![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
3 things that determine myocardial oxygen demand
|
1. wall stress
2. HR 3. contractility |
|
|
Wall stress equation
|
Pr/2h
|
|
|
Profusion pressure happens during?
|
diastole
|
|
|
hypoxia in myocardium leads to formation of which vasodilators?
|
1. ADENOSINE
2. lactate 3. acetate 4. H+ 5. CO2 |
|
|
variant angina is due to?
|
coronary artery spasm
|
|
|
stable angina
|
1. chronic
2. exertion 3. transient changes in EKG |
|
|
stable angina shows what on EKG?
|
Temporary ST depression
|
|
|
Variant angina ( Prinzmetal)
|
1. at rest
2. morning 3. ST elevation |
|
|
When does prinzmetal angina usually occur?
|
At rest in the morning.
|
|
|
A pattern of increased frequency and duration of angina describes what type of angina?
|
unstable angina
|
|
|
what type of angina has unopposed vasoconstriction?
|
unstable angina
|
|
|
stable angina Tx strategies?
|
1. increase O2 supply, reduce O2 demand
2. Tx artherosclerosis 3. prophylaxis against thrombosis |
|
|
drug classes of anti anginals?
|
1. Nitrates
2. Beta blockers 3. calcium channel blockers |
|
|
name 4 organic nitrates
|
1. Glyceryl trinitrate
2. Isosorbide dinitrate 3. isosorbide mononitrate 4. Amyl nitrite |
|
|
which nitrate drug is used to Tx cyanide poisoning?
|
amyl nitrate
|
|
|
amyl nitrite and __________
is used to Tx cyanide poisoning? |
methylene blue
|
|
|
Uses of nitrates
|
1. acute angina
2. prophylaxis 3. Beta blocker intolerance 4. Ca channel blocker intolerance 5. cyanide poisoning |
|
|
MOA of amyle nitrite and methylene blue?
|
amyle nitrite converts hemoglobin to methemoglobin. Cyanide binds methemoglobin and methylene blue reduces the methemoblobin and gets rid of the cyanide.
|
|
|
Nitrates therapy does what?
|
vasodilates
1. venules >> arterioles 2. coronary arteries 3. inhibits platelet aggregation |
|
|
Which medication worsens an angina attack by increasing coronary steal?
|
dipyrimadole. It dilates the normal arteries.
|
|
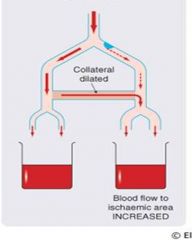
This shows the action of which drug?
|
nitrate. Nitrates dilate the collaterals and increase blood flow to the ischemic area.
|
|
|
nitrates increases _________ in the cell and leads to smooth muscle _________?
|
increases cGMP and smooth muscle dilation
|
|
|
phosphodiesterase 5 does what?
|
It breaks down cGMP to GMP.
|
|
|
Inhibition of PDE 5 will cause?
|
Increase in cGMP and vasodilation
|
|
|
adverse effects of nitrates?
|
1. flushing
2. headache 3. orthostatic hypotension 4. reflex tachycardia 5. syncope 6. methemglobinemia |
|
|
Large IV doses of nitroglycerine can cause?
|
methemglobinemia
|
|
|
Describe Monday Morning sickness?
|
workers in explosive factories got used to nitrate exposure but after a weekend of being nitrate free, on Monday they got headaches.
|
|
|
Way to not develop tolerance to therapeutic effects of nitrates?
|
nitrate free interval in the night.
|
|
|
Combining nitrates and _______ can lead to hyptensive shock?
|
PDE inhibitors b/c they prevent breakdown of cGMP and prolong effects of nitrates.
|
|
|
What medication decreases effects of nitrates?
|
migraine meds
|
|
|
Which nitrate type is most potent and has the longest half life?
|
trinitrates.
|
|
|
Which nitrate type is the least potent and has the longest half life?
|
mononitrate
|
|
|
which nitroglycerin formulation has the shortest onset and shortest duration?
|
sublingual
|
|
|
which nitrate has the shortest onset of action?
|
inhaled amyl nitrite
|
|
|
For long term angina prescribe which nitrate formulation?
|
ISDN, ISMN
|
|
|
What do have to tell pt's about their nitrate meds?
|
1. volatile- keep in cool, dry place
2. 6 months- after that they are not good. |
|
|
Stable angina - Beta blockers
|
1. reduce work load
2. stop reflex tachycardia. |
|
|
Stable angina-Beta blockers Side effects
|
1. bradycardia
2. bronchospasms 3. fatigue 4. depression 5. rebound HTN |
|
|
Beta blockers in diabetic pt
|
Masks hypotension.
Sweating is only sign. |
|
|
Beta blockers side effects
if pt incurs bronchospasms what should you do? |
switch to B1 selective
|
|
|
name 3 L-type calcium channel blockers?
|
1. Nifedipine
2. Verapamil 3. Diltiazem |
|
|
Nifedipine blocks?
|
vascular L-type Ca channels
|
|
|
Verapamil blocks?
|
cardiac L-type Ca channels
|
|
|
Diltiazem blocks?
|
cardiac and vascular L type Ca channels
|
|
|
calcium channel blockers therapeutic effects in stable angina?
|
1. decrease contractility
2. cause venodilation 3. increase coronary perfusion |
|
|
Nifedepine
|
1. Variant angina
2. reduces Preload, afterload 3. S/E constipation, gingival hyperplasia. |
|
|
Bepiridil
|
1. blocks Na and Ca channels
2. used for Chronic stable angina 3. S/E heart failure when used w/ Beta blockers |
|
|
Bepiridil plus Beta blockers causes heart failure by?
|
slowing AV conduction
|
|
|
Verapamil
|
1. V for Ventricle
2. stable angina, variant angina 3. Slows AV conduction 4. DONT COMBINE W/ BETA BLOCKERS 5. DONT USE AFTER MI |
|
|
Verapimil S/E ?
|
1. constipation
2. gingival hyperplasia |
|
|
Diltiazem
|
1. stable and variant angina
2. mixed properties 3. S/E bradycardia |
|
|
Tx for Variant Angina?
|
1. Nitrates
2. Calcium channel blockers |
|
|
MI and angina Tx?
|
nitrates and beta blockers
|
|
|
asthma and angina Tx?
|
nitrate and calcium channel blocker
|
|
|
diabetes and angina Tx?
|
nitrate and calcium channel blocker
|
|
|
chronic renal disease and angina?
|
nitrate and calcium channel blocker
|
|
|
Acute coronary syndrome
|
1. emergent
2. usually followed by MI 3. occur in pt w/ CAD 4. Use Beta blockers, nitrate, morphine |
|
|
Clopidogrel - (Plavix)
|
1. Antiplatelet drug
|
|
|
ACS management
|
1. beta blockers
2. nitrates 3. morphine 4. Clopidogrel 5. Possible PCI or CABG |
|
|
ACS management. Opioids are used for?
|
1. reduce pain
2. decrease SNS activation (CNS effect) |
|
|
name a more potent anti platelet agent?
|
GPIIB/IIIa
|
|
|
ACS STEMI use ?
|
thrombolytics
|
|
|
Post ACS management?
Short term |
1. clopidogrel, GPIIb/IIIa
2. anti arrythmics |
|
|
Post ACS management?
Long term |
1. Risk factors
2. ACE inhib 3. Beta blockers 4. antiplatelets 5. Statins |

