![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
any characteristic that can be passed from parent to offspring
|
trait
|
|
|
passing of traits from parent to offspring
|
heredity
|
|
|
a linear sequence of genes on a strand of DNA
|
chromosome
|
|
|
the position of an allele on a chromosome
|
locus
|
|
|
two forms of a gene
|
allele
|
|
|
stronger of two genes expressed in the hybrid (capital R)
|
dominant gene
|
|
|
gene that shows up less often in a cross; represented by lower case r
|
recessive gene
|
|
|
gene combination for a trait
|
genotype
|
|
|
the physical feature resulting from a genotype
|
phenotype
|
|
|
presence of two identical alleles at a given chromosomal locus
|
homozygous
|
|
|
presence of two different alleles at a given chromosomal locus
|
heterozygous
|
|
|
cross involving a single trait
|
monohybrid cross
|
|
|
cross involving two traits
|
dihybrid cross
|
|
|
what goes on the axis of monohybrid cross
|
heterozygous (Rr) X heterozygous (Rr)
|
|
|
Parent generation of monohybrid cross called what? offspring gen called what?
|
F1 generation; F2 generation
|
|
|
Give proof for Mendel's law of dominance
|
RR X rr = 100% dominant phenotype
|
|
|
Give proof of Mendel's law of segregation
|
Rr X Rr = 75% dominant phenotype and 25% recessive phenotype
|
|
|
Give proof of Mendel's law of independent assortment
|
RrYy X RrYy= 9:3:3:1 phenotype
|
|
|
genes are present on ___(#) pairs of strands of DNA molecules
|
23
|
|
|
what is a multigenic trait? give ex
|
more than one gene encodes for phenotype (diabetes)
|
|
|
What is meant by quantitative trait? give example
|
traits that vary in the extent to which they are expressed in each individual (height, weight)
|
|
|
when not every individual who has the genotype expresses the phenotype
|
incomplete penetrance (this is an exception to inheritance)
|
|
|
what is meant by multifactorial trait? give example
|
both environmental and genetic components. (hemochromatosis)
|
|
|
Explain co-dominance. What is it an example of?
|
when both alleles are expressed in the heterozygote (like in blood groups). example of an exception to mendel's law
|
|
|
Sex-linked inheritance is an example of what?
|
an exception to mendel's law
|
|
|
explain mitochondrial inheritance. what is this an example of?
|
in addition to th 23 chromosomes found within the cell's nucleus, other genetic material is found in mitochondrial chromosomes. ONLY MOTHER MITOCHONDRIAL CHROMOSOME is inherited (bc girls rock). this is an exception to mendel's law.
|
|
|
when genes are only expressed from a chromosome originating in one of the parents, due to silencing of other chromosomes
|
genetic imprinting (another exception to mendel's law)
|
|
|
both copies of each chromosome come from a single parent
|
uniparental disomy (an exception to mendel's law)
|
|
|
the severity of the genotype increases from genertaion to generation. give example
|
genetic anticipation (triplet repeat expansion)
|
|
|
explain Hardy-Weinberg
|
for a stable (non-evolving) population, the allele and genotype frequencies are constant from gen to gen (p2+2pq+q2=1)
|
|
|
true or false. pedigree analysis is used to determine the pattern of inheritance of traits in humans.
|
true
|
|
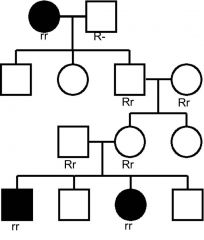
which mode of inheritance?
|
autosomal recessive
|
|
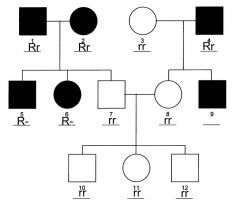
which type inheritance?
|
autosomal dominant
|
|
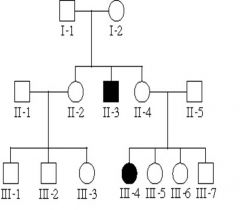
which mode inheritance?
|
x-linked recessive
|
|
|
what type of disorder is CF?
|
recessive
|
|
|
How many caucasians are carriers of CF?
|
3%
|
|
|
explain the normal vs mutated gene inCF
|
normal= normal protein, cycstic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) regulates ion transport across cell membranes.
mutated: CFTR causes ion imbalance which leads to abnormalities in the pancreas, skin, intestine, sweat glands, and lungs |
|
|
A recessive pattern of inheritance means that ___% of offspring will get gene if both parents heterozygous.
If both parents infected (rr), what % will have gene? |
25%; 100%
|
|
|
dominant or recessive?
an affected individual will have inheritied the gene from at least one affected parent |
dominant
|
|
|
dominant or recessive?
the disease may have been the result of a new mutation that occurred during gamete formation |
dominant
|
|
|
what makes studying genetics in humans so complicated?
|
so many variations! are, height, weight, gender, ethnicity, environmentla factors, etc
(animal studies are much easier to control!) |
|
|
Which type of study design?
uses patients who already have a phenotype and look back to see if there are genotype characteristics of these patients that differ from those who don't have the outcome. |
case control
|
|
|
Which type study design
uses patients who have a purported genotype and look forward to see if there are resulting phenotypic characteristics that differ from those who don;t have the genotype |
cohort
|
|
|
Which type study design
relates the phenotype and genotype characteristics of the parents to the phenotype and genotype characteristics of hte offspring to detect specific phenotypes that occur more frequently in offspring with a specific genotype. |
trio
|
|
|
the study of how genes encode the structure and function of living things from the level of the individual molecules to that of organisms
|
molecular biology
|
|
|
true or false?
all genes encode for proteins? |
false (tRNA, rRNA, miRNA)
|
|
|
using genetic information to predict whether a drug will help make a ptient well or ill
|
pharmacogenomics
|
|
|
the study to genetic influences on an individual's respons to drugs. involves the analysis of a specific gene or group of genes may be used to predict responses to a specific drug or drug class
|
pharmacogenetics
|
|
|
study of genetic influences that applies all the genes. May be used to search for novel drug targets and/or key determininants of drug rxns.
|
pharmagenomics
|
|
|
What different responses can different indiviudals have to the same drug?
|
full response
partial response no response severe adverse reaction |
|
|
describe the factors that influence the variation in drug response
|
gender
body mass age environmental factors disease genetic factors diet co-medicatino |
|
|
how many constant base pairs are present in the human genome? How many variable? how many capture the full human variation? How many cpharmaceutically sign?
|
2.9 billion
3 million 100,000 <10,000 |
|
|
explain the current impact of pharmacogenomics
|
1. Broadly adopted in the area of drug discovery (by both private and public companies)
2. Called the future of medicine (personalized medicine) |
|
|
Name four future trends in pharmacogenomics.
|
1. Point of care (doctor's office/pharmacy) genetic testing
2. population screening 3. population sequencing 4. personal genomics |
|
|
which field studies the rules governing variation?
|
genetics
|
|
|
which field studies how gene encodes traits?
|
molecular biology
|
|
|
which field studies gene organization?
|
genomics
|
|
|
How many genes are there?
|
30,000-50,000
|
|
|
which field studies how drugs exert their effect on the body (studies how drugs interact with cellular molecules and act by inhibiting or stimulating the "target" molecule?
|
pharmacology
|
|
|
which field studies how drug transport and distribution in the body influences drug efficacy and toxicity?
|
pharmaceutics
|
|
|
which field studies the ability of a drug to make a person sick?
|
toxicology
|
|
|
which field studies gene combinations as they exist in the human population, how they arose, and how they spread?
|
population biology
|
|
|
tru or false?
drugs act because of their ability to affect the health of the human population, not of the individuals. |
true
|
|
|
which fiels studies the characteristics of a very large group of objects or individuals based upon a random sample of objects or individuals obtained from that group. (the probability that a drug will have a beneficial effect on a large # of ppl can be predicted based on a controlled trial with a smaller #)
|
statistics
|
|
|
why is pharmacogenomics important to the pharmacist?
|
1. new patient expectations
2. new doctor's expectations 3. new technology 4. new job responsibilities 5. new market trends 6. more business |

