![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
intrinsic factors affecting CO, SV and stroke work
|
control of intracellular calcium levels (affecting contractility)
|
|
|
catecholamine affects in heart failure
|
exacerbate myocardial ischemia
calcium overload of myocardial tissue energy deprivation free radical production arrhythmias cell death impaired beta receptor responsiveness |
|
|
extrinsic factors affecting CO, SV and stroke work
|
preload
afterload |
|
|
pharmacological approach to treating CHF (7)
|
positive inotropes
vasodilators inodilators receptor agonist inotropes/vasodilators 3rd gen beta adrenergic antagonists diuretics ACEI |
|
|
3 compensatory mech of failing heart
|
hypertrophy
increase sympathetic activity activate renin-angiotensin system |
|
|
Digoxin mechanism of action
|
positive inotropy
prolongs refractory period in AV node Decreased conduction through SA and AV nodes |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides?
|
disrupts ('poisons') the Na-K-ATP-ase pump
|
|
|
CHF pt response to digitalis
|
decreased HR
decreased SVR decreased heart size decreased LVEDV and pressure decreased pulmonary congestion improved renal function |
|
|
How is digoxin eliminated?
|
in the urine, unchanged
|
|
|
How is digitoxin eliminated?
|
extensively metabolized in the liver and excreted in the feces
|
|
|
phosphodiesterase inhibitors
|
amrinone
milrinone they increase the intracellular conc of cAMP |
|
|
shorter acting?
digoxin or digitalis |
digoxin
|
|
|
central acting alpha 2 antihypertensives
|
clonidine
guanabenz guanfacine methyldopa act at the vasomotor center; stim alpha 2 receptors; inhibit NE release; decreases sympthatetic outflow & ***leaves parasympathetic activity predominating |
|
|
adrenergic neuron blocking antihypertensives
|
reserpine
guanethidine guanadrel |
|
|
anti-HTN alpha 1 blockers
|
prazocin
terazocin doxazocin indoramine tamsulocin |
|
|
What is first "dose" effect and which drug(s) exhibit this?
|
hypotension &/or syncope with the 1st dose; dose should be low and admin at night
prazocin |
|
|
What is the significance of beta blocking diabetic patient?
|
beta blockade blocks the feedback mechanism of tachycardia, a warning sign of impending hypoglycemia
|
|
|
nebivolol
|
beta blocker
in kidneys - blocks renin release; induces NO formation via beta 2 agonism in renal artery and glomerulus -->renal vasodilation |
|
|
True or False
Chronic beta blockade produces receptor up regulation |
TRUE
|
|
|
beta blocker(s) with ISA
|
pindolol
carvedilol |
|
|
True or False
Skeletal muscle is affected by calcium channel blockers |
FALSE
calcium is stored in sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle and is not dependent on extracellular calcium levels |
|
|
common side effect of CCB
|
gingival hyperplasia
|
|
|
What drugs produce the side effect of gingival hyperplasia?
|
CCB
phenytoin cyclosporin |
|
|
Which vasodilator has the side effect of cyanide toxicity?
|
nitroprusside
|
|
|
Which anti-HTN have a side effect of a dry cough?
|
ACEI
|
|
|
alliskerin
|
direct renin inhibitor - inhibits angiotensinogen conversion
no need to adjust dose for renal or hepatic impairment, or for the elderly |
|
|
side effect of alliskerin
|
angioedema
|
|
|
antiarrhythmics work in one of 4 ways. List them.
|
block sodium channels
block calcium channels influence potassium channels block sympathetic effects |
|
|
What is considered slow conduction tissue(s) in the heart?
|
SA & AV nodes
|
|
|
What is considered fast conduction tissue(s) in the heart?
|
purkinje fibers
|
|
|
class I antiarrhythmics
|
block sodium channels
Ia-"use dependent"; slows phase 0 (depolarization) and delays phase 3 (repolarization) Ib- blocks sodium and enhances potassium channels Ic- "non-use dependent"; slows phase 0 with little effect on phase 3 |
|
|
class II antiarryhthmics
|
beta blockers - slows HR & decreases AV node conduction velocity
propanolol, acebutolol, esmolol |
|
|
Give examples of class I antiarrhythics.
|
Ia - quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide
Ib - lidocaine, tocainide Ic - encainide, flecainide I(other) - mexiletine |
|
|
class III antiarrhythmics
Give examples. |
block potassium channels - increases refractoriness, QT interval & ERP
bretyllium, amiodarone, sotalol |
|
|
class IV antiarrhythmics
Give examples. |
block calcium channels - slows HR & decreases AV conduction velocity
verapamil, diltiazem |
|
|
class V antiarrhythmics
Give examples. |
adenosine agonists --> decreases AV node conduction velocity
adenosine |
|
|
What drug is the protype class Ia antiarrhythmic? How does it work?
|
quinidine
it blocks sodium channels; slows phase 0 (decreases conduction velocity) and delays phase 3 (increased refractoriness) it is dose dependent, i.e. use-dependent |
|
|
Why are antiarrhythmics more effective on atrial tissue than ventricular?
|
because of the direct effect on sodium channels and indirect anticholinergic effects --> both decrease conduction velocity and increase ERP
|
|
|
How does quinidine work in a-flutter?
|
it decreases conductive velocity and increases" the circuit
|
|
|
quinidine works best in atrial or ventricular tissue? Why?
|
atrial
ventricular function is driven by calcium. Quinidine blocks sodium channels |
|
|
major side-effects of quinidine.
|
Torsade de Pointes
hypokalemia prolonged QT cinchonism embolism (quinidine is highly protein bound and can displace anticoagulants) |
|
|
In what class is procainamide? what are its side effects?
|
antiarrhythmics Ia
systemic lupus like rxn |
|
|
antiarrhythmic class Ib is used for?
|
ventricular arrhythmias
they have a short half life |
|
|
primary use of class II antiarrhythmic drugs?
|
SVT caused by AV node re-entry
PVC's suppress ectopic pacemaker |
|
|
amiodarone toxicity results in:
|
corneal deposits
photosensitivity torsade de pointes |
|
|
phase 0 - sodium influx
phase 1 - chloride movement phase 2 - calcium & sodium channels are fighting with each other phase 3 - potassium eflux phase 4 - resting potential |
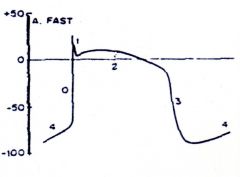
ID the various phases of this action potential
|

