
|
What are key characteristics of articaine 1- Where is it metabolized |

|
|
|
What is epinephrine effects on the cardiovascular system |
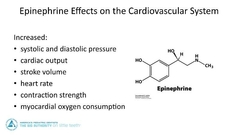
|
|
|
Should epinephrine be used in cardiac patients |

|
|
|
How many milligrams of Lidocaine and articaine are in 1 carpule And how much volume is in 1 carpule |
34 mg = lidocane 68 mg = articaine Volume = 1.8L/ cartridge |
|
|
What is the Concentration effect and the 2nd gas effect of nitrous oxide |

|
|
|
What are the effects of nitrous oxide |

|
|
|
What are the adverse effects of nitrous oxide |
|
|
|
What are the indications for nitrous oxide use |

|
|
|
What is the MTHFR deficiency and how does nitrous oxide affect it |

|
|
|
What are we concerned about with children born prematurely as it relates to sedation |

|
|
|
What are the concerns with obesity as it relates to sedation |

When Calculating drug doses total body weight may increase the likelihood of administration supra therapeutic dose |
|
|
What are the NPO Guidelines for Sedation |

|
|
|
What are the AAPD Guideline for monitoring ventilation in a moderately sedated patient |

|
|
|
What are the documentation guidelines 4 monitoring a moderately sedated patient |

|
|
|
How often should Blood pressure be monitored during sedation |

|
|
|
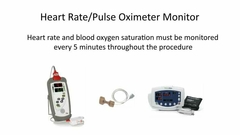
How often should heart rate and oxygen be monitor during sedation |
|
|
|
What is a prechordial stethoscope |

|
|
|
What are some common oral sedation drugs and what classification of drugs are they |

|
|
|
Chloral hydrate 1- what Type of drug 2- Where's it metabolized 3- What are some adverse effects 4- Is it reversible 5- Are there any adverse interaction |

|
|
|
Meperidine 1- Type of drug 2- Adverse effects 3- Adverse interaction 4- Where's it metabolized 5- Contraindications |

|
|
|
Midazolam 1- Is it reversible 2- What are its therapeutic effects 3- Where's it metabolized 4- Precautions |

|
|
|
Diazepam 1- Is it reversible 2- Therapeutic effects |

|
|
|
Hydroxyzine 1- Type of drug 2- Is it reversible 3- Therapeutic effect 4- How is it metabolized 5- Adverse effects |

|
|
|
How does Herbal medication effects sedation Drugs |

|
|
|
What are some black Box/ FDA warnings on sedation drugs |

|
|
|
Flumazenil 1- What is it 2- What are its properties 3- Initial onset/ Maximum effect 4- Dose |

|
|
|
Naloxone 1- What is it 2- Onset 2- Dose |

|
|
|
What are the cascade of events when you get into a medical emergency With sedation |

|
|
|
How do you manage Laryngospasm |

|
|
|
What's the Larson maneuver |

|
|
|
How do you manage airway obstruction |

|
|
|
How do you manage apnea |

|
|
|
What's the formula for sizing endotracheal Tube |

|
|
|
What were the trends in adverse sedation events |

|
|
|
What were the trends in death associated with most Pediatric sedation |

|

