![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
α2 - adernergic agonist
|
CLONIDINE
HTN, ADHD, Withdrawals no change in MM Anticholinergic side effect WARNING: severe rebound HTN with withdrawal |
|
|
α1-Blockers
|
"...OSIN"
HTN, Reynaud's no change in MM Orthostatic Hypotension, Reflex Tachycardia Edema Dizziness, lack of energy, drowsiness |
|
|
β-Blocker
|
"...OLOL"
HTN BETTER MM w/ co-morbidiy (Angina, MI, CHF) Hypotension, Bradycardia, MASK BG IN DIABETES FATAL reboudn HTN↓ exercise tolerance AV block |
|
|
Intrinsic Sympathomimetic Activity (ISA)
|
Beta-blocker
ACEBUTOLOL No change in MM Does NOT REDUCE HR |
|
|
α1 / β1 / β2
|
CARVEDILOL
HTN, Heart Failure Improves MM Will not cause REFLEX TACHYCARDIA |
|
|
ACE-Inhibitors
|
"...PRIL"
HTN Improves MM, PREFERRED DRUG (especially with beta-blockers w/ Systolic CHF/MI) Hypotension, HYPERKALEMIA Bradykinin: Dry Hacking Cough, Angioedemia |
|
|
Angiotensin-2-Receptor Blockers (ARBs)
|
"...TAN"
HTN Hypotension, HYPERKALEMIA similar to ACE-Inh, BUT less likely to have Bradykinin ADRs |
|
|
Calcium Channel Blocker (CCBs)
|
"...PINE"
HTN, Angina, Reynaud's Disease, Improves MM PINE stronger Vasodilator than Cardiac CCBs Negative Inotrope/Chronotrope Reflex |
|
|
CCBs (Cardiac)
|
DILTIAZEM
VERAPAMIL HTN, Angina, Atrial Fib/Tachycardia Like Beta-Blockers: Negative Inotrope/Chronotrope |
|
|
Thiazide Diuretics
|
"...ONE"
"...ZIDE" Hydrocholorthiazide HTN, edema Preferred Drug, Improves MM Hypotension / Orthostatic Hypotension Hypokalemia |
|
|
Loop Diuretics
|
"...(N/M)IDE"
FUROSEMIDE HTN Not 1st line druge; NOT reduce MM Most powerful Diuretic Hypotension / Orthostatic Hypotension Hypokalemia |
|
|
What class of diuretics is the most powerful?
why? |
Loop diuretics
-direct acting vasodilator properties -TREATS: edema associated with CHF |
|
|
K+ sparing diuretics (Aldosterone Blockers)
|
"...ONE"
spironolACTONE eplerENONE HTN NOT 1st line; weak diruetic MUST BE USED in conjunction w/ ACE-Inh/Beta-Blocker to improve MM HYPERKALEMIA |
|
|
What is the most common ADRs with ALL HTN drugs?
|
Hypotension
Orthostatic Hypotension |
|
|
ADRs for:
α1/β1/β2-Blockers |
CARVEDILOL
(same as β-Blockers) EXCEPT: Does not cause Reflex Tachycardia |
|
|
ADRs for:
ACE-Inhibitors |
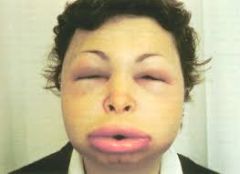
"...PRIL"
Hypotension Hyperkalemia Bradykinin ADRS: dry hacking cough, angioedema, rash WARNING: NSAIDs may cause ACUTE RENAL FAILURE |
|
|
ADRs for:
ARBs |
"...TAN"
(similar to ACE-Inh) Hypotension Hyperkalemia NSAIDs warning? Except NO BRADYKININ side effects |
|
|
ADRs for:
CCB (non Cardiac) |
"...PINE"
All CCBs: (Vasodilators cause) Dizziness, Hypotension, Flushing, Peripheral Edema Just PINEs -Reflex Tachycardia |
|
|
ADRs for:
CCB (Cardiac) |
DILTIAZEM
VARAPEMIL All CCBs: (Vasodilators cause) Dizziness, Hypotension, Flushing, Peripheral Edema Just Cardiac CCBs -AV Heart Block -Bradycardia |
|
|
ADRs for:
Thiazide Diuretics |
"...ONE"
"...ZIDE" Hydrocholorthiazide Hypotension Orthostatic Hypotension Dehydration Hypokalemia Electrolyte/Acid-Base Imbalance Gout attack (hyperuricemia) |
|
|
ADRs for:
Loop Diuretics |
"...IDE"
Hypotension Orthostatic Hypotension SIGNIFICANT: -Dehydration -Hypokalemia -Electrolyte/Acid-Base Imbalance Gout attack (hyperuricemia) |
|
|
3 Classes of Drugs most likely to cause (increase K+):
HYPERKALEMIA |
ACE-Inh
ARBs K+ sparing Diuretics too much K+ supplements |
|
|
5 Classes of Drugs most likely to cause (decrease K+):
HYPOKALEMIA |
Thaizide Diuretics
Loop Diuretics Corticosteroids β2 Agonist Insulin |
|
|
ADRs for:
K+ Sparing Diuretics |
"...ONE"
spironolACTONE = GYNECOMASTIA eplerENONE Hyperkalemia |
|
|
Discuss why thiazide diuretics are better to treat hypertension than loop diuretics
|
Thiazides IMPROVES MM
|
|
|
List the antihypertensives most likely to cause orthostatic hypotension
|
Loop diuretics
thiazide diuretics alpha 1, 2 blockers |
|
|
List the two drugs discussed in class often used to treat orthostatic hypotension:
|
Midodrine (α1-agonist)
Fludrocortisone |
|
|
Discuss how to avoid excessive nocturnal diuresis in patients taking loop diuretics
|
DO NOT take after 6pm
|
|
|
List clinical symptoms of Hypokalemia/Hyperkalemia:
why it is important to report these when identified |
Muscle Problems (weakness, fatigue, cramps)
Cardiac Problems (Arythmias, Hypotension, etc) Too Much/Too Little: FATAL |
|
|
patient education:
how to deal with orthostatic hypotension |
pump feet
hydrate get up slow no alcohol no outside activity (when hot) squat, not bend at waist |

